Table of Contents
- Definition of Catabolism
- Process of Catabolism
- Enzymes Involved in Catabolism
- Importance of Catabolism
- Examples of Catabolism
- Regulation of Catabolism
- Conclusion
Definition of Catabolism
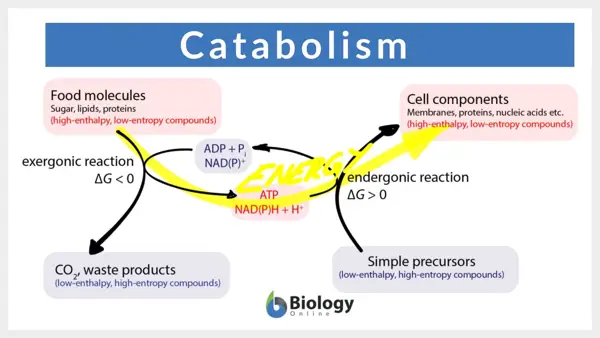
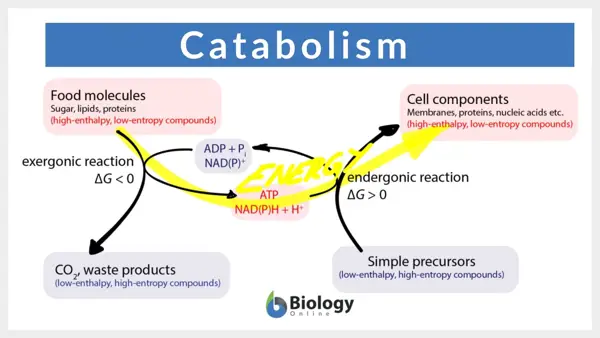
Catabolism is the set of metabolic pathways that break down molecules into smaller units to release energy for the cell. This process involves the breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy in the form of ATP.
Process of Catabolism
The process of catabolism begins with the breakdown of macromolecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. These molecules are broken down into smaller components such as glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids through a series of chemical reactions. These reactions release energy that is used by the cell for various biological processes.
Catabolism is the process of breaking down complex molecules into simpler ones to release energy. In biology, catabolism involves various metabolic pathways that result in the degradation of large molecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. This process is essential for providing the necessary energy for cellular functions and activities. Through catabolism, cells are able to extract energy stored in molecules like glucose and convert it into ATP, the primary energy currency of cells. Overall, catabolism plays a crucial role in the overall metabolism of living organisms, allowing them to maintain essential functions and sustain life.
Enzymes Involved in Catabolism
Several enzymes are involved in the catabolic pathways, including lipases, proteases, and amylases. These enzymes catalyze the breakdown of specific molecules into their constituent parts, allowing the cell to extract energy efficiently.
In biology, catabolism refers to the metabolic processes that break down complex molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy in the process. Enzymes play a crucial role in catabolism by catalyzing the chemical reactions that drive the breakdown of these molecules.
There are several key enzymes involved in catabolism, including:
1. Proteases: Proteases are enzymes that break down proteins into amino acids. They play a vital role in the digestion of food and the recycling of cellular proteins.
2. Lipases: Lipases are enzymes that break down fats and lipids into fatty acids and glycerol. They are essential for the digestion and absorption of dietary fats.
3. Amylases: Amylases are enzymes that break down carbohydrates such as starch and glycogen into simple sugars like glucose. They are crucial for energy production in cells.
Overall, enzymes involved in catabolism are essential for the efficient breakdown of complex molecules, providing cells with the energy and building blocks they need to function properly.
Importance of Catabolism
Catabolism is essential for the cell to generate energy for its survival and functioning. Without catabolic processes, cells would not be able to break down nutrients and generate ATP, the primary energy currency of the cell.
Catabolism is a fundamental process in biology that involves breaking down complex molecules into simpler ones to release energy for cellular activities. It is essential for the survival and functioning of living organisms, as it provides the necessary energy for growth, development, and maintenance of bodily functions.
Catabolism plays a crucial role in various metabolic pathways, such as glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. These pathways help convert nutrients from food into energy that cells can use to perform their functions.
