Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Background on HIV Testing
- Finger Prick Blood Tests: How Do They Work?
- Measuring Accuracy of Finger Prick Blood Tests
- Benefits of Finger Prick Blood Tests for HIV
- Limitations of Finger Prick Blood Tests
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive exploration of the accuracy of finger prick blood tests for HIV. In this article, we aim to provide a detailed understanding of how these tests work and shed light on their effectiveness in detecting HIV infection.
Background on HIV Testing
Before delving into the specifics of finger prick blood tests, it's essential to grasp the broader context of HIV testing methods, including the traditional blood tests performed in healthcare settings. Understanding these alternatives will help us gauge the innovation and convenience brought by finger prick tests.
In the field of HIV testing, finger prick blood tests have gained popularity due to their convenience, ease of use, and quick results. These tests, also known as rapid tests or point-of-care tests, aim to detect the presence of HIV antibodies in a person's blood sample.
Accuracy plays a crucial role when it comes to HIV testing as it determines the reliability of the results. Finger prick blood tests have shown to be highly accurate, with a high level of sensitivity and specificity. Sensitivity refers to the test's ability to correctly identify individuals who have HIV infection, while specificity measures the test's ability to correctly identify individuals who do not have HIV.
Studies have indicated that most finger prick blood tests have a sensitivity of more than 99%, meaning they accurately detect HIV infection in nearly all individuals who are truly infected. Similarly, the specificity of these tests is also high, ranging from 98% to 100%. This means that false-positive results, indicating HIV infection when the person is not actually infected, are rare.
However, it's important to note that no test is 100% accurate, and there is a small possibility of false results. False negatives, where the test fails to detect HIV infection despite the person being infected, can occur, especially during the window period – the time between initial infection and the production of detectable levels of antibodies. Therefore, it is recommended to repeat the test after the window period if initial results are negative but there is a continued risk of exposure.
Furthermore, finger prick blood tests are considered screening tests. In cases where a positive result is obtained, confirmatory testing through laboratory-based assays is necessary to confirm the HIV diagnosis. These laboratory tests are highly sensitive and specific, providing accurate results.
In conclusion, finger prick blood tests for HIV are generally accurate, offering a reliable and accessible method for detecting HIV infection. However, individuals who receive positive results should seek confirmatory testing for definitive diagnosis and proper healthcare management.
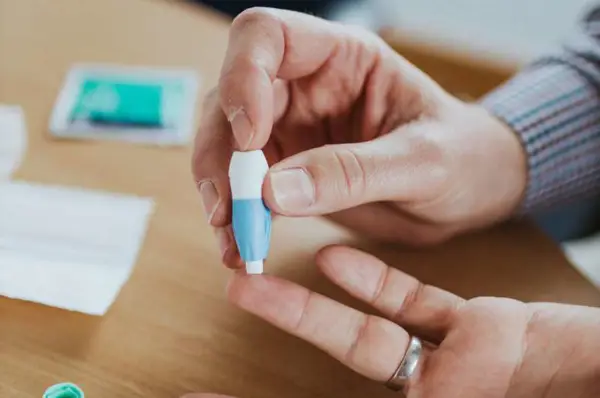
Finger Prick Blood Tests: How Do They Work?
This section explains the technical aspects of finger prick blood tests for HIV, highlighting the process, equipment, and collection procedure. By grasping the mechanism behind these tests, we can better appreciate their accuracy and reliability in detecting HIV infection.
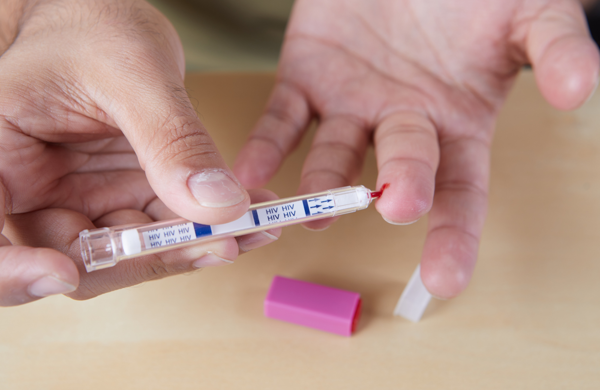
Finger prick blood tests are a convenient and less invasive way to obtain blood samples for various medical purposes, including HIV testing. Instead of traditional venous blood draws, these tests allow healthcare professionals to collect a small amount of blood through a simple finger prick.
