Table of Contents
- Introduction to Packet Loss
- Causes of High Packet Loss
- Effects of High Packet Loss
- Measuring and Analyzing Packet Loss
- Strategies to Reduce Packet Loss
- Best Practices for Network Administrators
- Conclusion
Introduction to Packet Loss
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Quisque mattis enim nisl, vitae elementum mi consectetur non.
Causes of High Packet Loss
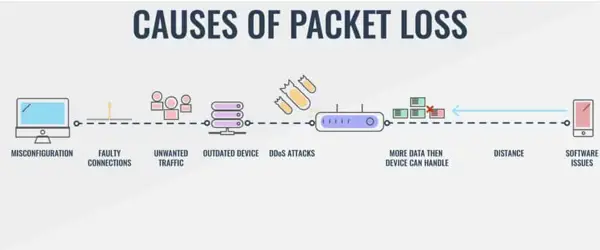
Curabitur tristique cursus fermentum. Fusce consectetur eros mauris, eu hendrerit tellus aliquet nec.
1. Network Congestion:
One of the primary causes of high packet loss in the internet is network congestion. When a network becomes congested due to excessive data traffic, the routers and switches handling the traffic may struggle to keep up. This can result in packets being dropped, leading to higher packet loss.
2. Hardware or Equipment Issues:
Faulty or malfunctioning hardware or network equipment can also contribute to high packet loss. Issues such as outdated routers, faulty cables, or network interface cards (NICs) can disrupt the proper transmission of packets, causing loss of data packets along the way.
3. Distance and Latency:
Distance and latency in network connections can impact packet loss as well. Longer distances between devices can introduce more opportunities for packet loss due to increased travel time. Similarly, high latency connections can result in delayed or lost packets.
4. Wireless Interference:
In wireless networks, interference from other devices or networks can lead to higher packet loss. Microwave ovens, cordless phones, or other wireless devices operating on similar frequencies can disrupt the signal and cause packet loss.
5. Network Jitter:
Network jitter refers to the variability in packet arrival times. If the network experiences inconsistent latency, packets may arrive out of order or be dropped, leading to packet loss. Jitter can be caused by various factors like network congestion, inadequate buffer sizes, or improper routing configurations.
6. Firewall or Security Settings:
Overly strict firewall or security settings can sometimes result in packet loss. These settings may be too restrictive and drop legitimate packets, leading to increased packet loss for network connections.
7. Bandwidth Limitations:
If the available bandwidth for a network connection is insufficient to handle the amount of data being transmitted, it can lead to high packet loss. This often happens during periods of heavy network usage or when the network is shared among many users.
In conclusion, high packet loss in the internet can be caused by network congestion, hardware issues, distance and latency, wireless interference, network jitter, firewall or security settings, as well as bandwidth limitations. Understanding these causes can help in troubleshooting and improving network performance.

Effects of High Packet Loss
Nulla tristique consectetur tellus ac lacinia. Vivamus dictum a eros sit amet placerat.
High packet loss refers to the loss of a significant number of data packets during transmission over the internet. This can have several negative effects on internet connectivity and user experience:
- Increased Latency: Packet loss can result in increased latency or delay in data transmission. When packets are lost, they need to be retransmitted, causing additional delay in receiving the required information.
- Poor Voice and Video Quality: High packet loss can lead to distorted audio and video during real-time communication. This is particularly problematic in applications such as video conferencing, online gaming, and voice over IP (VoIP) calls.
- Reduced Throughput: Packet loss can affect the overall throughput of a network connection. As packets need to be resent due to loss, available bandwidth is wasted on retransmissions, resulting in reduced data transfer speeds.
- Incomplete Data: If critical packets are lost, it may lead to incomplete data being received. This can cause errors and disrupt the proper functioning of applications that rely on accurate data transmission.
- Poor User Experience: Continuous high packet loss can lead to frustrating user experiences, such as web pages taking longer to load, frequent video buffering, or interrupted audio streams.
It is important for internet service providers and network administrators to address and minimize packet loss to ensure reliable and efficient internet connectivity for users.

Measuring and Analyzing Packet Loss
Maecenas euismod, justo id fringilla dapibus, odio est vulputate est, sed luctus mi risus eu nisi.
Packet loss refers to the phenomenon where packets of data being transmitted across a network fail to reach their destination. This can happen due to various factors such as network congestion, faulty hardware, or weak signal strength.
In high packet loss situations, it becomes crucial to accurately measure and analyze the extent of the problem in order to identify the underlying causes and implement appropriate solutions.
Measuring Packet Loss
There are several tools and techniques available to measure packet loss in an internet connection. One commonly used method is to use the ping command, which sends small packets of data to a target server and measures the round-trip time. If a packet is lost, the ping utility reports a time-out or loss percentage.
Other advanced tools like traceroute can also be employed to measure packet loss along the network path between a source and a destination. This helps in pinpointing the specific routers or network segments where the loss is occurring.
Analyzing Packet Loss
Once the packet loss is measured, the next step is to analyze the collected data to understand the causes and impacts. Packet loss analysis often involves examining various network statistics and logs.
It is important to differentiate between occasional packet loss, which may be tolerable, and persistent or high packet loss, which can severely degrade network performance. In the case of high packet loss, further investigations are required to identify potential bottlenecks or network issues.
Common causes of high packet loss include excessive network congestion, hardware faults, faulty cables, or problematic network configurations. By analyzing the packet loss patterns and related metrics, such as latency and jitter, network administrators can identify the specific cause and take appropriate actions to rectify the situation.
In conclusion, measuring and analyzing packet loss in situations of high packet loss is vital for maintaining a reliable and efficient network. With the right tools and techniques, network administrators can identify and resolve the underlying issues, ensuring optimal performance and user experience.

