Table of Contents
1. Red Meat
Eating too much red meat can lead to higher levels of iron in the blood, which can increase the risk of blood clots.
2. Processed Foods
Processed foods often contain high amounts of sodium and trans fats, both of which can contribute to blood clot formation.
Processed Foods and Blood Clots
Processed foods are those that have been altered from their natural state through various methods such as canning, freezing, or adding preservatives. These foods are often high in unhealthy fats, sugars, and sodium, which can contribute to a variety of health issues, including the formation of blood clots.
When we consume processed foods, our bodies may become inflamed, leading to an increased risk of blood clot formation. This is because these foods can disrupt the balance of chemicals in our blood that help regulate clotting. In addition, processed foods can also contribute to high cholesterol levels, which can further increase the risk of blood clots.
To reduce your risk of blood clots, it is important to limit your intake of processed foods and focus on eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. By making healthier food choices, you can help support overall cardiovascular health and reduce the likelihood of developing blood clots.
3. Sugar
Excessive sugar consumption can lead to inflammation in the body, which may increase the likelihood of blood clots.
Sugar is known to have negative effects on the body, including increasing the risk of blood clots. Consuming foods will make sugar your go up inflammation and elevated levels of certain substances in the blood that can contribute to the formation of blood clots.
It is important to be mindful of your sugar intake and opt for healthier food choices to reduce the risk of blood clots. Incorporating a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help improve overall health and decrease the likelihood of blood clots.
Remember to always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice on managing your diet and reducing the risk of blood clots.
4. Sodium
High sodium intake can raise blood pressure and contribute to the development of blood clots.
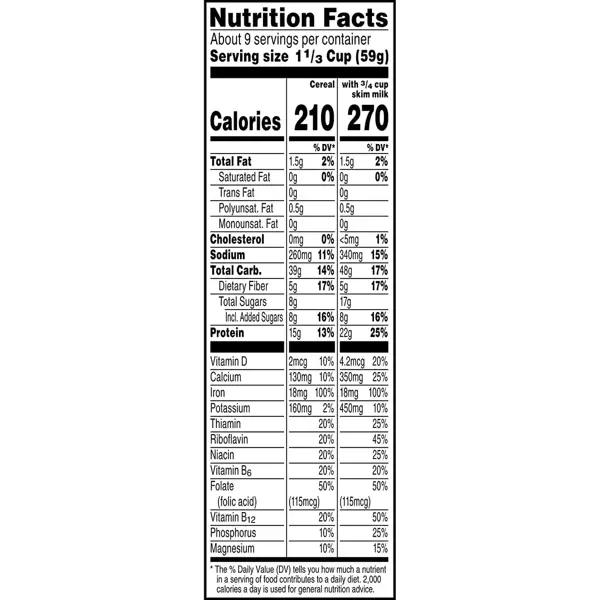
Consuming foods high in sodium can exacerbate blood clotting in the body. Sodium is a mineral that can increase blood pressure, leading to an increased risk of blood clots. It is important to be mindful of your sodium intake and opt for low-sodium options whenever possible. By reducing your sodium intake, you can help prevent blood clots and improve your overall cardiovascular health. Make sure to read nutrition labels and choose foods that are low in sodium to protect your heart and blood vessels.
5. Trans Fats
Trans fats found in processed and fried foods can raise bad cholesterol levels and increase the risk of blood clots.
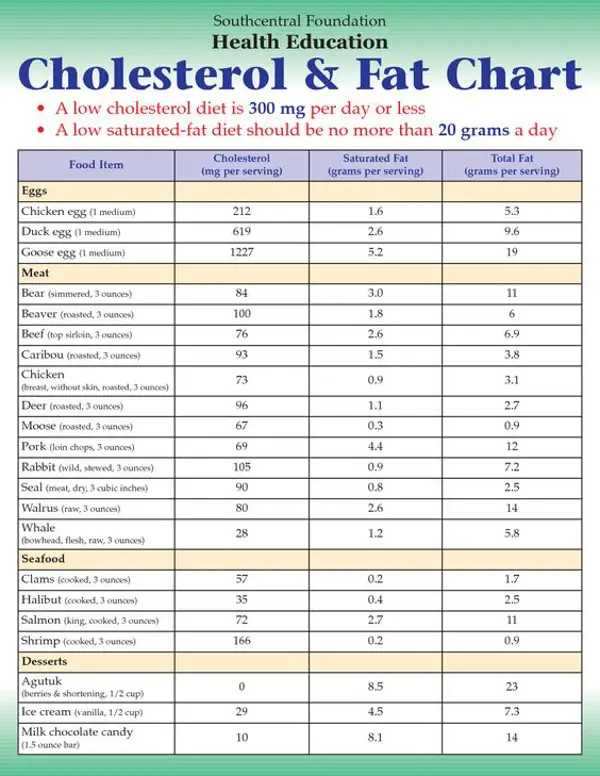
Trans fats are a type of unhealthy fat that can be found in processed foods such as fried foods, pastries, and certain types of margarine. Consuming foods high in trans fats can have negative effects on your health, particularly when it comes to blood clotting.
Trans fats have been shown to increase the levels of LDL cholesterol, also known as "bad" cholesterol, in the body. This can lead to a higher risk of developing blood clots, which can be extremely dangerous. Blood clots can block blood flow to vital organs, leading to serious health problems such as heart attacks and strokes.
It's important to read food labels carefully and avoid products that contain trans fats. Instead, opt for healthier fats such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats found in foods like avocados, nuts, and olive oil. Making these simple changes can help protect your heart and prevent the negative effects of trans fats on your health.

6. Alcohol
Excessive alcohol consumption can thin the blood and increase the risk of clot formation.
Alcohol can have a negative impact on blood clotting. Consuming alcohol in excess can lead to an increased risk of developing blood clots, which can be harmful to one's health. It is important to be mindful of the amount of alcohol consumed, especially if you are already at risk for blood clots. Make sure to talk to your healthcare provider about how alcohol may affect your specific health condition and take steps to minimize your risk. Remember, moderation is key when it comes to alcohol consumption and your overall health.

7. Caffeine
While moderate caffeine intake is generally safe, excessive consumption can lead to dehydration and increase the risk of blood clots.
Caffeine, commonly found in coffee, tea, and certain energy drinks, has been linked to an increased risk of blood clot formation. This is because caffeine can constrict blood vessels, making it harder for blood to flow freely through the body. When blood flow is restricted, it is more likely for clots to form, potentially leading to serious health issues such as heart attacks or strokes.
It is important to be mindful of your caffeine intake, especially if you have a history of blood clots or other cardiovascular problems. Consider limiting your consumption of caffeinated beverages and opting for decaffeinated options instead. Additionally, incorporating foods that are known to promote healthy blood flow, such as leafy greens, fatty fish, and berries, can help counteract the negative effects of caffeine on blood clots.
Overall, being aware of the impact of caffeine on blood clot formation and making mindful choices about your diet can help mitigate potential risks to your cardiovascular health.

Key Takeaways
- Avoiding red meat, processed foods, sugar, sodium, trans fats, alcohol, and excessive caffeine can help prevent blood clots.
- Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can promote cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of blood clots.
- Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized dietary recommendations to manage blood clot risk.
FAQ
Q: Can certain foods help prevent blood clots?
A: Yes, foods such as leafy greens, fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, and berries with antioxidant properties can help reduce the risk of blood clots.
Q: Are there any lifestyle changes that can help prevent blood clots?
A: Maintaining a healthy weight, staying physically active, and avoiding smoking can also contribute to reducing the risk of blood clots.


Recent Comments