Table of Contents
Introduction
High levels of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) and non-HDL (non-high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol in the body can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases. However, through lifestyle modifications and dietary changes, you can effectively lower these cholesterol levels and promote heart health. This comprehensive guide will provide you with essential strategies to help you reduce LDL and non-HDL cholesterol naturally.
Understanding LDL and Non-HDL Cholesterol
In this section, we will explain what LDL and non-HDL cholesterol are, how they impact your health, and why it is important to keep their levels in check. By understanding these concepts, you can make informed decisions to improve your cholesterol profile.
What is LDL Cholesterol?
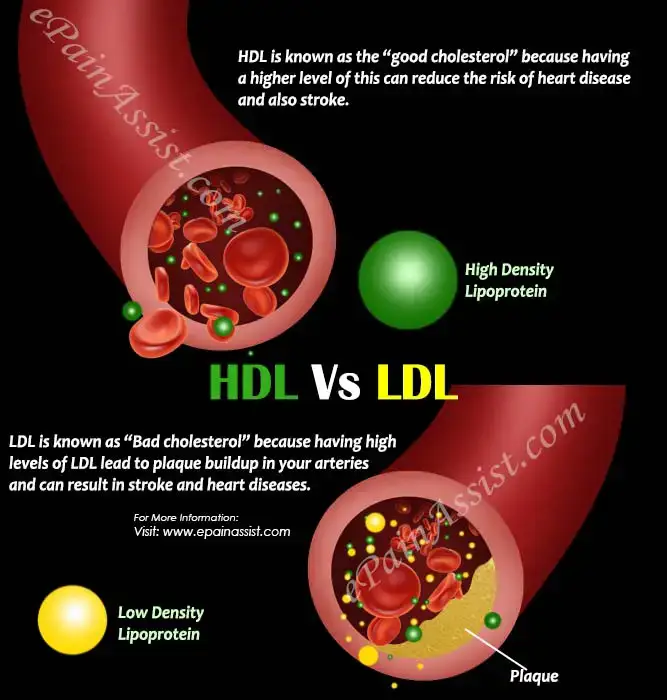
LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol is often referred to as "bad" cholesterol. It is a waxy, fat-like substance that can build up in the walls of your arteries, narrowing them and leading to various cardiovascular diseases.
What is Non-HDL Cholesterol?
Non-HDL cholesterol includes all types of cholesterol except for HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol. It consists of LDL cholesterol and other harmful fats in the blood. Non-HDL cholesterol is considered a better predictor of heart disease risk compared to LDL cholesterol alone.
How to Lower LDL and Non-HDL Cholesterol
- 1. Eat a Healthy Diet: Opt for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid foods high in saturated fats and trans fats.
- 2. Regular Exercise: Engage in moderate-intensity aerobic exercises like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming for at least 150 minutes per week.
- 3. Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing excess weight can help reduce LDL and non-HDL cholesterol levels.
- 4. Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can raise cholesterol levels, so limit your intake to moderate amounts.
- 5. Quit Smoking: Smoking damages your blood vessels and lowers your good cholesterol levels. Quitting smoking can improve your overall cholesterol profile.
- 6. Medication: In some cases, your healthcare provider may prescribe cholesterol-lowering medications if lifestyle changes are not enough to bring your cholesterol levels under control.
Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate course of action for managing your cholesterol levels.
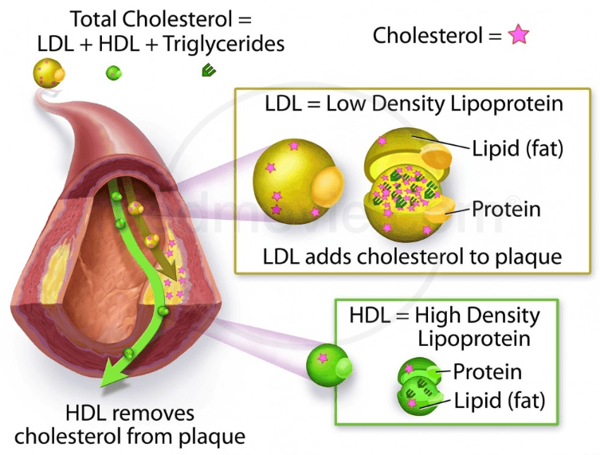
Balanced Diet and Portion Control
Learn about the importance of a balanced diet in maintaining healthy cholesterol levels and discover which foods you should include in your meals to promote a heart-healthy lifestyle. We will also discuss portion control techniques that can assist you in managing your cholesterol intake.
Eating a balanced diet and practicing portion control are essential for lowering LDL and non-HDL cholesterol levels. These two factors play a significant role in maintaining heart health and preventing the risk of heart disease.
