Table of Contents
- What is Serum Non HDL Cholesterol?
- Why is Serum Non HDL Cholesterol Important?
- Determining the Normal Range
- Risk Factors Associated with Abnormal Levels
- Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Non HDL Cholesterol Level
- Impact on Cardiovascular Health
- Conclusion
1. What is Serum Non HDL Cholesterol?
Serum Non HDL Cholesterol refers to the amount of cholesterol found in the bloodstream that is not contained within the high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles. Unlike HDL cholesterol, non HDL cholesterol includes low-density lipoprotein (LDL), very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), and other cholesterol-rich lipoproteins.
2. Why is Serum Non HDL Cholesterol Important?
Understanding the importance of serum non HDL cholesterol levels is crucial as it is a better predictor of cardiovascular risk compared to other cholesterol measures. Elevated non HDL cholesterol levels contribute to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Why is Serum Non HDL Cholesterol Important?
Serum non HDL cholesterol refers to the level of cholesterol in the blood that is not contained within high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles. This measurement includes all other types of cholesterol, such as low-density lipoprotein (LDL), very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), and other non-HDL cholesterol particles.
The normal range for serum non HDL cholesterol varies depending on age, gender, and overall health. Generally, a desirable level is considered to be below 130 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter). However, specific target ranges may differ for individuals with certain medical conditions or a higher risk of heart disease.
It is important to monitor serum non HDL cholesterol levels because elevated levels are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. Non HDL cholesterol is considered a better predictor of cardiovascular risk than just measuring total cholesterol or HDL cholesterol alone. High levels of non HDL cholesterol can lead to the accumulation of cholesterol in the arteries, which can eventually cause blockages and restrict blood flow to vital organs.
Lowering serum non HDL cholesterol can be achieved through lifestyle modifications such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, weight management, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. In some cases, medication may be prescribed by a healthcare professional to help lower cholesterol levels.
In conclusion, maintaining a healthy range of serum non HDL cholesterol is essential for overall heart health. Regular check-ups and proper management of cholesterol levels can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases and improve overall well-being.
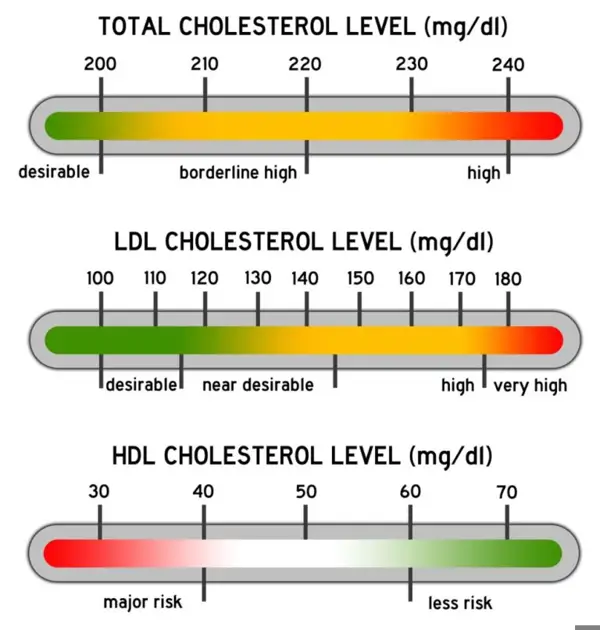
3. Determining the Normal Range
The normal range of serum non HDL cholesterol levels varies depending on factors such as age, gender, and existing health conditions. However, generally, a non HDL cholesterol level below 130 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) is considered healthy for adults.
Serum non-HDL cholesterol is a key measure used to assess an individual's risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. By determining the normal range of non-HDL cholesterol levels, healthcare professionals can identify individuals at increased risk and take appropriate measures to manage their cholesterol levels.
To determine the normal range, a comprehensive analysis of non-HDL cholesterol levels in a large sample population is conducted. This analysis considers factors such as age, gender, and overall health status. The data collected from these studies allows for the establishment of a baseline range within which non-HDL cholesterol levels are considered normal.
Typically, the normal range for serum non-HDL cholesterol falls between specific upper and lower limits. However, it's important to note that the normal range may vary slightly depending on the laboratory and methodology used for testing.
