Table of Contents:
Oxygen:
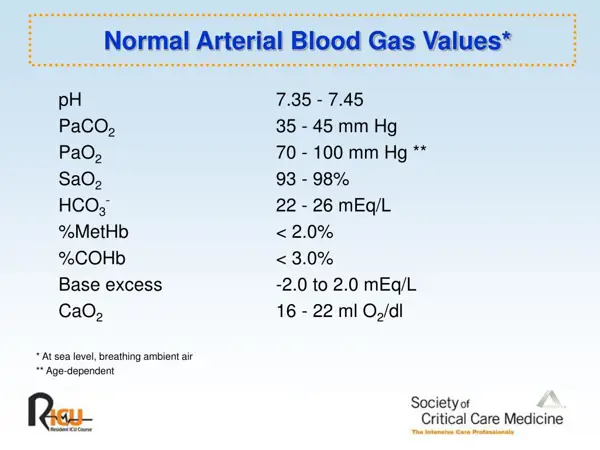
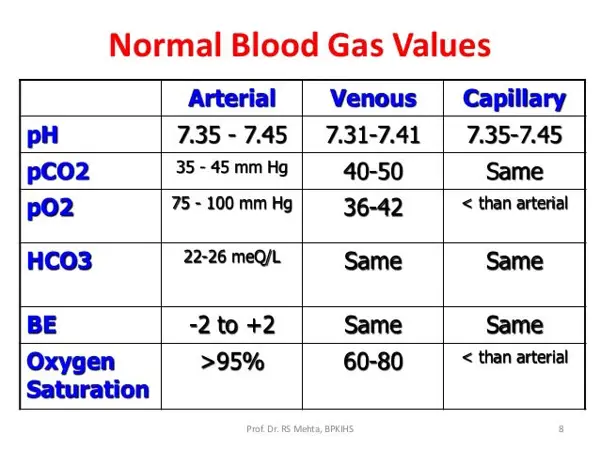
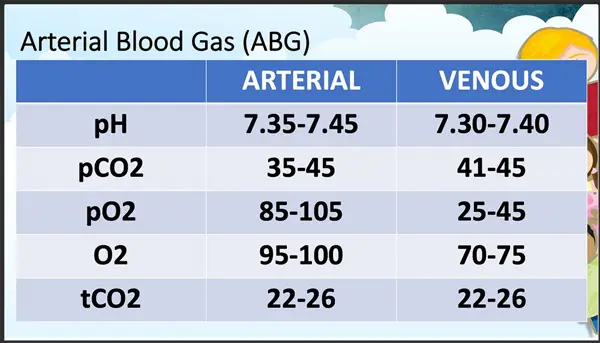
The normal range for arterial blood oxygen levels (PaO2) is between 75-100 mm Hg. Low oxygen levels can indicate respiratory or cardiovascular issues.
Carbon Dioxide:
The normal range for arterial blood carbon dioxide levels (PaCO2) is between 35-45 mm Hg. Abnormal levels can be a sign of respiratory dysfunction.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a waste product produced by cells in the body during metabolism. Normal values of CO2 in blood gases range from 35-45 mmHg.
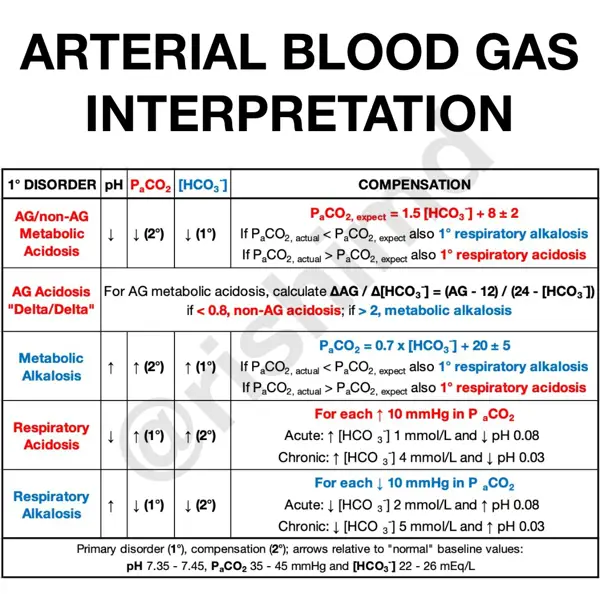
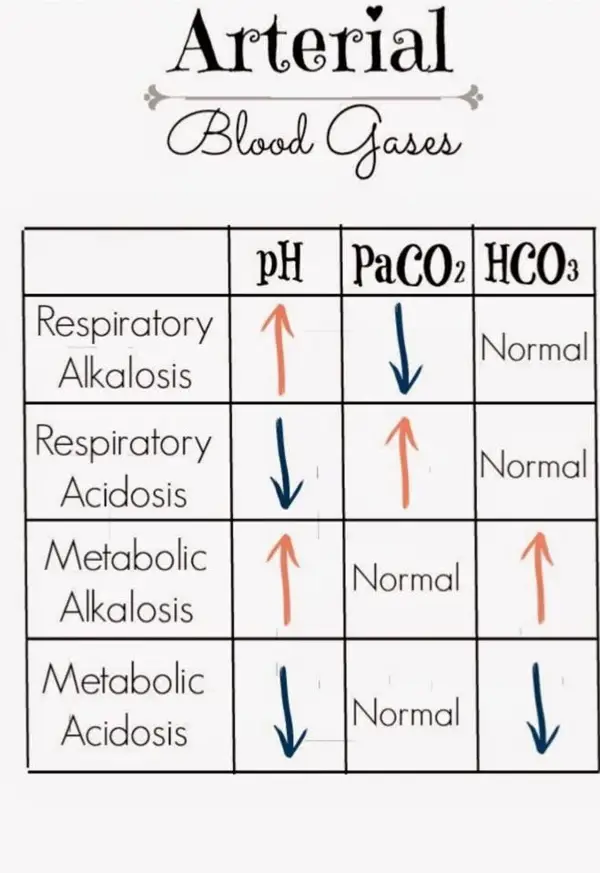
CO2 levels in the blood are important for maintaining the body's pH balance. Too much CO2 can lead to respiratory acidosis, while too little CO2 can lead to respiratory alkalosis.