Strategies to Reduce Packet Loss
Pellentesque eget arcu mi. Ut bibendum magna felis, ut facilisis nunc vestibulum et.
Packet loss refers to the loss of data packets during transmission over a network, leading to poor internet performance and disrupted communication. In high-speed internet connections, the issue of packet loss becomes even more crucial as it can significantly impact the user experience. This HTML article outlines some effective strategies to mitigate packet loss and ensure a smooth and reliable internet connection.
1. Use Quality Network Hardware
The first step to reduce packet loss is to use high-quality network hardware, such as routers, switches, and network interface cards. Investing in reliable equipment can minimize the chances of packet loss due to hardware malfunctions or outdated technology.
2. Optimize Network Bandwidth
Packet loss can occur when the network is congested or when bandwidth limits are exceeded. To address this, consider optimizing your network bandwidth by using Quality of Service (QoS) techniques, traffic shaping, or prioritizing specific types of data. By efficiently managing your network's resources, you can reduce the occurrence of packet loss.
3. Perform Regular Network Maintenance
Regular maintenance and monitoring of your network infrastructure are crucial for identifying and resolving potential causes of packet loss. Ensure that your routers, switches, and cables are functioning properly, and promptly address any network issues or errors that may contribute to packet loss.
4. Implement Error Correction Mechanisms
By using error correction mechanisms, such as Forward Error Correction (FEC), you can minimize the impact of packet loss. FEC adds redundant information to each packet, allowing the receiver to reconstruct lost packets. Implementing such mechanisms can greatly improve the overall reliability of your internet connection.
5. Prioritize Real-Time Applications
For applications that require low-latency and real-time communication, it is essential to prioritize their network traffic. VoIP calls, video conferencing, online gaming, and other real-time applications can be adversely affected by packet loss. By giving them higher priority over other less time-sensitive traffic, you can ensure a smoother experience for these applications.
Reducing packet loss in high-speed internet connections is crucial for ensuring an optimal user experience. By implementing these strategies, such as using quality hardware, optimizing network bandwidth, performing regular maintenance, implementing error correction mechanisms, and prioritizing real-time applications, you can significantly reduce the occurrence of packet loss and enjoy a more reliable and seamless internet connection.
Best Practices for Network Administrators
Aenean ac neque ligula. Cras venenatis nibh non semper fermentum. Duis vulputate viverra turpis et scelerisque.
High packet loss in a network can severely impact its performance and disrupt connectivity. Network administrators need to follow certain best practices to address this issue effectively. Here are some key practices:
1. Monitoring and Analysis
Regularly monitor network performance to detect and identify any occurrences of high packet loss. Utilize network monitoring tools to measure and analyze packet loss metrics in real-time. This helps in early detection and prevention of potential network issues.
2. Diagnosing the Cause
Thoroughly investigate the root cause of high packet loss. It can be due to network congestion, hardware failure, faulty cabling, or misconfigured routers. By identifying the underlying cause, network administrators can implement appropriate solutions.
3. Bandwidth Management
Implement bandwidth management techniques such as Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize critical traffic over less important ones. This helps in reducing packet loss by ensuring that important data receives higher priority and proper allocation of network resources.
4. Network Redundancy
Establish redundant network paths and devices to minimize the impact of packet loss. Redundancy ensures that if one path or device fails, the network traffic can be rerouted through an alternate path, reducing the overall packet loss rate.
5. Updating Firmware and Patches
Regularly update network equipment firmware and apply security patches to prevent known issues that can contribute to packet loss. Keeping network devices up to date ensures they have the latest bug fixes and optimizations, improving overall network stability.
6. Optimize Network Configuration
Tweak network configuration settings such as buffer sizes, timeouts, and congestion control algorithms to optimize packet delivery. Properly configuring routers, switches, and firewalls can help mitigate packet loss issues and enhance network performance.
7. Network Capacity Planning
Conduct capacity planning exercises to ensure your network can handle the expected traffic volume without excessive packet loss. Scaling network infrastructure, adding more bandwidth, or upgrading hardware in a timely manner helps accommodate increasing demands and prevents packet loss.
8. Regular Network Maintenance
Schedule regular network maintenance activities to check and address any potential sources of packet loss. This includes inspecting cables, verifying device configurations, and replacing faulty components. Preventive maintenance helps identify and resolve issues before they impact network performance.
Implementing these best practices can significantly reduce high packet loss in a network, resulting in improved reliability, lower latency, and better overall user experience.

Conclusion
Sed sollicitudin dignissim nisl in sagittis. Vestibulum tristique odio vitae ipsum rutrum dignissim.
Key Takeaways
- Packet loss can severely impact internet network performance.
- Understanding the causes and effects of packet loss is essential.
- Proper measurement and analysis help identify and troubleshoot packet loss issues.
- Implementing strategies can help reduce packet loss and improve network efficiency.
- Network administrators play a vital role in maintaining a reliable network.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Q: What is packet loss?
A: Packet loss refers to the unsuccessful transmission or reception of data packets within a network. - Q: How does packet loss affect internet connectivity?
A: High packet loss can cause network congestion, increased latency, and disrupt real-time applications such as video calls or online gaming. - Q: How can I measure packet loss on my network?
A: Various tools like Ping, Traceroute, or specialized network monitoring software can help measure packet loss. - Q: Can packet loss be prevented?
A: While it cannot be completely prevented, proactive measures like improving network infrastructure and employing quality of service (QoS) techniques can mitigate packet loss.


Recent Comments