Table of Contents:
1. Nitrogenous Bases
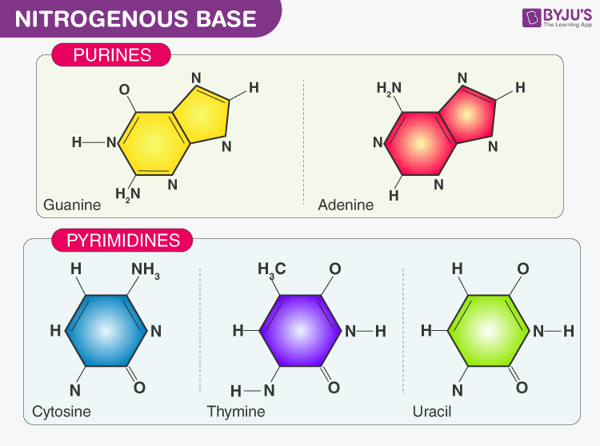
Nitrogenous bases are the building blocks of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. They include adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These bases pair up in a specific manner: A with T and C with G.
2. Codons
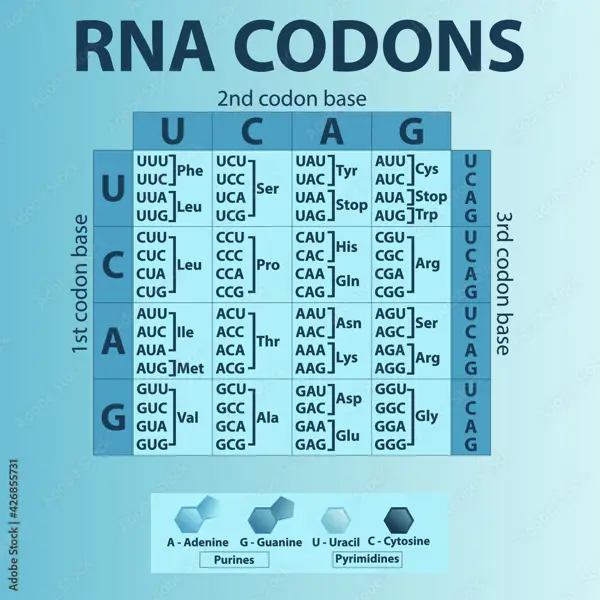
Codons are sequences of three nitrogenous bases that represent specific amino acids during protein synthesis. The genetic code is read in groups of codons, each coding for a specific amino acid or a start/stop signal.
In genetics, codons are the basic building blocks of DNA that determine the sequence of amino acids in a protein. Each codon consists of three nitrogenous bases, which are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T).
The sequence of nitrogenous bases in a codon corresponds to a specific amino acid. For example, the codon "AUG" codes for the amino acid methionine. A series of codons strung together along a strand of DNA or RNA forms a gene, which ultimately determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein.
Once a gene is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA), it is translated by ribosomes, which read the codons and assemble the corresponding amino acids into a protein. This process, known as protein synthesis, is crucial for the growth, development, and function of living organisms.
In conclusion, the relationship between nitrogenous bases, codons, amino acids, and proteins is essential for the proper functioning of cells and organisms. Through the intricate code of DNA, the genetic information stored in codons ultimately dictates the structure and function of proteins in the body.
3. Amino Acids
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. There are 20 different amino acids, each coded for by one or more codons in the genetic code. Amino acids are linked together in a specific order to form proteins.
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, which are essential for the growth and repair of tissues in the body. These amino acids are formed by the combination of nitrogenous bases found in our DNA.
The genetic code within our DNA is made up of sequences of nitrogenous bases known as codons. These codons serve as the instructions for the synthesis of specific amino acids during protein production.
When a specific codon is read during the process of protein synthesis, the corresponding amino acid is added to the growing protein chain. This sequence of codons and amino acids determines the structure and function of the protein being created.
In conclusion, nitrogenous bases, codons, amino acids, and proteins are all interconnected in the intricate process of protein synthesis. The genetic information coded in our DNA directs the formation of specific amino acids, which then come together to create the diverse array of proteins necessary for the functioning of our bodies.
4. Proteins
Proteins are large molecules made up of one or more polypeptide chains, which are composed of amino acids linked together. Proteins play essential roles in the structure, function, and regulation of cells and tissues.
In molecular how proteins polypeptides related quizlet amino acids which are coded for by sequences of nitrogenous bases in DNA. These sequences are called codons and they specify the order in which amino acids are added to a growing protein chain during translation.
The relationship between nitrogenous bases, codons, amino acids, and proteins is crucial for the functioning of living organisms. Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid, and the sequence of codons determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein.
This process of translating DNA into proteins is essential for various cellular functions, including growth, repair, and energy production. Without the accurate coding and decoding of nitrogenous bases into amino acids, proteins would not be able to perform their diverse roles in the body.
Overall, the intricate relationship between nitrogenous bases, codons, amino acids, and proteins highlights the complexity and precision of molecular biology processes in living organisms.

Key Takeaways:
- Nitrogenous bases form the basis of DNA and RNA molecules.
- Codons are sequences of three bases that represent specific amino acids during protein synthesis.
- Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, coded for by codons in the genetic code.
- Proteins are complex molecules made up of amino acids and play vital roles in biological processes.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: How are nitrogenous bases related to codons?
A: Nitrogenous bases are the individual components of codons, which are sequences of three bases that code for specific amino acids.
Q: What is the role of amino acids in protein synthesis?
A: Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and are linked together in a specific order dictated by codons in the genetic code.


Recent Comments