Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Body Fat
- Body Fat and Insulin Resistance
- Body Fat and Glucose Levels
- Body Fat and Diabetes Risk
- Strategies to Maintain a Healthy Body Fat Level
- Conclusion
Introduction
Understanding the relationship between body fat and blood sugar levels is crucial for maintaining overall health and preventing the onset of chronic conditions such as diabetes. In this article, we delve into the impact of body fat on blood sugar levels, exploring their complex connection and shedding light on their effects on our well-being.
Understanding Body Fat
Before examining the influence of body fat on blood sugar levels, it is essential to comprehend what body fat is and how it is distributed throughout our bodies. We explore the different types of body fat, including visceral and subcutaneous fat, and their respective roles in regulating metabolism.
Body fat, also known as adipose tissue, plays a significant role in our overall health and metabolism. Not only does it provide insulation and energy storage, but it also affects various bodily processes, including blood sugar regulation.
When it comes to blood sugar levels, body fat has both direct and indirect influences. One primary factor is the release of hormones from adipose tissue, such as leptin and adiponectin. These hormones regulate appetite, insulin sensitivity, and glucose metabolism, thus affecting blood sugar control.
Excessive body fat, especially in the abdominal area, increases the risk of developing insulin resistance, a condition where the body becomes less responsive to the effects of insulin. Insulin resistance leads to higher blood sugar levels and a higher likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes.
Additionally, excess body fat can lead to chronic inflammation in the body. Inflammation interferes with insulin signaling, impairing the ability of cells to absorb glucose effectively. As a result, blood sugar levels remain elevated, increasing the risk of diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
Furthermore, body fat distribution matters concerning blood sugar regulation. Those with more visceral fat (fat surrounding internal organs) tend to have higher blood sugar levels compared to individuals with subcutaneous fat (fat located beneath the skin). This difference occurs because visceral fat releases more inflammatory substances that disrupt insulin signaling.
Managing body fat levels through a healthy lifestyle is essential for blood sugar control. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and weight management play key roles in reducing body fat and improving insulin sensitivity. Incorporating strength training and cardiovascular exercises can help burn excess fat, especially in the abdominal area.
In conclusion, understanding the relationship between body fat and blood sugar is crucial for maintaining optimal health. Excessive body fat, especially in the abdomen, increases the risk of insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels. Managing body fat levels through exercise and a healthy diet is key to preventing these issues and promoting overall well-being.
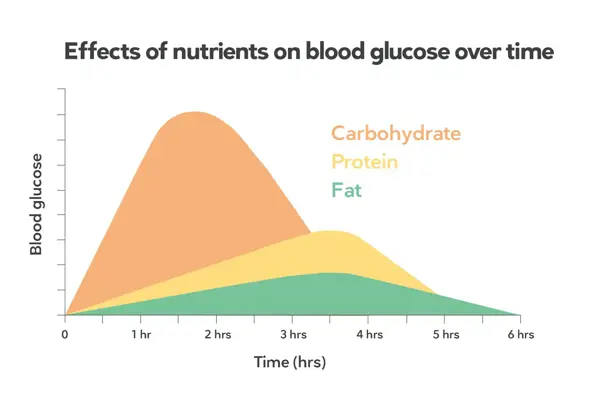
Body Fat and Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is a significant factor in the relationship between body fat and blood sugar levels. In this section, we investigate how excess body fat can lead to insulin resistance, hindering the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels and potentially resulting in various health complications.
Body fat and insulin resistance have a significant impact on blood sugar levels.
Body Fat:
When our body accumulates excess fat, especially in the abdominal region, it increases the risk of developing insulin resistance. The presence of excessive body fat disrupts the balance of hormones and can interfere with insulin's ability to regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
Insulin Resistance:
Insulin resistance is a condition in which cells in our body become less responsive to insulin. When insulin resistance occurs, glucose (sugar) cannot efficiently enter our cells for energy production, leading to an elevation in blood sugar levels.
Impact on Blood Sugar:
The accumulation of body fat can promote insulin resistance, making it more challenging for insulin to effectively control blood sugar levels. When this occurs, blood sugar levels tend to remain higher than normal, leading to an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Managing Body Fat and Blood Sugar:
Regular physical activity, a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and maintaining a healthy body weight are essential for managing body fat and blood sugar levels. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, one can minimize the risk of developing insulin resistance and its associated complications.

Body Fat and Glucose Levels
Here, we examine the intricate interplay between body fat and glucose levels. We delve into the mechanisms through which excess body fat affects glucose metabolism and disrupts the delicate balance required for maintaining optimal blood sugar levels.
Body fat plays a significant role in determining blood sugar levels. Excess body fat, particularly abdominal fat, can lead to an increased risk of developing insulin resistance, a condition where the body's cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin.
