Table of Contents
- What is Non HDL Cholesterol?
- What is Cholesterol Ratio?
- Why are they Important?
- How to Calculate Non HDL Cholesterol?
- How to Calculate Cholesterol Ratio?
- What Factors Affect Non HDL Cholesterol and Ratio?
- Tips for Managing Non HDL Cholesterol and Ratio
What is Non HDL Cholesterol?
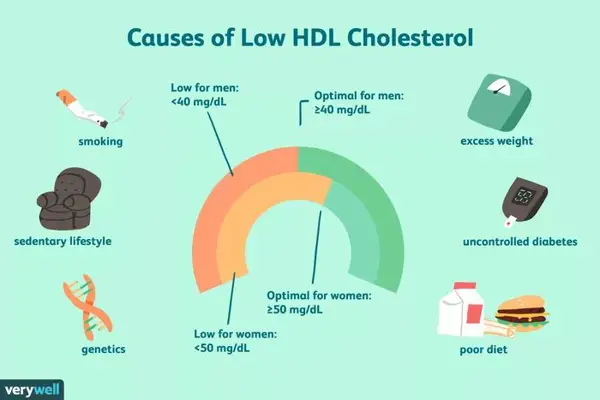
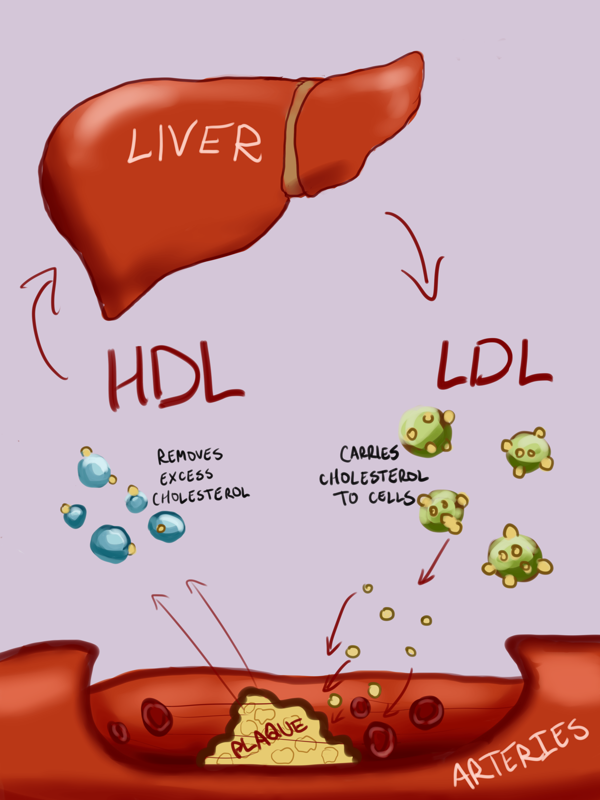
Non HDL cholesterol includes all the "bad" cholesterol in your blood, such as LDL and VLDL cholesterol. It is an important indicator of your risk for heart disease.
What is Cholesterol Ratio?
Cholesterol ratio vs ldl ratio of total cholesterol to HDL cholesterol. It is a key indicator of cardiovascular health, with lower ratios being more favorable.
Cholesterol ratio is a measure that helps assess your risk of heart disease by comparing your total cholesterol level to your high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol level. This ratio can provide valuable information about the health of your heart and arteries.
Non-HDL cholesterol refers to all types of cholesterol except for HDL cholesterol. It includes low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) cholesterol, and other triglycerides. Non-HDL cholesterol is considered a better predictor of heart disease risk compared to total cholesterol or LDL cholesterol alone.
The cholesterol ratio is calculated by dividing your total cholesterol by your HDL cholesterol. A lower ratio is considered better, as it indicates a lower risk of heart disease. For example, a ratio of 3.5 or lower is considered optimal.
Monitoring your cholesterol levels and cholesterol ratio regularly can help you take steps to lower your risk of heart disease through lifestyle changes and, if needed, medication.

Why are they Important?
Non HDL cholesterol and cholesterol ratio are both important markers for assessing your risk of cardiovascular disease. High levels of non HDL cholesterol and unfavorable cholesterol ratios can indicate an increased risk of heart disease.
Non-HDL cholesterol and the non-HDL cholesterol to HDL cholesterol ratio are important markers of cardiovascular health.
Non-HDL cholesterol includes all the bad cholesterol in the blood, such as LDL and VLDL cholesterol, which can contribute to the development of plaque in the arteries and increase the risk of heart disease. Monitoring non-HDL cholesterol levels is crucial in assessing an individual's risk of cardiovascular events.
The non-HDL cholesterol to HDL cholesterol ratio is also significant because it provides a more accurate measure of heart disease risk than just looking at non-HDL cholesterol levels alone. A higher ratio indicates a greater risk of heart disease, while a lower ratio suggests a lower risk.
By tracking these values and working to lower non-HDL cholesterol levels and improve the ratio, individuals can reduce their risk of developing heart disease and other cardiovascular complications. It is essential to pay attention to these markers as part of a comprehensive approach to maintaining heart health and overall well-being.
How to Calculate Non HDL Cholesterol?