The process starts by cleansing the finger with an alcohol swab to ensure cleanliness. Once the finger is dry, a small, disposable lancet is used to puncture the skin, usually on the fingertip. The puncture is shallow and typically causes minimal discomfort.
Once the blood sample is collected, it is transferred to a test strip or cartridge that contains reagents designed to detect specific markers or antibodies related to the condition being tested. In the case of HIV, the test will detect the presence of HIV antibodies in the blood sample.
These test strips or cartridges are then inserted into a handheld device or testing kit. The device analyzes the blood sample and provides the result within a few minutes. Some kits may require additional steps, such as adding a specific solution or reagent, which are clearly explained in the test kit instructions.
How Accurate Are Finger Prick Blood Tests for HIV?
Finger prick blood tests for HIV are generally highly accurate. They have undergone rigorous testing and are designed to detect HIV antibodies accurately. However, it is important to note that no test is 100% foolproof.
The accuracy of HIV tests can vary depending on various factors, such as the stage of infection, the timing of the test, and the specific test kit used. False-positive and false-negative results can occur, albeit rarely.
If you receive a positive result from a finger prick blood test, it is essential to confirm it with a laboratory-based blood test conducted by a healthcare professional. Laboratory-based tests provide more accurate and reliable results.
Overall, finger prick blood tests for HIV offer a quick and convenient screening method, especially for individuals who prefer self-testing or for areas with limited access to healthcare facilities. However, confirmatory testing through a laboratory-based blood test is recommended to ensure the accuracy of the result.
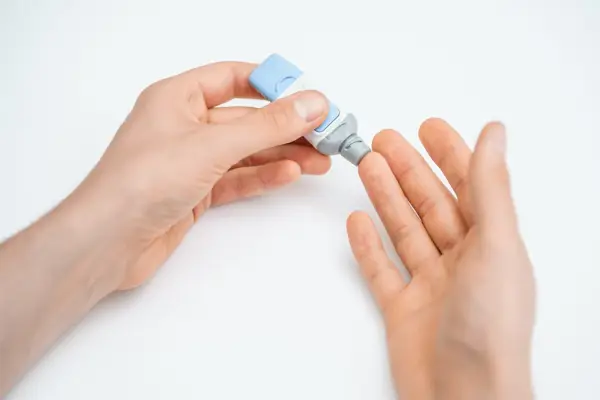
Measuring Accuracy of Finger Prick Blood Tests
Here, we assess the reliability of finger prick blood tests in terms of accuracy. We examine the various factors that may influence test results, such as window periods and potential user errors, allowing you to gain insights into the test's overall effectiveness.
Finger prick blood tests are commonly used for rapid HIV screening due to their convenience, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility. These tests detect the presence of antibodies to HIV in a small sample of blood taken from a fingertip. While finger prick tests are quick and easy to administer, it is important to understand their accuracy in detecting HIV infection.
Accuracy of Finger Prick Blood Tests
The accuracy of finger prick blood tests for HIV can vary depending on several factors, including the type of test used and the time since potential exposure. Generally, these tests have high sensitivity and specificity, which means they can accurately detect HIV antibodies when present and produce few false-positive or false-negative results.
Studies have shown that modern finger prick blood tests for HIV have a sensitivity of over 99% and a specificity of over 98%. Sensitivity refers to the ability of a test to correctly identify individuals with HIV, while specificity refers to the ability of a test to correctly identify individuals without HIV. These high accuracy rates indicate that finger prick tests are reliable in detecting HIV infection.
