Table of Contents
- What is High Potassium Level?
- Causes of High Potassium Levels
- Symptoms and Diagnosis
- Effects on Health
- Treatment Options
- Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
- Managing High Potassium Levels
What is High Potassium Level?
High potassium level, also known as hyperkalemia, refers to the condition where there is an excessive amount of potassium in the blood. This can disrupt normal bodily functions and may require medical attention.
Causes of High Potassium Levels
Explore the various factors that can lead to high potassium levels in the blood, including kidney problems, certain medications, and dietary choices.
High potassium levels in a blood test, known as hyperkalemia, can occur due to various reasons. Some common causes include:
1. Kidney Problems
Kidneys play a vital role in regulating potassium levels in the body. If the kidneys are not functioning properly, they may not be able to excrete excess potassium effectively, leading to high levels in the blood.
2. Certain Medications
Some medications, such as certain diuretics (water pills), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and ACE inhibitors, can interfere with potassium balance in the body, potentially causing potassium levels to rise.
3. Adrenal Gland Disorders
Adrenal gland disorders, like adrenal insufficiency or Addison's disease, can impact the regulation of potassium in the body, resulting in higher levels in the blood.
4. Excessive Potassium Intake
Consuming excessive amounts of potassium through foods, supplements, or intravenous administration can overwhelm the body's ability to maintain proper levels, leading to hyperkalemia.
5. Tissue Damage
Injuries, burns, or other conditions that cause significant tissue damage can release potassium into the bloodstream, potentially elevating the potassium levels.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment if high potassium levels are detected in a blood test. Hyperkalemia can have various symptoms and complications, so proper management is essential for maintaining overall health.
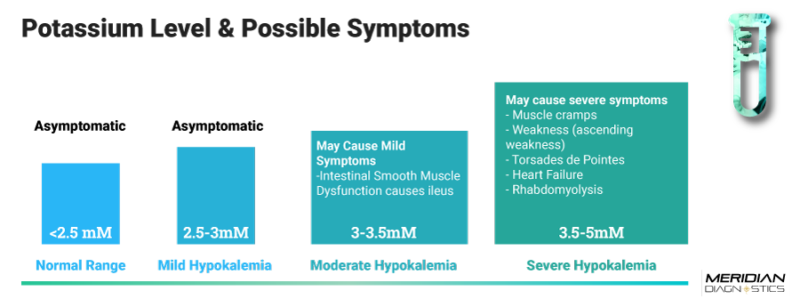
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Learn about the common signs and symptoms of high potassium levels and understand how it can be diagnosed through blood tests and other medical examinations.
High potassium levels, also known as hyperkalemia, occur when there is an excessive amount of potassium in the bloodstream. This can lead to various symptoms and require proper diagnosis for appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of High Potassium Levels
The symptoms of high potassium levels may vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Irregular heartbeat or palpitations
- Muscle weakness or paralysis
- Nausea and vomiting
- Difficulty breathing
- Abdominal pain or cramping
- Fatigue or weakness
- Tingling or numbness
Diagnosing High Potassium Levels
Diagnosing high potassium levels typically involves a blood test, known as a serum potassium test. This test measures the amount of potassium present in the bloodstream. High levels are usually indicated if the potassium level exceeds the normal range, which is generally between 3.5 to 5.0 millimoles per liter (mmol/L).
Additional tests, such as an electrocardiogram (ECG) or urine tests, may be performed to assess the severity of the condition and determine its underlying cause. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
If you suspect high potassium levels or experience any of the symptoms mentioned, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly for appropriate evaluation and treatment.
Effects on Health
Discover the potential health risks associated with high potassium levels and how it can affect different bodily systems, including the heart and muscles.
Having high potassium levels, also known as hyperkalemia, can have various effects on a person's health. Potassium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. However, when its levels become excessively high, it can lead to certain health complications.
Some of the potential effects of high potassium levels in the blood include:
- Cardiac Issues: High potassium levels can disrupt the normal electrical activity in the heart, leading to an irregular heartbeat or even cardiac arrest in severe cases.
- Muscle Weakness: Excessive potassium can interfere with proper muscle functioning, causing weakness or paralysis.
- Gastrointestinal Problems: Hyperkalemia can lead to digestive issues such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
- Difficulty Breathing: In extreme cases, high potassium levels may affect the muscles involved in breathing, leading to shortness of breath or respiratory distress.
- Renal Impairment: The kidneys play a vital role in maintaining the balance of potassium levels in the body. If potassium levels become too high, it can strain the kidneys and potentially result in kidney damage or impairment.
If you suspect that you have high potassium levels, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. They may recommend dietary changes, medication adjustments, or other interventions to bring potassium levels back to normal and mitigate potential health risks.
Remember, this is a general overview and not a substitute for professional medical advice. It is always best to consult a healthcare provider for personalized guidance.
Treatment Options
Find out the available treatment options for high potassium levels, such as medication, dietary modifications, and dialysis, depending on the severity of the condition.
1. Dietary Changes
One of the initial steps in treating high potassium levels in the blood is making dietary modifications. You may need to limit your intake of foods high in potassium, such as bananas, oranges, potatoes, tomatoes, and leafy greens. Your healthcare provider can provide you with a comprehensive list of low-potassium foods to include in your diet.
2. Medication
In some cases, your doctor may prescribe medication to help lower your potassium levels. This may include diuretics, which increase urine production, or potassium-binding resins that help remove excess potassium from the body.
3. Fluid Intake
Increasing your fluid intake can also aid in lowering high potassium levels. Drinking more water can help dilute the potassium in your blood and promote its excretion through urine.
4. Dialysis
In severe cases or when other treatments are not effective, dialysis may be necessary. Dialysis is a medical procedure that helps filter and remove excess potassium from the bloodstream.
5. Avoid Certain Medications and Supplements
Some medications and supplements can contribute to high potassium levels. Your doctor may advise avoiding certain medications or supplements known to raise potassium levels to prevent further complications.
6. Regular Monitoring
Regular blood tests will be necessary to monitor your potassium levels. Your healthcare provider will determine the frequency of these tests based on your specific situation.
Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options for high potassium levels. This HTML serves as a brief overview and should not be used as a substitute for medical advice.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Learn about preventive measures and lifestyle changes that can help manage and prevent high potassium levels in the blood, including dietary restrictions and regular exercise.
High potassium levels in the blood, also known as hyperkalemia, can be a cause for concern as it can lead to various health problems. However, there are several preventive measures and lifestyle changes that can help in managing and reducing high potassium levels effectively.
Prevention
Preventing high potassium levels involves adopting healthy habits and taking necessary precautions. Here are some preventive measures to consider:
- Dietary modifications: Avoid or limit consumption of foods high in potassium such as bananas, oranges, potatoes, tomatoes, and avocado.
- Monitor medications: Certain medications can contribute to increased potassium levels. Regularly review and consult with your healthcare provider to assess medication effects.
- Hydration: Stay well-hydrated as it helps in maintaining the balance of electrolytes in the body, including potassium.
- Avoid excessive use of supplements: Overuse of potassium supplements can contribute to elevated levels. Only take supplements under medical supervision.
- Avoid excessive alcohol intake: Alcohol can affect kidney function, which can disrupt potassium levels. Limit alcohol consumption or avoid it altogether.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to preventive measures, certain lifestyle changes can assist in managing high potassium levels:
- Regular exercise: Engage in physical activities as exercise helps in regulating blood pressure, kidney function, and overall health, including potassium levels.
- Quit smoking: Smoking can adversely affect kidney function and electrolyte balance. Quitting smoking is beneficial for overall health.
- Stress management: Chronic stress can impact hormonal balance and blood pressure, which may lead to high potassium levels. Adopt stress reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or hobbies.
- Regular blood tests: Regularly monitor potassium levels through blood tests as recommended by your healthcare provider to ensure early detection and prompt management.
- Medical follow-up: It is essential to maintain regular visits with your healthcare provider to monitor potassium levels, manage any underlying conditions, and receive appropriate guidance and treatment.
Remember, always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice regarding your high potassium levels. They can guide you in making appropriate lifestyle changes and prescribe suitable treatments if necessary.

