Table of Contents
- Introduction
- How Protein Affects Blood Sugar
- Protein vs. Carbohydrates
- Protein Quality and Blood Sugar
- Best Sources of Protein for Blood Sugar Control
- Potential Side Effects
- Conclusion
Introduction
Protein is an essential macronutrient that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. Many people wonder how protein consumption affects blood sugar levels. In this article, we will explore the relationship between protein and blood sugar to understand its impact on overall health.
How Protein Affects Blood Sugar
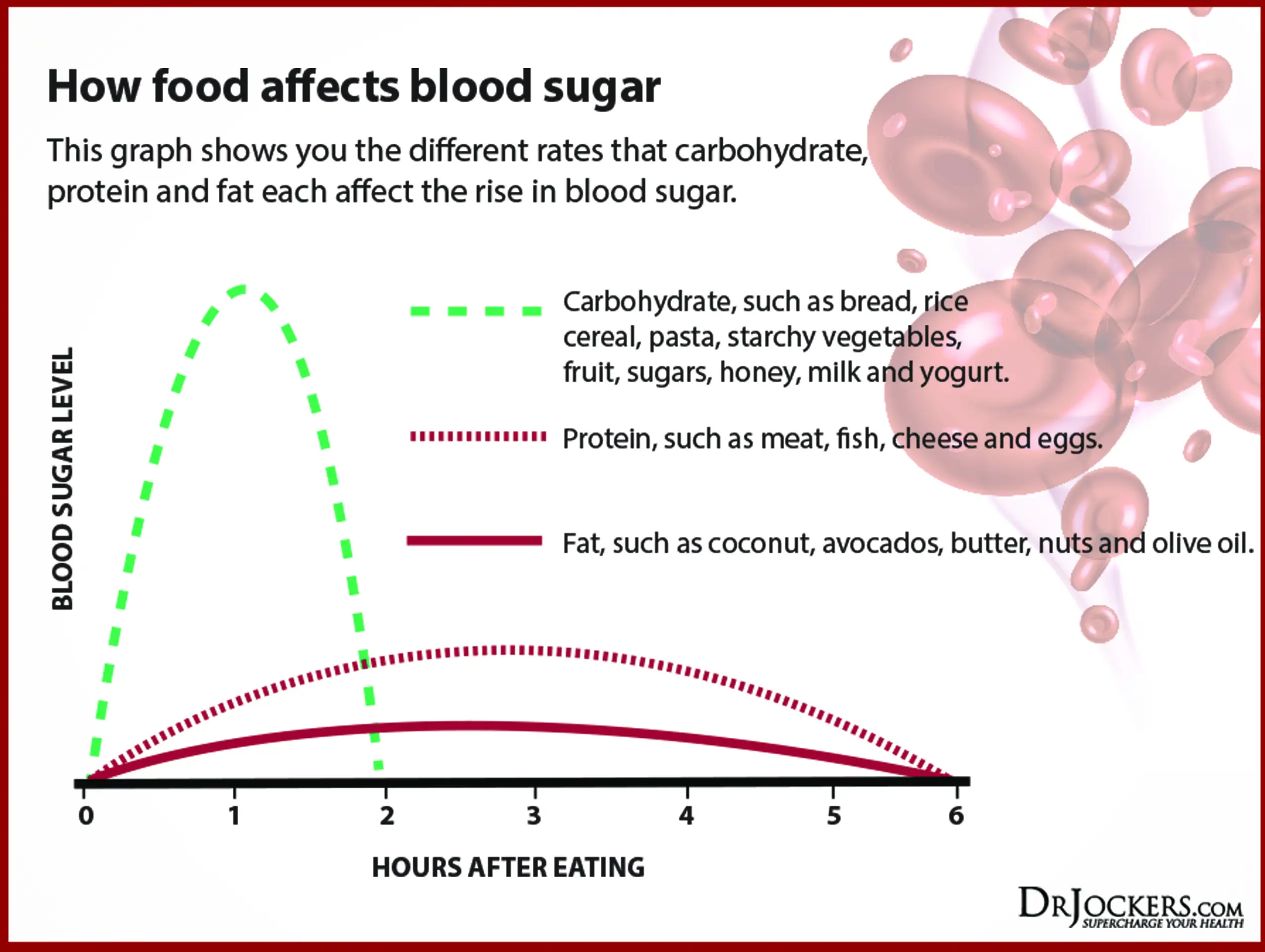
Contrary to carbohydrates, protein has a minimal effect on blood sugar levels. When consumed, protein stimulates the release of glucagon, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar. Additionally, protein takes longer to break down, leading to a slower rise in blood sugar compared to carbohydrates.