What is LDL and Non-HDL Cholesterol?
LDL cholesterol, also known as "bad" cholesterol, is a type of cholesterol that can build up in the arteries, leading to blockages and increasing the risk of heart disease. Non-HDL cholesterol, on the other hand, includes LDL cholesterol as well as other harmful cholesterol particles.
Tips for a Balanced Diet:
- Increase Fiber Intake: Include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts in your diet. These foods are high in dietary fiber and can help reduce cholesterol levels.
- Choose Healthy Fats: Opt for sources of healthy fats, such as avocados, olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish. These fats can help improve cholesterol profiles.
- Reduce Saturated and Trans Fats: Limit the consumption of saturated and trans fats found in red meat, fried foods, and processed snacks. These fats can raise LDL cholesterol levels.
- Incorporate Lean Protein: Choose lean protein sources, such as skinless poultry, fish, legumes, and tofu, to maintain muscle health without adding excessive saturated fats.
- Limit Added Sugar and Salt: Reduce your intake of sugary drinks, desserts, and processed foods that contain high amounts of added sugars. Also, watch your salt intake as it may contribute to high blood pressure.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink an adequate amount of water daily to support overall health and assist in digestion.
Practicing Portion Control:
Portion control helps maintain a healthy weight, which in turn positively affects cholesterol levels. Here are some tips to help you practice portion control:
- Use Smaller Plates: Choose smaller plates and bowls to help control portion sizes.
- Read Food Labels: Pay attention to serving sizes mentioned on food packages and consume accordingly.
- Eat Mindfully: Eat slowly and savor each bite, paying attention to your body's hunger and fullness cues.
- Avoid Overeating: Be mindful of portion sizes and avoid going for seconds unless genuinely hungry.
- Divide Your Plate: Fill half of your plate with vegetables, one-fourth with lean protein, and one-fourth with whole grains.
Remember, consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian is always recommended to create a personalized plan based on your specific health needs and cholesterol levels.
By following a balanced diet and practicing portion control, you can effectively lower LDL and non-HDL cholesterol, reduce the risk of heart disease, and maintain a healthier heart.

Regular Physical Activity
Physical exercise has numerous benefits for cardiovascular health, including cholesterol regulation. Find out the optimal exercise routines and activities that can effectively lower LDL and non-HDL cholesterol levels.
Regular physical activity plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. One of its many benefits is the ability to lower LDL (low-density lipoprotein) and non-HDL (non-high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels.
What is LDL Cholesterol?
LDL cholesterol is commonly referred to as "bad" cholesterol because it can contribute to the build-up of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
What is Non-HDL Cholesterol?
Non-HDL cholesterol includes LDL cholesterol as well as other harmful cholesterol particles. It provides a comprehensive measure of all cholesterol not considered to be the beneficial HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol.
How Does Regular Physical Activity Lower LDL and Non-HDL Cholesterol?
Regular physical activity can positively impact cholesterol levels in several ways:
- Increasing HDL cholesterol: Physical activity raises the levels of HDL cholesterol, which helps remove LDL cholesterol from the arteries.
- Stimulating enzymes: Exercise activates enzymes that help move LDL cholesterol from the blood and convert it into less harmful forms.
- Improving overall cardiovascular health: Regular exercise strengthens the heart and improves circulation, leading to better cholesterol management.
- Aiding weight control: Physical activity, combined with a healthy diet, can help maintain a healthy weight or assist in weight loss. Excess weight is often associated with high cholesterol levels.
What Types of Physical Activity Are Beneficial?
Aim for a combination of aerobic exercises, such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming, along with strength training exercises. The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity each week, in addition to muscle-strengthening activities at least two days a week.
Consult Your Healthcare Provider
Before starting any new exercise routine, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider, especially if you have existing health conditions or concerns. They can provide guidance specific to your needs and help ensure your safety while exercising.
Remember, regular physical activity is just one aspect of maintaining healthy cholesterol levels. A balanced diet, limiting saturated and trans fats, along with other lifestyle changes, may also be necessary to achieve optimal results.
Dietary Supplements
In this section, we explore natural supplements that may assist in lowering LDL and non-HDL cholesterol. Learn about their effectiveness, recommended dosages, and possible side effects.
High levels of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) and non-HDL (non-high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol can significantly increase the risk of heart disease. Fortunately, incorporating certain dietary supplements into your routine can help in reducing these cholesterol levels.
1. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, commonly found in fish oil supplements, have shown to lower LDL and non-HDL cholesterol levels. These supplements can be easily added to your daily diet. Consult with your healthcare provider for the appropriate dosage for your specific needs.
