Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Overview of Gout
- Impact of Diet on Gout Symptoms
- Foods to Avoid
- Lifestyle Changes to Manage Gout
- Medication Options for Gout
- Prevention Tips for Gout
Introduction
Gout is a form of arthritis that can cause severe pain, swelling, and stiffness in the joints. While there are several factors that contribute to gout, such as genetics and overall health, diet plays a crucial role in managing the condition.
Overview of Gout
In this section, we will provide a brief overview of what gout is, its symptoms, and how it is diagnosed. Understanding the basics of gout will help you comprehend the significance of diet in managing the condition.
Gout is a form of arthritis that causes severe joint pain, inflammation, and swelling. It occurs when there is a buildup of uric acid in the blood, leading to the formation of sharp, needle-like crystals in the joints. One of the main contributing factors to gout is the consumption of certain foods that are high in purines, which get converted into uric acid in the body. Here, we discuss some of the common foods that can trigger gout attacks.
Foods That Cause Gout
- Red Meat: High intake of red meat, such as beef, lamb, and pork, can increase the risk of gout as they are rich in purines.
- Seafood: Shellfish, like shrimp, crab, lobster, and mussels, are known to have high purine content, making them a potential trigger for gout.
- Organ Meats: Liver, kidneys, and other organ meats are extremely high in purines, and their consumption should be limited for individuals with gout.
- Sugary Drinks: Sweetened beverages, including sodas and fruit juices, have been associated with an increased risk of gout.
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption, especially beer and liquor, can lead to a gout flare-up. Alcohol not only increases the production of uric acid but also impairs its excretion.
Preventing Gout Attacks
While it may be challenging to completely eliminate purine-rich foods, especially those that are considered to be enjoyable, moderation is key. By practicing portion control and adopting a healthy eating plan, individuals can minimize the risk of gout attacks. Drinking plenty of water, maintaining a healthy weight, and limiting alcohol intake are additional lifestyle modifications that can be helpful.
Avoiding or limiting the consumption of foods high in purines is crucial for managing gout. Following a balanced diet and making healthier food choices can greatly contribute to preventing gout attacks and improving overall joint health.

Impact of Diet on Gout Symptoms
Discover the link between diet and gout symptoms. This section explores the various ways in which certain foods can trigger or exacerbate gout attacks. You'll learn how a healthy, balanced diet can help reduce the risk of flare-ups.
Gout is a form of arthritis caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints. It leads to severe pain, swelling, and stiffness. Diet plays a crucial role in managing gout symptoms, and certain foods are known to trigger gout attacks. The National Health Service (NHS) highlights these foods that can contribute to gout:
- Red Meat: Consuming high amounts of red meat, such as beef, lamb, and pork, increases the risk of gout. These meats are rich in purines, which get converted into uric acid when broken down.
- Seafood: Some types of seafood, including shellfish, anchovies, sardines, and mackerel, are high in purines and can worsen gout symptoms. It's advisable to limit their consumption.
- Organ Meats: Organ meats like liver, kidneys, and sweetbreads are extremely high in purines and should be avoided or consumed sparingly by individuals with gout.
- Processed Foods: Processed foods often contain high levels of purines, artificial additives, and preservatives that can trigger gout attacks. Examples include hot dogs, bacon, sausages, and ready meals. A healthy, whole-foods-based diet is recommended.
- Alcohol: Alcohol, especially beer, is known to raise uric acid levels and contribute to gout flare-ups. Individuals with gout are advised to limit or avoid alcohol consumption altogether.
- Sugary Drinks: Beverages like soda, sweetened juices, and energy drinks are high in fructose, which can elevate uric acid levels. These should be consumed in moderation or replaced with healthier alternatives like water or herbal teas.
It's important to note that individual triggers may vary, and certain people with gout may be more sensitive to specific foods. It's advisable to consult a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized dietary recommendations and guidance in managing gout symptoms.