How Protein Affects Blood Sugar
Protein consumption has minimal impact on raising blood sugar levels compared to carbohydrates and fats. Unlike carbohydrates, proteins have a minimal effect on blood sugar because they do not directly convert into glucose. However, certain factors can indirectly influence blood sugar levels in relation to protein consumption.
When protein is consumed in large quantities, it can stimulate the production of insulin, a hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. This can lead to a slight increase in blood sugar levels. However, the impact of protein on blood sugar is considerably lower than that of carbohydrates.
Moreover, consuming protein-rich foods alongside carbohydrates can slow down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, resulting in a more gradual increase in blood sugar levels. This is especially beneficial for individuals with diabetes, as it can help prevent spikes in blood sugar levels after meals.
In summary, while protein consumption may have a minimal impact on raising blood sugar levels, it is not a major concern for individuals managing their blood sugar. Incorporating a balanced diet that includes an appropriate amount of protein can contribute to overall health without significantly affecting blood sugar levels.
Disclaimer: It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to receive personalized advice on managing blood sugar levels and protein consumption, especially if you have specific health conditions.

Protein vs. Carbohydrates
Understanding the difference between protein and carbohydrates is vital when considering blood sugar levels. Unlike carbohydrates, protein does not raise blood sugar levels significantly, making it a suitable dietary choice for individuals managing their blood sugar.
Understanding the impact of different nutrients on blood sugar levels is crucial for maintaining a healthy diet. When it comes to protein and carbohydrates, there is a significant difference in how they affect blood sugar.
Carbohydrates are the main source of energy for the body and are quickly broken down into glucose, raising blood sugar levels. On the other hand, protein has a minimal impact on blood sugar as it does not directly convert into glucose.
Consuming protein-rich foods, such as lean meats, eggs, and dairy products, triggers the release of insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar. However, the rise in blood sugar caused by protein is generally smaller and slower compared to carbohydrates.
While carbohydrates can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, proteins have a slower and more gradual effect. This slower absorption rate is beneficial for those with diabetes or individuals looking to manage their blood sugar levels effectively.
It is important to note that consuming excessive amounts of protein may lead to a slight increase in blood sugar levels, but the impact is still much smaller compared to carbohydrates. Therefore, incorporating a balanced mix of protein and carbohydrates in your diet is essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
In conclusion, protein has a minimal impact on raising blood sugar compared to carbohydrates. It provides a steady release of glucose and triggers the release of insulin, aiding in blood sugar regulation. By understanding these differences, individuals can make informed choices about their dietary intake and manage their blood sugar levels more effectively.

Protein Quality and Blood Sugar
The quality of protein consumed can influence blood sugar levels. Consuming lean protein sources such as skinless chicken, fish, and legumes has a minimal effect on blood sugar. On the other hand, processed protein foods, high in additives and unhealthy fats, may negatively impact blood sugar control.
Protein plays an essential role in our overall health and well-being. It is responsible for numerous bodily functions, including building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes and hormones, and supporting the immune system. However, when it comes to blood sugar levels, the impact of protein can vary depending on its quality and quantity.
Protein is made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of our bodies. When we consume protein-rich foods, our bodies break down these amino acids and convert them into glucose through a process called gluconeogenesis. This conversion is relatively slow compared to carbohydrates, resulting in a slower and more sustained increase in blood sugar levels.
The quality of protein we consume also influences its impact on blood sugar. Complete proteins, found in animal sources such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products, contain all the essential amino acids our bodies need. These proteins have a moderate effect on blood sugar levels due to their balanced amino acid composition.
In contrast, incomplete proteins, primarily derived from plant-based sources like legumes, grains, nuts, and seeds, lack one or more essential amino acids. While they are still beneficial for our health, they may not have as profound an impact on blood sugar as complete proteins. Combining different plant-based protein sources can help ensure a complete amino acid profile and improve their effect on blood sugar levels.
Furthermore, the quantity of protein consumed also matters. Consuming excessive amounts of protein can potentially elevate blood sugar levels. However, this mainly applies to individuals with specific health conditions such as kidney problems or those who already have compromised glucose metabolism. In general, moderate protein intake as part of a well-balanced diet is unlikely to cause significant spikes in blood sugar levels.