Managing High Potassium Levels
Discover effective strategies and self-care practices to manage high potassium levels on a daily basis, including monitoring your diet, staying hydrated, and following prescribed medications.
When you have high potassium levels in your blood, it is important to take necessary steps to manage it. Here are some tips:
- Avoid high potassium foods, such as bananas, oranges, spinach, and potatoes.
- Limit your intake of salt and salt substitutes.
- Drink plenty of water to help flush out excess potassium from your body.
- Avoid potassium-containing medications and supplements unless prescribed by your doctor.
- Engage in regular physical activity, as exercise can help lower potassium levels.
- Follow a balanced and healthy diet recommended by a registered dietitian or nutritionist.
- Monitor your potassium levels regularly through blood tests as advised by your healthcare provider.
- If necessary, your doctor may prescribe medications to help manage your high potassium levels.
Remember, it is essential to work closely with your healthcare team to determine the best course of action for managing your high potassium levels. They will provide you with personalized guidance based on your specific condition.
For more information, consult your healthcare provider or visit a reputable medical website.
Created by: Your Name

Key Takeaways
- High potassium levels in the blood, known as hyperkalemia, can be harmful to the body.
- It can be caused by various factors, including kidney problems and certain medications.
- Common symptoms include muscle weakness, irregular heartbeat, and numbness or tingling sensations.
- Diagnosis is usually made through blood tests and other medical examinations.
- Treatment options may involve medication, dietary modifications, and dialysis.
- Preventive measures include following a balanced diet, limiting potassium-rich foods, and staying active.
- Managing high potassium levels involves regular monitoring, staying hydrated, and adhering to prescribed treatments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can high potassium levels be life-threatening?
A: In severe cases, high potassium levels can lead to life-threatening conditions such as cardiac arrhythmias. Prompt medical attention is crucial in such situations.
Q: Can certain medications contribute to high potassium levels?
A: Yes, certain medications like ACE inhibitors, potassium-sparing diuretics, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can elevate potassium levels in the blood.
Q: Are there any dietary restrictions for individuals with high potassium levels?
A: Yes, it is important to limit the intake of potassium-rich foods like bananas, oranges, tomatoes, and potatoes to manage potassium levels in the blood.
Q: Can exercise help in managing high potassium levels?
A: Regular exercise can help maintain overall health and may indirectly contribute to the management of high potassium levels. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.


Recent Comments