Foods to Avoid
Get detailed insights into the foods that are known to increase uric acid levels, leading to gout attacks. By understanding which foods to limit or avoid, you can make informed choices and create a gout-friendly meal plan.
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood. Uric acid crystals can accumulate in the joints, causing inflammation and severe pain. Managing your diet is crucial in reducing gout flare-ups and controlling the symptoms.
Foods to Avoid
- Organ meats: Liver, kidney, and other organ meats are high in purines, which increase uric acid levels and can trigger gout attacks.
- Seafood: Certain types of seafood, such as anchovies, sardines, mussels, scallops, and herring, are rich in purines and should be limited or avoided.
- Red meat: Beef, pork, and lamb are high in purines. If you consume these meats, do so in moderation and choose lean cuts.
- Alcohol: Beer and spirits, particularly beer, are known to worsen gout symptoms. They not only increase uric acid levels but also impair the body's ability to excrete it.
- Sugary beverages: Soft drinks, fruit juices with added sugar, and other sugary drinks should be limited or replaced with water or unsweetened beverages. High-fructose corn syrup found in many sweetened drinks can elevate uric acid levels.
- High-fructose fruits: Fruits such as grapes, cherries, and oranges contain moderate to high levels of fructose, which can contribute to uric acid buildup. While fruits are generally healthy, it is advisable to consume them in moderation if you have gout.
- Processed foods: Processed snacks, fast food, and pre-packaged meals often contain high amounts of saturated fats, refined sugars, and additives that can exacerbate gout symptoms.
Remember, each individual may have different triggers for gout flare-ups. It is important to work with your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to develop a personalized diet plan that suits your specific needs and helps manage your gout effectively.
For more information and personalized advice, consult the official NHS website or reach out to a healthcare professional.
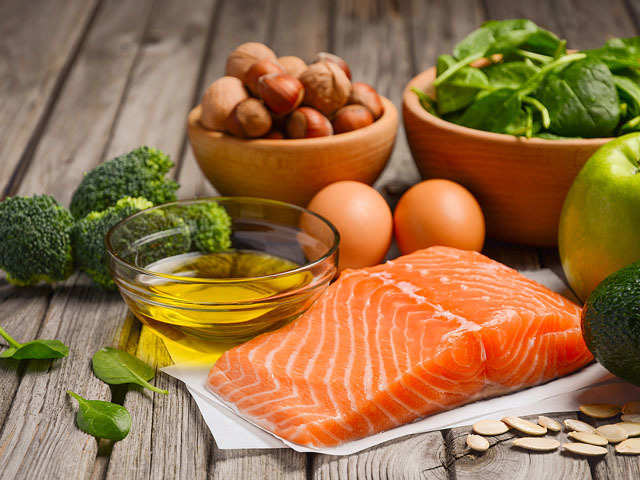

Lifestyle Changes to Manage Gout
Aside from dietary modifications, certain lifestyle changes can significantly improve gout symptoms and prevent future flare-ups. Learn about the importance of hydration, maintaining a healthy weight, and incorporating regular exercise into your routine.
Gout is a type of arthritis that occurs when uric acid builds up in the bloodstream, leading to the formation of crystals in the joints. Making certain lifestyle changes, especially in your diet, can help manage gout symptoms. It is essential to be aware of the foods that can cause gout and take necessary precautions to avoid them.
Foods to Avoid:
- High-Purine Meats: Certain meats, such as organ meats, game meats, and processed meats like sausages and bacon, are high in purines. Purines can raise uric acid levels, making gout worse.
- Seafood: Certain seafood like anchovies, sardines, mussels, scallops, and trout have high purine content and should be avoided.
- Alcohol: Beer and spirits can increase uric acid levels and trigger gout attacks. It is best to limit or avoid alcohol consumption, especially beer.
- Sugary Beverages: Soft drinks and fruit juices with added sugars should be avoided, as they have been linked to higher uric acid levels and increased gout risk.
- High-Fructose Foods: Fructose, a type of sugar, can increase uric acid levels. Foods and beverages with high-fructose corn syrup, sweetened with sugar or honey, should be limited or avoided.
Foods to Include:
- Low-Fat Dairy Products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese can help lower uric acid levels. Opt for low-fat or skim varieties.
- Complex Carbohydrates: Foods rich in complex carbohydrates like whole grains, brown rice, and oats are beneficial for managing gout.
- Plant-Based Proteins: Include plant-based protein sources like beans, lentils, and tofu in your diet. These are lower in purines compared to animal-based proteins.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Most fruits and vegetables are considered safe for gout sufferers. Cherries, berries, citrus fruits, and dark leafy greens may even have anti-inflammatory effects.
- Water: Staying hydrated is important for managing gout. Drink plenty of water to help flush out excess uric acid from your body.
It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized dietary recommendations based on your specific condition and needs. Making gradual and sustainable lifestyle changes can significantly help in managing gout and improving overall well-being.
Medication Options for Gout
In some cases, medication may be necessary to control gout symptoms effectively. This section provides an overview of the medications commonly prescribed for gout and their mechanisms of action.
Gout is a form of arthritis that causes sudden and severe joint pain, swelling, and inflammation. One way to manage gout is by controlling your diet, as certain foods can trigger gout attacks or worsen the symptoms. The National Health Service (NHS) provides a comprehensive list of foods that can potentially cause gout:
- Organ meats (liver, kidneys, sweetbreads)
- Red meat (beef, lamb, pork)
- Seafood (shellfish, sardines, anchovies)
- Yeast and yeast extracts
- High-fructose corn syrup
- Sugary beverages
- Alcohol (particularly beer and spirits)
- Processed foods
If you have been diagnosed with gout, it is crucial to work with your healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate medication options for your specific case. The primary goals of gout medication are to reduce pain, manage inflammation, and lower the uric acid levels in your body. Here are some common medication options used in gout treatment:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): These drugs help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation during gout attacks.
- Colchicine: This medication is specifically designed to relieve gout pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroids: Steroids are sometimes prescribed to reduce inflammation during severe gout attacks when other options are ineffective.
- Uric acid-lowering drugs: These medications aim to reduce the levels of uric acid in your body to prevent gout attacks. Examples include allopurinol and febuxostat.
It's important to note that medication alone may not be sufficient to manage gout effectively. Alongside medication, adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a well-balanced diet and regular exercise, can greatly contribute to gout management and prevention.
Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options for gout. They can provide the best guidance based on your individual needs and medical history.