Furthermore, catabolism helps regulate the balance of molecules within the body by removing waste products and recycling them into usable resources. This process also plays a key role in the body's ability to respond to changes in energy demands and environmental conditions.
Overall, catabolism is an essential process in biology that ensures the efficient use of energy and resources, supporting the overall health and functioning of living organisms.
Examples of Catabolism
Examples of catabolic processes include glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and beta-oxidation of fatty acids. These pathways involve the breakdown of glucose, citric acid, and fatty acids, respectively, to generate energy for the cell.
Catabolism is a metabolic process in biology that involves breaking down complex molecules into simpler ones to release energy. Some examples of catabolism include:
- Breaking down carbohydrates such as glucose into smaller molecules like pyruvate through glycolysis.
- Breaking down fats into fatty acids and glycerol through the process of lipolysis.
- Breaking down proteins into amino acids through the process of proteolysis.
- Breaking down nucleic acids into nucleotides through the process of nucleolysis.
Regulation of Catabolism
Catabolic pathways are tightly regulated by the cell to ensure energy production is balanced and efficient. Various feedback mechanisms and enzyme regulations control the rate of catabolic reactions to meet the energy demands of the cell.
Catabolism is the process by which large molecules in the body are broken down into smaller ones, releasing energy in the process. This energy is used to fuel various cellular activities and processes. Regulation of catabolism is essential for maintaining a balance in the body and ensuring that energy production is efficient.
Several factors can influence the regulation of catabolism, including enzymes that facilitate the breakdown of molecules, hormonal signals that control the rate of catabolic processes, and environmental factors such as temperature and pH levels.
Overall, catabolism plays a crucial role in biology by providing the necessary energy for cells to function properly. Understanding the regulation of catabolism is key to maintaining a healthy balance within the body and ensuring that energy production is optimized.
Conclusion
In conclusion, catabolism is a crucial process in biology that allows cells to break down complex molecules and release energy for their survival. Understanding the mechanisms of catabolic pathways can provide insights into metabolic disorders and potential therapeutic interventions.
Key Takeaways
- Catabolism is the process of breaking down molecules to release energy for the cell.
- Enzymes play a crucial role in catalyzing catabolic reactions.
- Regulation of catabolism ensures energy production is balanced and efficient.
FAQ
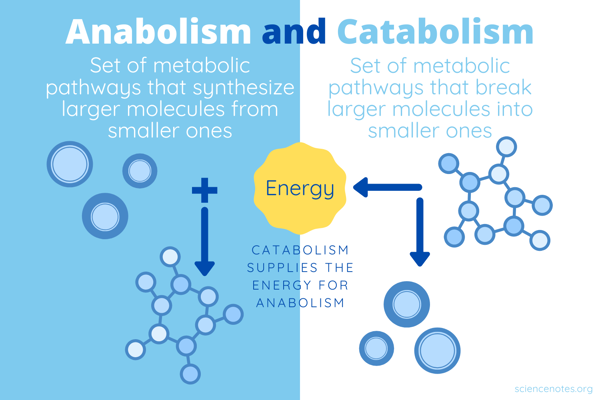
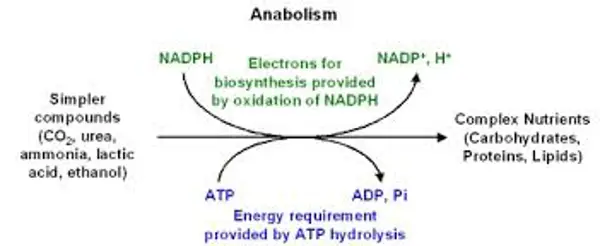
What is the difference between catabolism and anabolism?
Catabolism is the breakdown of molecules to release energy, while anabolism is the synthesis of molecules using energy. They are complementary processes that together regulate the metabolism of the cell.
How does catabolism contribute to overall cell function?
Catabolism provides the necessary energy for the cell to carry out various biological processes such as growth, repair, and movement. Without catabolism, cells would not have the energy required for survival.


Recent Comments