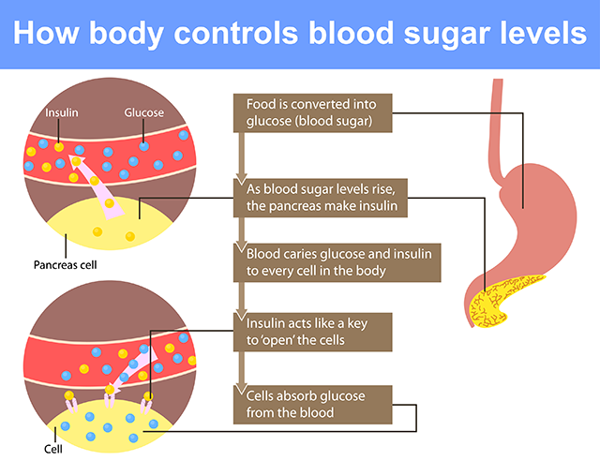
Insulin and Glucose
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels. When we eat carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose, a type of sugar. Insulin acts as a key that unlocks the cells to allow glucose to enter and be used for energy.
Effects of Excess Body Fat
When excess body fat is present, especially in the abdominal region, it releases inflammatory substances that interfere with the normal functioning of insulin. As a result, insulin resistance may occur, and the cells are not able to efficiently absorb glucose from the bloodstream. This leads to elevated blood sugar levels.
Risk of Diabetes
Persistent high blood sugar levels can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, a chronic condition where the body fails to properly regulate blood sugar. Insulin resistance caused by excess body fat is often a contributing factor in the development of this type of diabetes.
Managing Body Fat and Blood Sugar
Maintaining a healthy body weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity can help reduce excess body fat and lower the risk of developing insulin resistance. Engaging in aerobic exercise, strength training, and consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can support healthy body fat levels and optimal blood sugar regulation.
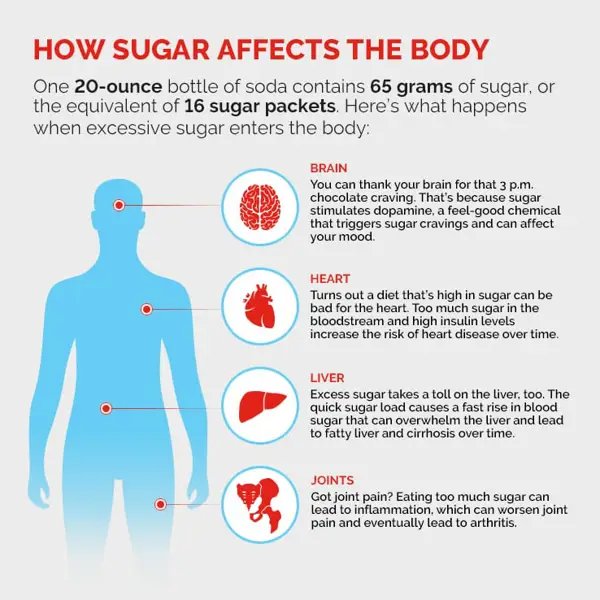
Body Fat and Diabetes Risk
The impact of body fat on diabetes risk cannot be overlooked. In this section, we discuss the association between elevated body fat levels and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. We also highlight the importance of body fat management as a preventive measure against this chronic condition.
Strategies to Maintain a Healthy Body Fat Level
Maintaining a healthy body fat level is crucial for overall well-being. In this section, we present a range of strategies to manage body fat effectively, including dietary modifications, regular physical activity, and lifestyle changes that can help individuals optimize their blood sugar levels and reduce associated health risks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how body fat affects blood sugar levels is vital for promoting optimal health and preventing conditions like diabetes. By implementing healthy lifestyle practices and adopting strategies to manage body fat, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining balanced blood sugar levels and enjoying a healthier life overall.
Key Takeaways
- Elevated body fat levels can lead to insulin resistance, which hampers the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels.
- Excess body fat disrupts glucose metabolism and can contribute to imbalances in blood sugar levels.
- High body fat levels are associated with an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Managing body fat through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and lifestyle modifications is essential for optimal blood sugar control.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can body fat directly cause diabetes?
No, body fat itself does not directly cause diabetes. However, excess body fat, particularly around the abdomen, is strongly associated with insulin resistance and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Q: How does losing body fat improve blood sugar control?
Losing body fat can enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce insulin resistance. This, in turn, improves the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels effectively, decreasing the risk of elevated glucose levels and related complications.
Q: Is all body fat harmful?
No, not all body fat is harmful. Subcutaneous fat, found just beneath the skin, serves as an energy reserve and insulation. It is the excess visceral fat surrounding vital organs that poses a greater risk to health and is closely linked to metabolic disorders.


Recent Comments