Prevention Tips for Gout
Prevention is key when it comes to managing gout. Discover practical tips and strategies to prevent gout attacks and reduce the frequency of flare-ups. These simple yet effective steps can make a significant difference in your quality of life.
Gout is a form of arthritis that occurs when excess uric acid accumulates in the blood, leading to the formation of crystals in the joints. Proper diet and lifestyle changes can help prevent gout attacks and manage the condition effectively.
Preventing Gout with Dietary Changes:
- Avoid high-purine foods: Purine-rich foods can contribute to increased uric acid levels. Limit consumption of organ meats (liver, kidney), seafood (anchovies, sardines), red meat, and processed meat products.
- Control alcohol intake: Alcohol, particularly beer, can raise uric acid levels. Moderate your alcohol consumption and avoid binge drinking.
- Limit sugary drinks and foods: Sweetened beverages and high-fructose corn syrup can increase uric acid production. Opt for water or unsweetened drinks instead.
- Choose low-fat dairy: Low-fat dairy products such as milk, yogurt, and cheese have been associated with a reduced risk of gout. Include them in your diet in moderation.
- Incorporate fruits and vegetables: Fruits and vegetables are low in purines and high in nutrients. Include plenty of them in your meals to promote overall health.
Lifestyle Tips for Managing Gout:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can contribute to higher uric acid levels. Engage in regular physical activity and follow a balanced diet to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water helps in flushing out uric acid from the body. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water per day.
- Avoid crash diets: Rapid weight loss diets or fasting can lead to an increase in uric acid levels. Opt for gradual and sustainable weight loss methods instead.
- Avoid prolonged fasting or starvation: Extended periods without eating can increase the production of uric acid. Maintain regular meal times and avoid extreme fasting.
- Manage stress: High levels of stress can trigger gout attacks. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques, exercising, or engaging in hobbies.
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance on managing gout. By following these prevention tips and making necessary lifestyle modifications, you can reduce the risk of gout attacks and improve your overall well-being.
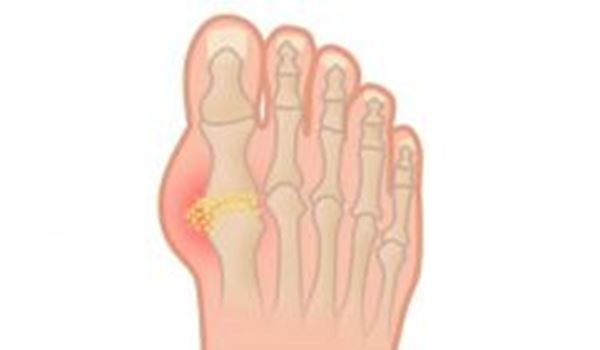
Key Takeaways
- Eating a healthy diet plays a crucial role in managing gout symptoms.
- Several foods are known to increase uric acid levels and should be limited or avoided.
- Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight and staying hydrated are important for gout management.
- Medications may be prescribed by a healthcare professional to control gout symptoms.
- Preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of gout attacks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 1. Can I ever consume foods that cause gout?
- While it's essential to limit certain foods, it doesn't mean you have to eliminate them completely. Moderation is key.
- 2. Can gout be cured with diet alone?
- A healthy diet is an integral part of managing gout, but other factors like medication and lifestyle changes may also be necessary.
- 3. How can I control gout flares?
- Avoiding trigger foods, taking prescribed medications, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are effective ways to control gout flares.
- 4. Is alcohol consumption linked to gout?
- Yes, alcohol, especially beer, can increase uric acid levels and trigger gout attacks. It is advisable to limit alcohol intake.
- 5. Should I consult a healthcare professional for gout management?
- Yes, a healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance, recommend suitable treatments, and monitor your condition closely.



Recent Comments