Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Serum Calcium?
- Normal Levels of Serum Calcium
- Causes of Abnormal Serum Calcium Levels
- Symptoms of Abnormal Calcium Levels
- Treatment for Abnormal Calcium Levels
- Conclusion
Introduction
Calcium is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in various physiological processes in the body. One of the key indicators of calcium levels in the body is serum calcium, which is the concentration of calcium in the blood. Maintaining normal levels of serum calcium is crucial for overall health and well-being.
What is Serum Calcium?
Serum calcium is the measurement of calcium in the blood and is typically expressed in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). It is an important parameter that helps assess the functioning of the parathyroid glands, bones, kidneys, and the digestive system.
Serum calcium refers to the level of calcium in the blood. Calcium is a mineral that plays a crucial role in many bodily functions, including bone health, muscle contractions, nerve function, and blood clotting.
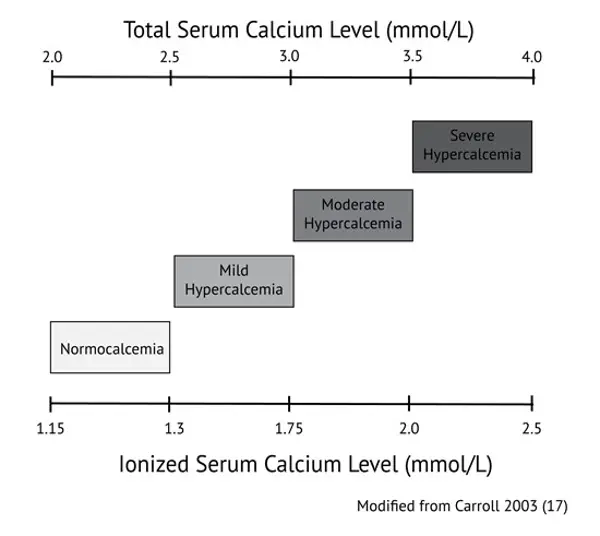
The normal range for serum calcium levels is typically between 8.5 and 10.2 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Having levels below or above this range can indicate an underlying health issue.
Low levels of serum calcium, known as hypocalcemia, can lead to symptoms such as muscle cramps, numbness or tingling in the hands and feet, and even seizures. High levels of serum calcium, known as hypercalcemia, can cause symptoms such as fatigue, nausea, and kidney stones.
It is important to maintain normal levels of serum calcium through a balanced diet rich in calcium-rich foods, such as dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified cereals. Regular monitoring of serum calcium levels may be recommended by healthcare providers for individuals at risk of imbalances.