Healthcare professionals compare an individual's non-HDL cholesterol level to the normal range to determine if it falls within a healthy range. If the non-HDL cholesterol level is found to be higher than the upper limit of the normal range, it may indicate an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. In such cases, lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and medications may be recommended to lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Regular monitoring of serum non-HDL cholesterol levels is crucial to identify any changes that may occur over time. This allows for timely interventions and appropriate management of cholesterol levels to maintain cardiovascular health.
In conclusion, determining the normal range in serum non-HDL cholesterol is an essential aspect of cardiovascular risk assessment. By establishing this range, healthcare professionals can effectively evaluate an individual's cholesterol levels and provide appropriate guidance to promote heart health.

4. Risk Factors Associated with Abnormal Levels
Abnormal serum non HDL cholesterol levels may be influenced by various factors including obesity, poor diet, physical inactivity, smoking, and genetic predisposition. It is important to address these risk factors to maintain optimal cardiovascular health.
Abnormal levels in serum non-HDL cholesterol, outside the normal range, can indicate potential health risks. Here are some risk factors associated with such abnormal levels:
- Unhealthy Diet: Consuming a diet high in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and refined carbohydrates can lead to elevated non-HDL cholesterol levels.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese is a major risk factor for abnormal cholesterol levels, including non-HDL cholesterol.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Leading a sedentary lifestyle without regular exercise can contribute to high levels of non-HDL cholesterol.
- Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and reduces good cholesterol levels, leading to an increase in non-HDL cholesterol.
- Family History: A family history of high cholesterol or cardiovascular diseases can increase the likelihood of abnormal non-HDL cholesterol levels.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, hypothyroidism, kidney disease, and liver disease, can disrupt cholesterol metabolism and contribute to non-HDL cholesterol abnormalities.
It is important to regularly monitor your cholesterol levels and maintain a healthy lifestyle to reduce the risk of developing heart diseases and other related health problems.
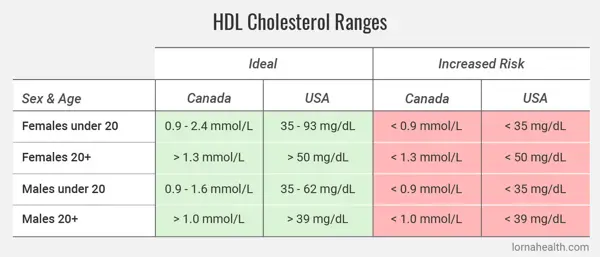
5. Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Non HDL Cholesterol Level
Here are some key lifestyle changes that can help in maintaining a healthy non HDL cholesterol level:
- Follow a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Avoid foods high in saturated and trans fats.
- Engage in regular physical activity.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
- Adopt a Healthy Diet: Incorporate a balanced diet that is low in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol. Focus on consuming foods rich in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in moderate-intensity aerobic activities for at least 150 minutes per week, or vigorous-intensity aerobic activities for 75 minutes per week. Exercise helps increase HDL cholesterol (the "good" cholesterol) and lower non HDL cholesterol.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking not only damages your lungs, but it also contributes to the increase of non HDL cholesterol. Quitting smoking improves your overall cardiovascular health and helps maintain a healthy non HDL cholesterol level.
- Control Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight can positively impact your non HDL cholesterol level. Aim to achieve and maintain a body mass index (BMI) within the healthy range.
- Regular Check-ups: Visit your healthcare provider regularly to monitor your cholesterol levels and overall health. Regular check-ups help identify any potential issues and enable you to make necessary adjustments to maintain a healthy non HDL cholesterol level.
It's important to remember that non HDL cholesterol levels vary depending on individual factors, so it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the specific target range suitable for you.
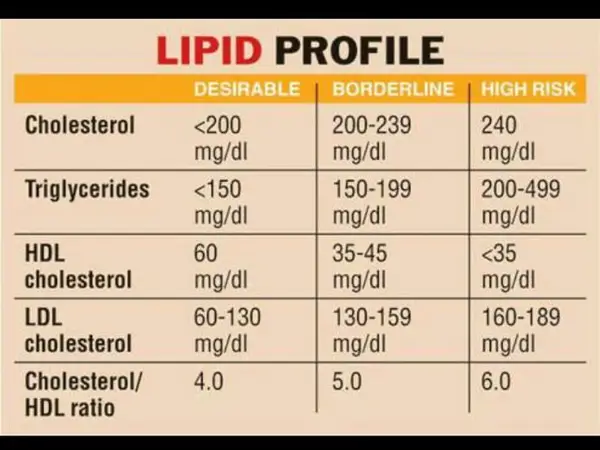
6. Impact on Cardiovascular Health
High serum non HDL cholesterol levels are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases such as coronary artery disease, heart attack, and stroke. By maintaining a healthy non HDL cholesterol level, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing these conditions.