2. Plant Sterols and Stanols
Plant sterols and stanols are natural substances found in plants that have cholesterol-lowering properties. They work by blocking the absorption of cholesterol from food in the intestines. Many functional food products and dietary supplements are fortified with plant sterols and stanols to help reduce LDL and non-HDL cholesterol levels.
3. Fiber Supplements
Dietary fiber is known to effectively lower LDL cholesterol levels. Increasing your daily intake of fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is recommended. If meeting the fiber requirement is a challenge, fiber supplements can be taken to ensure an adequate intake.
4. Green Tea Extract
Green tea extract contains compounds called catechins that have antioxidant properties and can aid in lowering LDL cholesterol. It is available in capsule form and can be consumed as a dietary supplement.
5. Garlic Extract
Garlic extract has been traditionally used to support cardiovascular health. Research suggests that garlic may help reduce LDL and total cholesterol levels. Garlic supplements are widely available and can be used as a complementary approach to managing cholesterol.
Remember, dietary supplements should not replace a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise. Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen to determine the appropriate dosage and ensure it is safe for your specific health condition.
Reducing Stress and Managing Mental Health
Discover the correlation between stress, mental health, and cholesterol levels. We will discuss various stress management techniques and provide tips for improving mental well-being, ultimately contributing to a healthier cholesterol profile.
In order to lower LDL and non-HDL cholesterol levels, it is essential to focus on reducing stress and managing mental health effectively. Stress has been known to negatively impact cholesterol levels, and managing it can significantly contribute to improving heart health. Here are some helpful tips:
1. Practice Stress-Reducing Techniques
Engage in activities that help alleviate stress such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or regular physical exercise. These techniques have proven to be effective in reducing stress levels and promoting a healthy mental state.
2. Maintain a Balanced Diet
Consuming a well-balanced diet low in saturated and trans fats can contribute to lower cholesterol levels. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your daily meals.
3. Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical exercise is crucial for maintaining good overall health. Exercise helps in managing stress, boosting cardiovascular health, and improving cholesterol levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
4. Get Sufficient Sleep
Adequate sleep is vital for managing stress and maintaining a healthy mental state. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep every night. Establish a regular sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine to improve your sleep patterns.
5. Seek Support
Don't hesitate to reach out for support if you're feeling overwhelmed. Share your concerns with loved ones, join support groups, or consider seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor. Talking about your emotions and concerns can significantly reduce stress levels and contribute to better mental health.
Remember, effectively managing stress and prioritizing mental health is crucial for lowering LDL and non-HDL cholesterol levels. By implementing these strategies into your daily routine, you can enhance your overall well-being and promote a healthy heart.
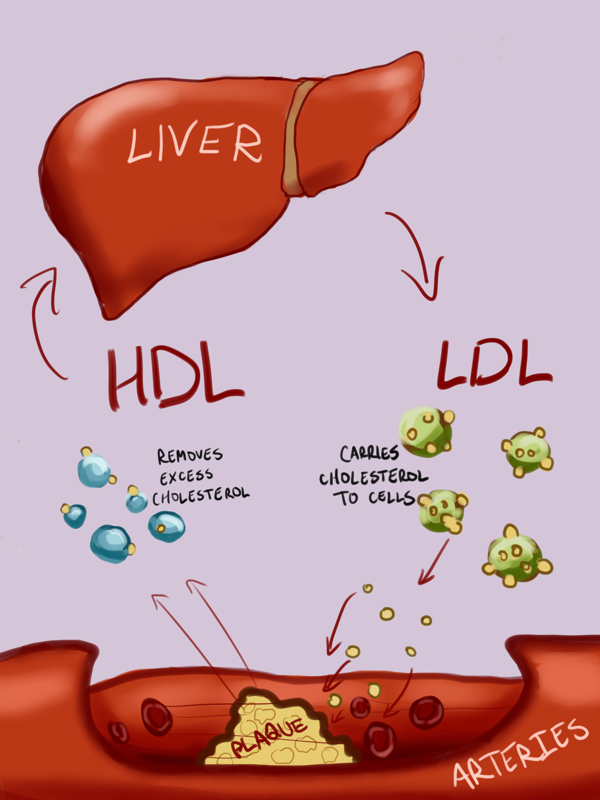
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Weight management plays a crucial role in cholesterol regulation. This section focuses on strategies to achieve and maintain a healthy weight through lifestyle changes and adopting long-term healthy habits.