Monitoring CO2 levels in blood gases is important for diagnosing and managing conditions such as respiratory failure, lung diseases, and metabolic disorders.
Overall, maintaining normal CO2 levels is crucial for the proper functioning of the body's respiratory and metabolic systems.
pH Level:
The normal pH range in arterial blood is between 7.35-7.45. pH levels outside of this range can indicate acid-base imbalances.
The pH level of blood gases is a measurement of how acidic or basic the blood is. The normal pH level of blood gases is between 7.35 and 7.45. If the pH level is lower than 7.35, it indicates acidosis, while a pH level higher than 7.45 indicates alkalosis.
It is important for the body to maintain a normal pH level in order to function properly. Changes in pH levels can affect enzyme activity, protein function, and cell metabolism. Monitoring and maintaining the pH level of blood gases is crucial for overall health.
Bicarbonate:
The normal range for bicarbonate levels in arterial blood is between 22-26 mEq/L. Bicarbonate levels are important for maintaining acid-base balance.
Bicarbonate (HCO3-) is an important component of the blood's buffering system, helping to maintain the body's pH balance. In normal values pressure blood gases, the typical range for bicarbonate is between 22-26 mmol/L.
Changes in bicarbonate levels can indicate various health conditions, such as metabolic acidosis or alkalosis. Monitoring bicarbonate levels as part of blood gas analysis is crucial in assessing a person's overall health and identifying any potential issues.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns about your bicarbonate levels or if you are experiencing symptoms that may indicate an imbalance in your blood gases.
Base Excess:
The normal range for base excess is between -2 to +2 mEq/L. Base excess measures the amount of excess base or acid in the blood.
Base Excess is a measurement that indicates the amount of excess base or acid present in the blood. In normal values of blood gases, the base excess is typically between -3 to +3 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L).
A base excess within this range suggests that the body's acid-base balance is stable and functioning properly. Any deviation from this range may indicate a metabolic acidosis or alkalosis, which could be caused by various health conditions.
It is important to monitor and maintain the base excess within the normal range to ensure proper physiological function and overall health.
Oxygen Saturation:
The normal range for oxygen saturation in arterial blood is 95-100%. This measure indicates the percentage of hemoglobin that is saturated with oxygen.
Oxygen saturation refers to the amount of oxygen that is carried in the red blood cells in the body. Normal values of blood gases, including oxygen saturation, are important indicators of respiratory and cardiovascular health.
Normal Values of Oxygen Saturation:
- Normal arterial oxygen saturation levels are typically between 95% and 100%.
- A saturation level below 90% is considered low and may indicate hypoxemia, which can lead to oxygen deficiency in the body.
- Values above 100% are possible with supplemental oxygen therapy, but are not considered normal.
Monitoring oxygen saturation levels is crucial in medical settings, such as hospitals and emergency rooms, to assess and manage respiratory conditions and ensure adequate oxygen supply to the tissues.
FAQ:
What is the significance of blood gas values?
Blood gas values provide important information about respiratory and metabolic functions in the body. Abnormal values can indicate underlying health issues that need to be addressed.
How are blood gas levels measured?
Blood gas levels are typically measured using arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis, which involves drawing a sample of arterial blood and analyzing it for oxygen, carbon dioxide, pH, and other components.
What are the common causes of abnormal blood gas values?
Common causes of abnormal blood gas values include respiratory diseases, metabolic disorders, kidney failure, and certain medications. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause of abnormal values.
Key Takeaways:
- Normal blood gas values are crucial for maintaining overall health.
- Abnormal blood gas values can indicate respiratory or metabolic dysfunction.
- Blood gas levels are typically measured through arterial blood gas analysis.


Recent Comments