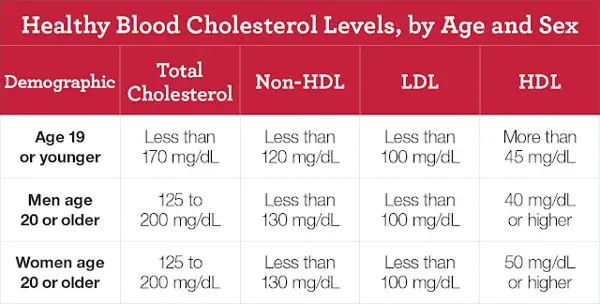
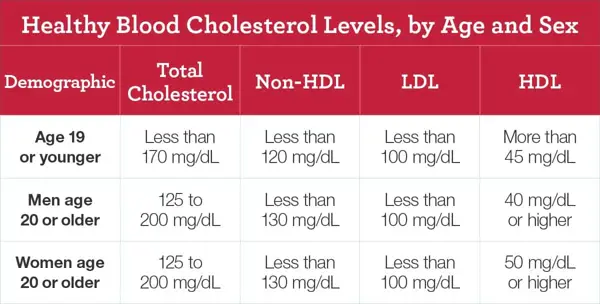
To calculate non HDL cholesterol, subtract your HDL cholesterol level from your total cholesterol level.
To calculate non-HDL cholesterol, you can follow these steps:
1. First, you need to have the results of your total cholesterol and your HDL cholesterol levels. These numbers can typically be found on a blood test report.
2. Subtract your HDL cholesterol level from your total cholesterol level to get your non-HDL cholesterol. This is because non-HDL cholesterol is calculated by subtracting the "good" HDL cholesterol from the total cholesterol.
3. Non-HDL cholesterol is considered a better predictor of heart disease risk compared to the total cholesterol to HDL cholesterol ratio. This is because it includes all the "bad" cholesterol, including LDL and very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) cholesterol.
By calculating your non-HDL cholesterol level, you can get a better understanding of your heart disease risk and work towards improving your overall cardiovascular health.
How to Calculate Cholesterol Ratio?
To calculate your cholesterol ratio, divide your total cholesterol by your HDL cholesterol level.
To calculate your cholesterol ratio, you first need to determine your non-HDL cholesterol level. Non-HDL cholesterol includes all the "bad" cholesterol in your blood, such as LDL cholesterol and very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) cholesterol. To find this number, subtract your HDL cholesterol level from your total cholesterol level.
Next, you will need to find your HDL cholesterol level. HDL cholesterol is considered the "good" cholesterol that helps to remove LDL cholesterol from your arteries. Once you have both of these numbers, you can calculate your cholesterol ratio by dividing your total cholesterol level by your HDL cholesterol level.
For example, if your total cholesterol level is 200 mg/dL and your HDL cholesterol level is 50 mg/dL, your cholesterol ratio would be 4:1. A lower ratio is generally better, as it indicates a lower risk of heart disease. It is recommended to keep your cholesterol ratio below 5:1.
Monitoring your cholesterol ratio can help you better understand your risk of heart disease and make informed decisions about your diet and lifestyle choices. It is important to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations based on your individual health needs.
What Factors Affect Non HDL Cholesterol and Ratio?
Factors such as diet, exercise, genetics, and medical conditions can all impact your non HDL cholesterol levels and cholesterol ratio. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help improve these markers.
Non-HDL cholesterol is a measure of the total cholesterol content in the blood that is not carried by high-density lipoproteins (HDL). It includes low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) cholesterol, and other lipoproteins that are considered atherogenic.
Several factors can affect non-HDL cholesterol levels and the non-HDL cholesterol to HDL cholesterol ratio. These factors include genetics, diet, physical activity, smoking, and underlying health conditions such as diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome.
A diet high in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and simple sugars can increase non-HDL cholesterol levels, while a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can help lower non-HDL cholesterol. Regular physical activity can also help improve cholesterol levels and decrease the non-HDL cholesterol to HDL cholesterol ratio.
Quitting smoking, managing stress, and controlling underlying health conditions can further help in maintaining healthy non-HDL cholesterol levels and ratio. It is important to regularly monitor cholesterol levels and work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan for managing non-HDL cholesterol and improving heart health.
Tips for Managing Non HDL Cholesterol and Ratio
Some tips for managing non HDL cholesterol and ratio include eating a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Non HDL cholesterol is a measure of all the "bad" cholesterol in your blood, including LDL, VLDL, and other triglycerides. It is an important marker for assessing cardiovascular risk.
1. Maintain a healthy diet:
Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your diet. Limit saturated and trans fats, as well as sugary and processed foods.
2. Stay physically active:
Regular exercise can help lower non HDL cholesterol levels and improve your overall cardiovascular health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
3. Quit smoking:
Smoking can raise your non HDL cholesterol levels and increase your risk of heart disease. Quitting smoking can have a positive impact on your cholesterol levels and overall health.
4. Manage your weight:
Being overweight or obese can increase your non HDL cholesterol levels. Losing even a small amount of weight can help improve your cholesterol levels and reduce your cardiovascular risk.
Non HDL Cholesterol vs. Ratio:
The non HDL cholesterol ratio is calculated by dividing your non HDL cholesterol level by your HDL cholesterol level. A higher ratio indicates a higher risk of cardiovascular disease. Aim for a ratio below 3.5 for optimal heart health.
Key Takeaways
- Non HDL cholesterol includes all "bad" cholesterol in the blood.
- Cholesterol ratio is the ratio of total cholesterol to HDL cholesterol.
- High levels of non HDL cholesterol and unfavorable cholesterol ratios are associated with increased risk of heart disease.
FAQ
What is the optimal cholesterol ratio?
The optimal cholesterol ratio is typically less than 4.0, with lower ratios being more favorable.
How can I lower my non HDL cholesterol?
You can lower your non HDL cholesterol by following a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and taking any prescribed medications as directed by your healthcare provider.



Recent Comments