Table of Contents
- Model 1: The Biomedical Model
- Model 2: The Biopsychosocial Model
- Model 3: The Social Model
- Key Takeaways
- FAQ
Model 1: The Biomedical Model
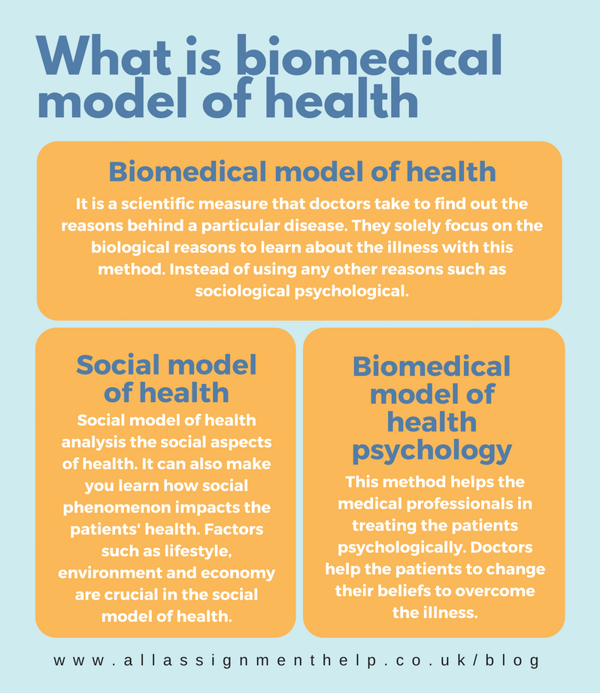
The biomedical model of health focuses on the physical aspects of disease and views health as the absence of illness. This model mainly relies on the diagnosis and treatment of diseases through medical interventions such as surgeries, medications, and other therapeutic approaches.
Model 2: The Biopsychosocial Model
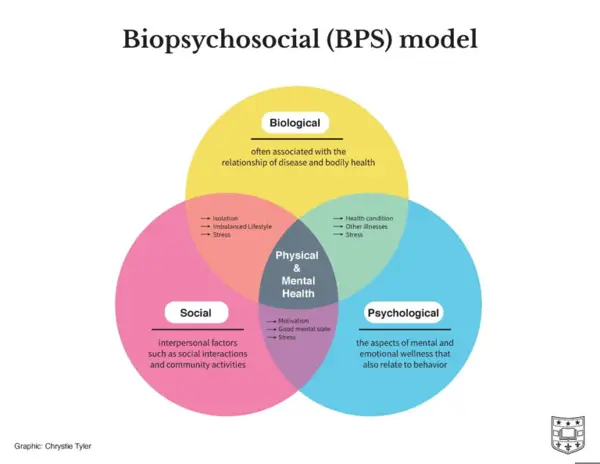
The biopsychosocial model acknowledges that health is influenced not only by biological factors but also by psychological and social factors. It emphasizes the interconnectedness of biological, psychological, and social aspects in understanding human health and well-being.
In the field of health, there are three main models that help us understand and approach health-related issues. One of these models is the Biopsychosocial Model.
The Three Models of Health:
- Model 1: The Biomedical Model: This model focuses on the physical aspects of health and diseases. It considers health solely as the absence of disease or any physical abnormality. The Biomedical Model predominantly emphasizes medical interventions, such as surgeries or medications, to treat health issues.
- Model 2: The Biopsychosocial Model: The Biopsychosocial Model takes a holistic approach to health by considering three interconnected dimensions – biological, psychological, and social. It recognizes that health is influenced by biological factors (e.g., genetics, physiological processes), psychological factors (e.g., thoughts, emotions, behavior), and social factors (e.g., culture, family, socioeconomic status). This model believes that all three dimensions are essential in understanding and addressing health-related concerns.
- Model 3: The Social Model: The Social Model of health focuses on the social determinants of health, emphasizing that health and well-being are influenced by factors beyond an individual's control. It looks at aspects like education, income, housing, and access to healthcare. This model aims to reduce health inequalities and promote social justice by addressing the root causes of health issues.
The Biopsychosocial Model provides a comprehensive framework that acknowledges the multifaceted nature of health and encourages a broader approach to healthcare. It promotes understanding and treating individuals not just based on their physical symptoms, but also by considering their psychological well-being and social context.
Model 3: The Social Model
The social model of health recognizes that health outcomes are deeply influenced by social determinants such as socio-economic status, education, employment, and access to healthcare. It highlights the need to address social inequalities and structural factors to improve overall health and well-being in populations.
The social model of health is one of the three primary models used to understand and promote health. It emphasizes the impact of social, economic, and environmental factors on individual and community well-being. Here, we will explore the three models of health in brief:
1. Medical Model
The medical model is the traditional approach to health that focuses primarily on the physical aspects of illness and disease. It emphasizes diagnosis, treatment, and management of symptoms using medical interventions such as medication and surgery. The medical model is mainly concerned with the individual and does not extensively consider broader social determinants of health.
2. Holistic Model
The holistic model, also known as the biopsychosocial model, takes a more comprehensive view of health. It recognizes that health is influenced by biological, psychological, and social factors. It emphasizes the interplay between these different dimensions and emphasizes the importance of treating the person as a whole rather than just addressing isolated symptoms or diseases.
3. Social Model
The social model of health acknowledges that health outcomes are shaped by the social, economic, and environmental conditions in which individuals and communities live. It highlights the role of social determinants of health, such as access to education, employment, housing, healthcare, and social support networks. The social model aims to address health inequities by addressing these underlying social factors.
In summary, while the medical model focuses on individual diagnosis and treatment, the holistic model considers the biological, psychological, and social dimensions of health. The social model recognizes the influence of social determinants on health outcomes and aims to address broader societal issues to improve population health.
Key Takeaways
- The biomedical model focuses solely on physical health and treating diseases.
- The biopsychosocial model takes into account biological, psychological, and social factors that impact health.
- The social model emphasizes the influence of social determinants on health outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How are the three models of health different?
A: The biomedical model emphasizes the physical aspects of health, the biopsychosocial model incorporates biological, psychological, and social factors, while the social model focuses on the impact of social determinants on health outcomes.
Q: Why is it important to understand these models?
A: Understanding these models helps broaden our perspective on health and encourages a more holistic approach to healthcare. It highlights the need to consider multiple factors influencing well-being and allows for a comprehensive analysis of health-related issues.
Q: Can these models be integrated into healthcare practices?
A: Yes, healthcare practices can benefit from an integrated approach that combines aspects from each model. This allows healthcare professionals to address not only the physical symptoms but also the psychological and social aspects affecting a patient's well-being.


Recent Comments