Cardiovascular health is greatly influenced by the levels of serum non-HDL cholesterol within the normal range. Non-HDL cholesterol refers to the total cholesterol content present in the bloodstream, excluding the high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol. Maintaining a healthy range of serum non-HDL cholesterol is essential for overall cardiovascular well-being.
Elevated levels of non-HDL cholesterol have been directly linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. Research studies have consistently shown that high non-HDL cholesterol levels contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition where fatty deposits build up within the arteries, narrowing their lumen and reducing blood flow.
Individuals with serum non-HDL cholesterol levels within the normal range experience several positive effects on their cardiovascular health. Firstly, maintaining a healthy non-HDL cholesterol level helps to reduce the risk of plaque formation in the arteries, thus preventing the onset of atherosclerosis. This leads to improved blood flow, reducing the chances of heart-related complications.
Secondly, optimal non-HDL cholesterol levels aid in the regulation of blood pressure. High non-HDL cholesterol can lead to increased blood pressure, which in turn puts extra strain on the heart and blood vessels. By keeping non-HDL cholesterol in check, individuals can prevent hypertension and reduce the risk of developing conditions like coronary artery disease and heart failure.
Lastly, maintaining a healthy range of non-HDL cholesterol has been found to positively influence other cardiovascular risk factors such as triglyceride levels and LDL cholesterol levels. By controlling non-HDL cholesterol, individuals can achieve a better lipid profile, leading to improved overall heart health.
In conclusion, ensuring that serum non-HDL cholesterol remains within the normal range is crucial for preserving cardiovascular health. By managing non-HDL cholesterol levels effectively through a combination of lifestyle changes, such as adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and potentially utilizing cholesterol-lowering medications when necessary, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases and lead a healthier life.
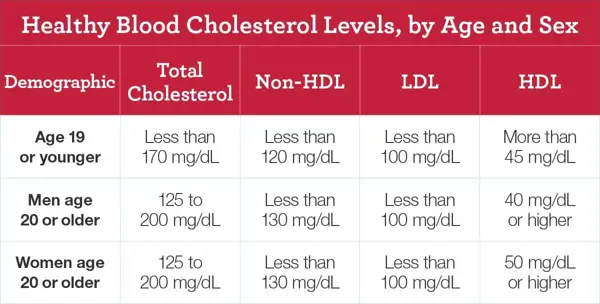
7. Conclusion
Maintaining a normal range of serum non HDL cholesterol is essential for optimal cardiovascular health. By understanding the significance of non HDL cholesterol and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, individuals can proactively prevent the development of cardiovascular diseases.
Key Takeaways
- Serum non HDL cholesterol consists of all cholesterol except the one present in HDL particles.
- Elevated non HDL cholesterol levels increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- A healthy non HDL cholesterol level for adults is generally below 130 mg/dL.
- Risk factors for abnormal levels include obesity, poor diet, physical inactivity, smoking, and genetics.
- Lifestyle changes like a balanced diet, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight help in managing non HDL cholesterol.
- High non HDL cholesterol is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Maintaining a normal non HDL cholesterol range significantly reduces the risk of heart-related conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can high non HDL cholesterol levels be managed without medication?
A1: In many cases, adopting a healthy lifestyle with diet and exercise can effectively manage high non HDL cholesterol levels. However, depending on the individual's health condition, medication may also be prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Q2: Are there any specific dietary recommendations to lower non HDL cholesterol?
A2: A diet rich in soluble fiber, healthy fats (such as monounsaturated fats and omega-3 fatty acids), and limited intake of saturated and trans fats can help lower non HDL cholesterol levels. Consulting a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is advisable for personalized dietary recommendations.
Q3: Can non HDL cholesterol levels be reduced through exercise alone?
A3: Regular exercise can contribute to reducing non HDL cholesterol levels. Combining aerobic activities, strength training, and maintaining an active lifestyle can help improve lipid profiles. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional before starting any exercise regimen, especially if there are underlying health concerns.


Recent Comments