In conclusion, protein quality and quantity both play a role in determining how much protein raises blood sugar. Consuming complete proteins from animal sources or combining different plant-based protein sources can have a moderate impact on blood sugar levels, while excessive protein intake may affect blood sugar in certain individuals. It is important to consult a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized advice on protein intake and blood sugar management.

Best Sources of Protein for Blood Sugar Control
To optimize blood sugar levels, it is crucial to include healthy protein sources in your diet. Excellent choices include lean meats, poultry, fish, tofu, low-fat dairy products, and plant-based proteins like lentils and quinoa. These options provide essential amino acids while minimizing the impact on blood sugar.
When it comes to managing blood sugar levels, it's essential to choose protein sources that have a minimal impact on raising blood sugar. Opting for the right types of protein can help maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevent spikes. Here are some of the best sources of protein that won't significantly raise blood sugar:
- Fish: Fish, such as salmon, tuna, and mackerel, is an excellent source of high-quality protein. It contains omega-3 fatty acids that can improve insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Poultry: Chicken and turkey are lean protein sources that offer essential nutrients without causing significant spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Eggs: Eggs are packed with protein and are low in carbohydrates. They provide a variety of essential amino acids and can be a part of a blood sugar-friendly diet.
- Greek Yogurt: Greek yogurt is a protein-rich option that also contains probiotics, which can support gut health and potentially enhance blood sugar control.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are protein-packed foods that also provide healthy fats, fiber, and other nutrients. They have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels when consumed in moderation.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of plant-based protein. They also have a low glycemic index, meaning they release sugar into the bloodstream slowly, preventing sudden blood sugar spikes.
It's important to note that the impact of protein on blood sugar levels can vary among individuals. Factors like portion size and the overall composition of a meal also play a role in determining the blood sugar response. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian is advised for personalized recommendations and guidance regarding protein consumption and blood sugar control.
Potential Side Effects
While protein offers numerous health benefits, excessive protein intake can lead to potential side effects such as kidney damage or increased urinary calcium excretion. It is important to consume protein in moderation and maintain a balanced diet to avoid any adverse effects.
Protein is an essential macronutrient required by our body for various functions. However, it's important to be aware of the potential side effects related to protein consumption, particularly its impact on blood sugar levels.
Protein has minimal effects on blood sugar levels when compared to carbohydrates. Unlike carbohydrates, which are broken down into glucose and quickly raise blood sugar levels, protein is metabolized more slowly. It doesn't cause a rapid spike in blood sugar, making it a favorable choice for individuals with diabetes or those aiming to manage their blood sugar levels.
Nevertheless, it's worth noting that excessive protein intake can have an impact on blood sugar levels. When we consume protein-rich foods, our body starts breaking down the protein into amino acids. These amino acids can be converted into glucose through a process called gluconeogenesis. Gluconeogenesis can potentially increase blood sugar levels, although to a lesser extent than carbohydrates.
The impact of protein on blood sugar levels also varies depending on the type and amount of protein consumed, as well as an individual's metabolism. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to determine the appropriate amount of protein intake for your specific needs and health condition.
Additionally, consuming protein in combination with carbohydrates can have a mitigating effect on blood sugar spikes. Including protein-rich foods in your meals can slow down the absorption of carbohydrates, helping to regulate blood sugar levels and prevent sudden spikes.
In conclusion, protein does have the potential to raise blood sugar levels, but its impact is considerably lower compared to carbohydrates. However, it is essential to maintain a balanced diet, regulate protein intake, and consult a healthcare professional to effectively manage blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
In summary, protein has a minimal impact on blood sugar levels compared to carbohydrates. Incorporating lean protein sources into your diet can provide essential nutrients while maintaining stable blood sugar levels. It is essential to be mindful of protein quality and portion sizes to support overall health and wellbeing.
Key Takeaways
- Protein has a minimal effect on blood sugar levels compared to carbohydrates.
- Glucagon release stimulated by protein helps regulate blood sugar.
- Choosing lean protein sources promotes stable blood sugar control.
- Excessive protein intake can lead to potential side effects and should be consumed in moderation.
FAQ
-
Does consuming protein raise blood sugar levels?
No, protein has a minimal effect on blood sugar levels and is suitable for individuals managing their blood sugar.
-
What are some examples of lean protein sources?
Lean protein sources include skinless chicken, fish, tofu, low-fat dairy products, lentils, and quinoa.
-
Can excessive protein intake be harmful?
Yes, excessive protein intake can potentially lead to kidney damage and increased urinary calcium excretion. It is important to consume protein in moderation.



Recent Comments