Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Effects of Alcohol on Glucose Metabolism
- Metabolic Process of Glucose in the Body
- Health Implications of Altered Glucose Metabolism
- Risks of Excessive Alcohol Consumption
- Prevention and Management
- Conclusion
Introduction
Alcohol consumption can have a significant impact on glucose metabolism in the body. This article explores how alcohol affects the metabolic process of glucose and the potential health implications of altered glucose metabolism.
Effects of Alcohol on Glucose Metabolism
Alcohol consumption can disrupt the normal functioning of glucose metabolism in several ways. It can inhibit glucose production in the liver, impair insulin sensitivity, and lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
Alcohol consumption can have significant effects on glucose metabolism in the body. When you drink alcohol, your liver prioritizes breaking down the alcohol over other metabolic processes, including glucose metabolism. This can lead to a decrease in blood glucose levels, causing hypoglycemia.
Additionally, alcohol can interfere with the production and function of insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. This can result in insulin resistance and impaired glucose uptake by cells, further disrupting glucose metabolism.
In the long term, chronic alcohol consumption can contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes by damaging the pancreas and increasing insulin resistance. It can also lead to fatty liver disease, which further impairs glucose metabolism.
Overall, it is important to be aware of the effects of alcohol on glucose metabolism and to drink in moderation to minimize these negative impacts on your health.
Metabolic Process of Glucose in the Body
Glucose is a vital source of energy for the body, and its metabolism involves a complex series of biochemical reactions. Insulin plays a key role in regulating glucose uptake by cells and storage in the form of glycogen.
Glucose is a simple sugar that serves as the primary source of energy for the cells in our body. When we consume food, especially carbohydrates, the body breaks down these nutrients into glucose, which is then transported to the cells via the bloodstream. Once inside the cells, glucose is either used for immediate energy or stored as glycogen for future use.
How Alcohol Affects Glucose Metabolism
Alcohol is a substance that is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream and can have a significant impact on glucose metabolism. When we consume alcohol, the body prioritizes metabolizing the alcohol over other nutrients, including glucose. This can lead to disruptions in the body's ability to properly regulate blood sugar levels.
Furthermore, alcohol can also impair the function of the liver, which plays a crucial role in regulating glucose levels. Chronic alcohol consumption can lead to liver damage and dysfunction, resulting in insulin resistance and elevated blood sugar levels.
In addition, alcohol can inhibit the production of glucose in the liver, leading to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar levels). This can be dangerous, especially for individuals with diabetes who may already have difficulty regulating their blood sugar levels.
Overall, it is important to be mindful of the impact of alcohol on glucose metabolism and to consume it in moderation to maintain optimal health.
Health Implications of Altered Glucose Metabolism
Altered glucose metabolism due to alcohol consumption can increase the risk of developing conditions such as diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and fatty liver disease. It can also contribute to weight gain and obesity.
Altered glucose metabolism can have significant implications on health, especially when it comes to conditions like diabetes. When glucose metabolism is disrupted, it can lead to high blood sugar levels, which can in turn lead to complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
How does alcohol affect weight metabolism?
Alcohol can have a significant impact on glucose metabolism. When consumed, alcohol is metabolized by the liver, which can disrupt the normal processes of glucose metabolism. Alcohol can cause fluctuations in blood sugar levels, leading to both high and low levels of glucose in the bloodstream. Chronic alcohol consumption can also contribute to the development of conditions like insulin resistance and fatty liver disease, further complicating glucose metabolism.
It is important to be mindful of alcohol consumption and its effects on glucose metabolism, especially for individuals who may already have underlying health conditions like diabetes. Moderation and monitoring of alcohol intake can help mitigate the negative effects on glucose metabolism and overall health.

Risks of Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can have a range of negative effects on overall health, including damage to the liver, brain, and other organs. It can also lead to nutrient deficiencies and impaired immune function.
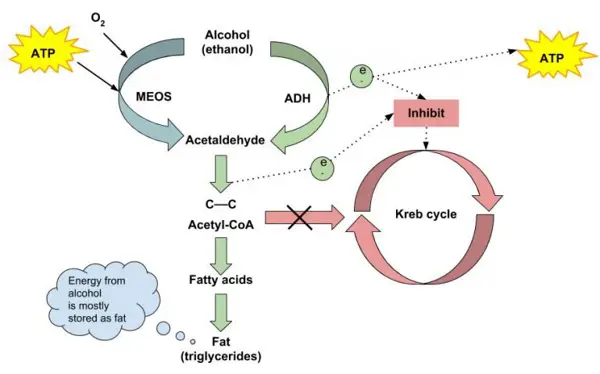
Excessive alcohol consumption can have a negative impact on glucose metabolism in the body. Alcohol is a toxic substance that can disrupt the body's normal functions, including the way it processes glucose.