Considerations for Accuracy
It is essential to consider certain factors that may influence the accuracy of finger prick blood tests for HIV:
- Window Period: The window period refers to the time between HIV infection and when the test can accurately detect antibodies. During this period, antibody levels may be too low to be detected, leading to false-negative results. For most finger prick tests, the window period is around 3 to 4 weeks.
- User Errors: Incorrect usage of the test kits, such as insufficient blood sample or improper testing procedures, can affect the accuracy of results. It is crucial to carefully follow the instructions provided with the test kit.
- Confirmatory Testing: In cases where a finger prick blood test shows a positive result, it is recommended to undergo additional confirmatory testing, typically through laboratory-based tests, to confirm the diagnosis. Confirmatory testing provides a more comprehensive evaluation and ensures accurate results.
Finger prick blood tests for HIV are generally accurate, with high sensitivity and specificity rates. However, it is important to consider the window period, potential user errors, and the need for confirmatory testing in cases of positive results. If you suspect HIV infection, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for appropriate testing and guidance.
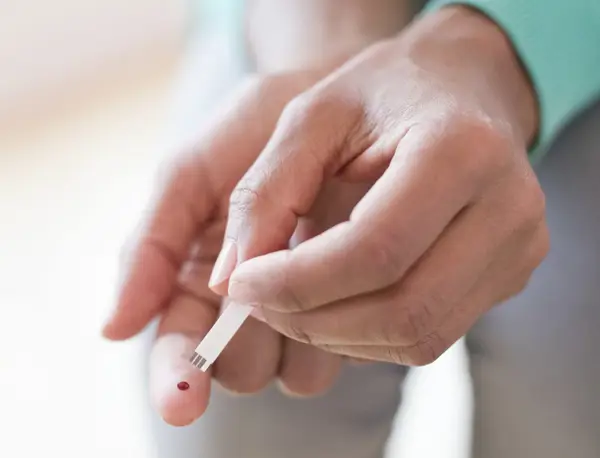
Benefits of Finger Prick Blood Tests for HIV
In this section, we discuss the advantages of finger prick blood tests compared to traditional testing methods. We outline their convenience, affordability, and the reduced waiting time for results, highlighting the impact these factors have on HIV detection rates and public health.
Finger prick blood tests for HIV offer numerous advantages and convenience for individuals seeking to get tested. They are also considered highly accurate in detecting HIV infections. This article discusses the benefits of these tests and their accuracy in HIV detection.
Benefits of Finger Prick Blood Tests for HIV
1. Accessibility: Finger prick blood tests can be conducted at various healthcare facilities, clinics, or even in-home testing kits, making them easily accessible for individuals.
2. Convenience: Unlike traditional blood tests that require a venous blood draw, finger prick tests involve a simple and quick process. This eliminates the need for a syringe or a needle and makes the testing procedure less intimidating and more convenient.
3. Rapid Results: Finger prick blood tests can provide results within minutes, saving time and reducing anxiety associated with waiting for test results.
4. Privacy: Finger prick blood tests can be performed in private settings, maintaining confidentiality and offering individuals the comfort to test in their preferred environment.
5. Lower Cost: Finger prick tests are generally more cost-effective compared to traditional blood tests. This affordability increases accessibility to testing for individuals.
Accuracy of Finger Prick Blood Tests for HIV
Finger prick blood tests are known to be highly accurate in detecting HIV infections. The tests use advanced technology to detect specific antibodies or antigens present in the blood, providing accurate results similar to traditional blood tests.
It is important to note that accuracy may vary based on factors such as the timing of the test, the sensitivity of the test kit used, and the individual's immune response. Therefore, it is recommended to follow up with a confirmatory blood test if the finger prick test results are positive.