Normal Levels of Serum Calcium
The normal range for serum calcium levels in adults is typically between 8.5 to 10.5 mg/dL. Anything outside of this range may indicate an underlying medical condition that requires attention.
Serum calcium levels are an important marker of overall health. Normal levels of serum calcium typically range from 8.5 to 10.5 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL).
Maintaining proper levels of serum calcium is essential for many bodily functions, including muscle contraction, nerve function, and bone health. Imbalances in serum calcium levels can lead to serious health problems, such as osteoporosis, kidney stones, and muscle cramps.
It is important to regularly creatinine serum calcium levels through blood tests and to consult with a healthcare provider if levels are found to be outside of the normal range. Making dietary adjustments and taking supplements may be necessary to help regulate serum calcium levels and maintain optimal health.
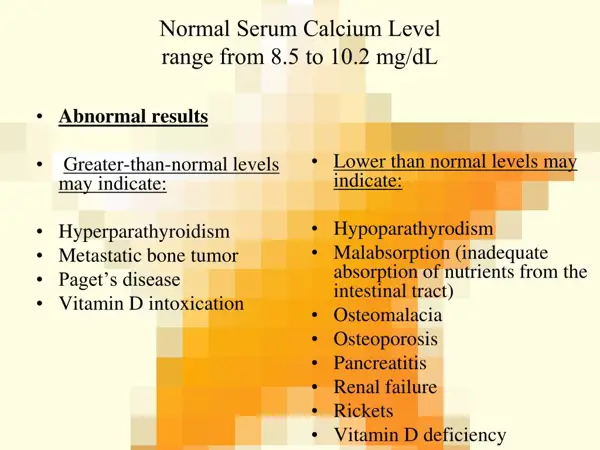
Causes of Abnormal Serum Calcium Levels
Abnormal serum calcium levels can be caused by various factors, including hyperparathyroidism, hypoparathyroidism, kidney disease, certain medications, and vitamin D deficiency.
Abnormal serum calcium levels can be caused by a variety of factors. Some common causes include:
1. Hyperparathyroidism: This condition occurs when the parathyroid glands produce too much parathyroid hormone, leading to high levels of calcium in the blood.
2. Hypoparathyroidism: On the other hand, hypoparathyroidism is characterized by low levels of parathyroid hormone, which can result in low levels of calcium in the blood.
3. Kidney disease: When the kidneys are not functioning properly, they may not be able to regulate calcium levels effectively, leading to abnormal levels in the blood.
4. Vitamin D deficiency: Vitamin D plays a crucial role in calcium absorption and metabolism. A deficiency in this vitamin can lead to abnormal calcium levels.
5. Certain medications: Some medications, such as diuretics, corticosteroids, and certain cancer treatments, can disrupt the balance of calcium in the blood.
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider if you suspect you have abnormal serum calcium levels, as they can help diagnose the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of Abnormal Calcium Levels
Signs and symptoms of abnormal calcium levels may include muscle weakness, fatigue, bone pain, frequent urination, kidney stones, and confusion. It is important to consult a healthcare provider if you experience any of these symptoms.
Normal levels of serum calcium play a crucial role in various bodily functions, such as bone health, muscle function, and nerve transmission. When calcium levels are too high or too low, it can lead to a range of symptoms that may indicate an underlying medical condition.
Symptoms of High Calcium Levels (Hypercalcemia)
- Fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- Muscle weakness
- Confusion
- Constipation
Symptoms of Low Calcium Levels (Hypocalcemia)
- Muscle cramps or spasms
- Numbness or tingling in the fingers and toes
- Irritability
- Confusion
- Difficulty swallowing
- Abnormal heart rhythms
- Seizures
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, especially if they are persistent or severe, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment for Abnormal Calcium Levels
The treatment for abnormal serum calcium levels depends on the underlying cause. It may involve lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, medications, or surgery in severe cases. Regular monitoring of calcium levels is essential to ensure optimal health.
Serum calcium levels can be classified as either too high (hypercalcemia) or too low (hypocalcemia). In cases where the calcium levels are abnormal, treatment may be necessary to bring the levels back within normal range.
Treatment for Hypercalcemia
If the serum calcium levels are too high, treatment options may include:
- Fluid hydration to help flush out excess calcium
- Medications to help lower calcium levels
- Treatment of the underlying cause, such as addressing an overactive parathyroid gland
Treatment for Hypocalcemia
If the serum calcium levels are too low, treatment options may include:
- Supplemental calcium and vitamin D to raise calcium levels
- Medications to help increase calcium absorption in the body
- Treatment of the underlying cause, such as addressing a vitamin D deficiency
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for abnormal calcium levels. Follow-up monitoring may also be necessary to ensure that calcium levels remain within normal range.

Conclusion
Maintaining normal levels of serum calcium is crucial for various bodily functions and overall health. By understanding the importance of calcium in the body and monitoring your serum calcium levels, you can promote better health and well-being.
Key Takeaways
- Normal serum calcium levels range between 8.5 to 10.5 mg/dL in adults.
- Abnormal calcium levels can be caused by various factors, including medical conditions and medications.
- Consult a healthcare provider if you experience symptoms of abnormal calcium levels.
- Treatment for abnormal calcium levels depends on the underlying cause.
- Regular monitoring of calcium levels is essential for optimal health.
FAQ
What can cause high serum calcium levels?
High serum calcium levels can be caused by hyperparathyroidism, certain types of cancer, excessive vitamin D intake, and certain medications.
What can cause low serum calcium levels?
Low serum calcium levels can be caused by hypoparathyroidism, kidney disease, magnesium deficiency, and vitamin D deficiency.


Recent Comments