Lowering LDL (low-density lipoprotein) and non-HDL (non-high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels is essential for maintaining a healthy heart. By managing your weight effectively, you can significantly improve these cholesterol markers and reduce your risk of cardiovascular diseases. Here are some key tips on how to achieve this:
1. Eat a Balanced Diet
Avoid foods high in saturated and trans fats, as they contribute to increased LDL and non-HDL cholesterol. Opt for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats like those found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts.
2. Control Portion Sizes
Be mindful of your portion sizes to prevent overeating and weight gain. Use smaller plates and bowls, and listen to your body's signals of fullness to avoid unnecessary calorie intake.
3. Engage in Regular Physical Activity
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise every week. Regular physical activity helps control weight, raises HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol (the "good" cholesterol), and reduces LDL and non-HDL cholesterol levels.
4. Limit Processed and Sugary Foods
Avoid or minimize consumption of processed foods, sugary drinks, and snacks high in added sugars. These can lead to weight gain, increase LDL and non-HDL cholesterol levels, and negatively impact overall health.
5. Monitor Your Cholesterol Levels
Get your cholesterol levels checked regularly. This will help you track your progress and make necessary adjustments to your lifestyle or medication as recommended by your healthcare provider.
6. Stay Hydrated
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated. This can help support weight management and promote overall health.
7. Seek Professional Guidance
Consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized advice and guidance on maintaining a healthy weight and managing your cholesterol levels effectively.
By implementing these lifestyle changes and adopting a holistic approach to your health, you can successfully lower your LDL and non-HDL cholesterol levels, achieve a healthy weight, and reduce the risk of heart diseases.
Medical Interventions
For individuals with persistently high cholesterol levels, medical interventions may be necessary. This section explains various treatment options available, including medication and medical procedures.
High levels of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) and non-HDL (non-high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol in the blood are known to increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases. However, there are several effective medical interventions that can help in lowering these cholesterol levels.
Dietary Modifications
One of the primary approaches to managing LDL and non-HDL cholesterol levels is through dietary modifications. This involves consuming a diet that is low in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol. Additionally, increasing the intake of fiber-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help lower cholesterol levels. Limiting the consumption of processed foods, sugary beverages, and alcohol is also recommended.
Statins
Statins are a class of medications that are commonly prescribed to individuals with high LDL and non-HDL cholesterol levels. They work by inhibiting an enzyme involved in cholesterol production, thereby reducing its levels in the bloodstream. Statins have been proven to be highly effective in lowering cholesterol and reducing the risk of heart disease. However, they should only be taken under the supervision of a healthcare professional due to potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
Ezetimibe
Ezetimibe is another medication that is prescribed to lower LDL and non-HDL cholesterol levels. It works by inhibiting the absorption of cholesterol from the intestines, leading to decreased levels in the bloodstream. This drug is often prescribed in combination with statins for enhanced cholesterol-lowering effects.
Exercise and Weight Management
Regular physical exercise and weight management play a crucial role in maintaining healthy cholesterol levels. Engaging in aerobic exercises, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, can help raise HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels while reducing LDL and non-HDL cholesterol. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and exercise is essential for overall cardiovascular health.
Other Medications
In certain cases, healthcare professionals may prescribe other medications like bile acid sequestrants, fibrates, or niacin to manage high LDL and non-HDL cholesterol levels. These medications work through various mechanisms to reduce cholesterol levels, and their usage is determined by the specific needs of each individual.
It is important to note that while medical interventions are effective, they should be complemented by lifestyle changes and regular check-ups with healthcare professionals. Adhering to a comprehensive treatment plan, which includes both medication and lifestyle modifications, is key to effectively managing cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Key Takeaways
- A balanced diet, portion control, and regular physical activity are fundamental in reducing LDL and non-HDL cholesterol levels.
- Natural supplements can be beneficial but should be taken under medical supervision.
- Managing stress and mental health can positively impact cholesterol profiles.
- Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for long-term cholesterol management.
- In some cases, medical interventions may be required to achieve optimal cholesterol levels.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I completely eliminate cholesterol from my diet?
A: While it's not possible to completely eliminate cholesterol from your diet, you can make choices that significantly reduce your cholesterol intake. Consuming foods low in saturated fats and trans fats is key.
Q: How long does it take to see improvements in cholesterol levels?
A: The time required to see improvements in cholesterol levels varies for each individual. However, with consistent adherence to a heart-healthy lifestyle, you can start observing positive changes within a few months.
Q: Are there any natural remedies for lowering cholesterol?
A: Alongside lifestyle modifications, several natural remedies, such as garlic, soluble fiber, and plant sterols, have shown potential in reducing LDL and non-HDL cholesterol levels. However, always consult a healthcare professional before using any natural remedies.


Recent Comments