Finger prick blood tests for HIV offer numerous benefits, including accessibility, convenience, rapid results, privacy, and lower cost. Moreover, these tests are highly accurate in detecting HIV infections, making them a reliable screening method. If you receive a positive result from a finger prick test, it is crucial to confirm it with a follow-up blood test for proper diagnosis and treatment.
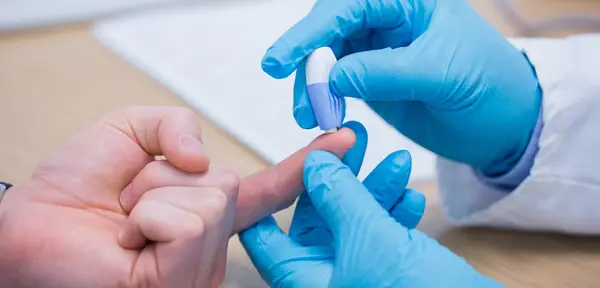
Limitations of Finger Prick Blood Tests
Despite their numerous benefits, finger prick blood tests for HIV do have limitations. This section explores those limitations, such as potential false positives/negatives and their impact on early diagnosis and subsequent treatment decisions.
Finger prick blood tests have become increasingly popular as a convenient and non-invasive method for various medical tests, including HIV testing. However, it is important to be aware of their limitations when it comes to accuracy in detecting HIV infection.
1. Sensitivity and Specificity:
Finger prick blood tests for HIV may not be as sensitive or specific as laboratory-based tests. These tests may have a higher chance of producing false-negative or false-positive results compared to traditional laboratory testing methods.
2. Window Period:
Like other HIV tests, finger prick blood tests have a window period, which refers to the time between HIV infection and when the test can accurately detect the virus. During this window period, even if a person is infected, the test may not provide accurate results. Thus, a negative result during the window period does not necessarily rule out HIV infection.
3. User Error:
The accuracy of finger prick blood tests for HIV also depends on the user's ability to follow the instructions properly. Any mistakes made during the testing process can affect the accuracy of the results obtained.
4. Professional Interpretation:
Finger prick blood tests may not provide a definitive diagnosis on their own. They are often used as preliminary screening tests, and positive results should be confirmed with additional laboratory-based tests conducted by healthcare professionals.
5. Viral Load:
Finger prick blood tests may not accurately measure the viral load, which is the amount of HIV in a person's blood. Measuring viral load is important for determining the stage of HIV infection and assessing treatment effectiveness.
In conclusion, while finger prick blood tests for HIV offer convenience and accessibility, it is important to recognize their limitations in terms of accuracy. For a confirmed HIV diagnosis, it is always advisable to consult healthcare professionals and undergo laboratory-based testing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this article offers an in-depth understanding of finger prick blood tests for HIV. We weigh their accuracy, benefits, and limitations, enabling individuals and healthcare professionals to make informed decisions regarding their usage.
Key Takeaways
- Finger prick blood tests for HIV provide an innovative and convenient alternative to traditional testing methods.
- The accuracy of these tests depends on factors such as the window period and user error.
- They offer several benefits, including affordability, faster results, and increased accessibility.
- Limitations include the potential for false results and the need for confirmation through further testing.
FAQ
- Q: Can finger prick blood tests accurately detect HIV?
- A: Finger prick blood tests are highly accurate in detecting HIV when conducted within the appropriate window period.
- Q: Are finger prick blood tests reliable for early detection of HIV?
- A: Finger prick blood tests may not always detect early HIV infection, as the test relies on detecting antibodies which take time to develop.
- Q: How long does it take to get results from a finger prick blood test?
- A: Results from finger prick blood tests are usually available within 20 minutes, making them much faster compared to traditional blood tests.
- Q: Are there any disadvantages to using finger prick blood tests for HIV?
- A: Finger prick blood tests have limitations, such as the potential for false positives/negatives and the need for confirmation through additional testing.
- Q: Are finger prick blood tests cost-effective?
- A: Yes, finger prick blood tests are generally more affordable than traditional blood tests, making them a cost-effective option.


Recent Comments