How does alcohol affect glucose metabolism?
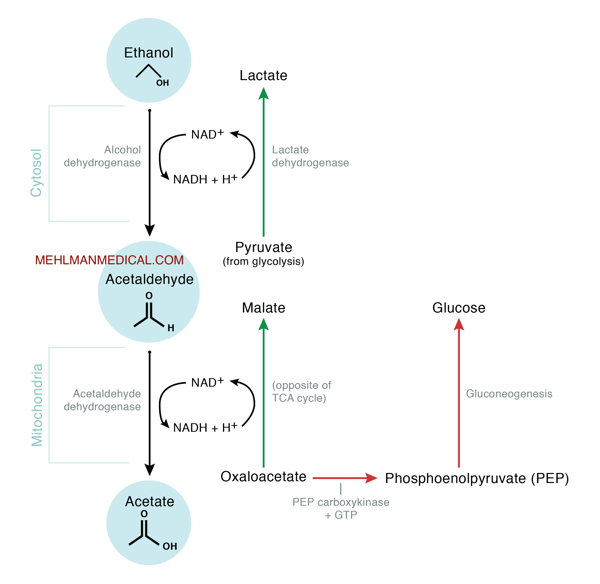
Alcohol is converted into acetate in the liver, which then disrupts the production of glucose in the body. This can lead to fluctuations in blood sugar levels and potentially increase the risk of developing conditions such as insulin resistance, diabetes, and hypoglycemia.
Additionally, excessive alcohol consumption can also contribute to weight gain and obesity, both of which are risk factors for impaired glucose metabolism and related conditions.
It is important to consume alcohol in moderation and be mindful of its impact on overall health, including glucose metabolism.
Prevention and Management
To mitigate the impact of alcohol on glucose metabolism, it is important to consume alcohol in moderation and maintain a balanced diet. Regular exercise and adequate hydration can also help support healthy glucose metabolism.
Alcohol consumption can have a significant impact on glucose metabolism in the body. When alcohol is consumed, it can disrupt the normal process of regulating blood sugar levels, leading to fluctuations that can be harmful to overall health.
Effects of Alcohol on Glucose Metabolism:
Alcohol can impair the liver's ability to produce glucose, which can lead to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar levels) in some individuals. Additionally, alcohol can interfere with the body's ability to process insulin, resulting in insulin resistance and ultimately, an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Prevention and Management Strategies:
1. Limit Alcohol Consumption: One of the most effective ways to prevent the negative effects of alcohol on glucose metabolism is to limit alcohol intake. Moderation is key to maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
2. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Individuals who consume alcohol regularly should monitor their blood sugar levels closely and seek medical advice if they notice any abnormalities.
3. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, and managing stress can all help support healthy glucose metabolism and offset some of the negative effects of alcohol consumption.
4. Seek Professional Help: Individuals who struggle with alcohol dependency should seek professional help to address their drinking habits and mitigate the impact on their overall health.
By implementing these prevention and management strategies, individuals can reduce the negative impact of alcohol on glucose metabolism and promote overall well-being.
Conclusion
Understanding the influence of alcohol on glucose metabolism is crucial for maintaining optimal health and well-being. By making informed choices about alcohol consumption and lifestyle habits, individuals can minimize the risks associated with altered glucose metabolism.
Key Takeaways
- Alcohol can disrupt glucose metabolism by inhibiting glucose production and impairing insulin sensitivity.
- Altered glucose metabolism due to alcohol consumption can increase the risk of diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
- Maintaining a balanced diet, moderate alcohol consumption, and regular exercise can support healthy glucose metabolism.
FAQ
Q: Can moderate alcohol consumption have any positive effects on glucose metabolism?
A: Some research suggests that moderate alcohol consumption may have beneficial effects on glucose metabolism, but excessive drinking can still have harmful effects.
Q: How does alcohol impact insulin sensitivity?
A: Alcohol can impair insulin sensitivity, leading to higher blood sugar levels and potential long-term effects on glucose metabolism.
Q: What are some warning signs of disrupted glucose metabolism due to alcohol consumption?
A: Symptoms may include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and unexplained weight changes. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment.


Recent Comments