Table of Contents
- Understanding the Protein and Calorie Relationship
- Protein Recommendations for Muscle Building
- Determining Your Calorie Intake
- The Importance of Protein Quality
- Optimal Timing and Distribution of Protein and Calories
- Supplementation for Enhanced Muscle Growth
- Sample Meal Plan for Muscle Building
Understanding the Protein and Calorie Relationship
Explore the fundamental relationship between protein and calories in the context of muscle building. Understand the role of protein in muscle synthesis and energy requirements for muscle growth.
Protein Recommendations for Muscle Building
Learn about the optimal protein intake for muscle building based on factors such as body weight, activity level, and training goals. Discover the importance of distributing protein intake throughout the day for maximum muscle protein synthesis.
To effectively build muscle, it is essential to consume adequate amounts of protein and calories. Protein is the key nutrient responsible for muscle repair, growth, and maintenance. Combined with a suitable exercise routine, proper protein intake helps in achieving your muscle-building goals.
Recommended Protein Intake
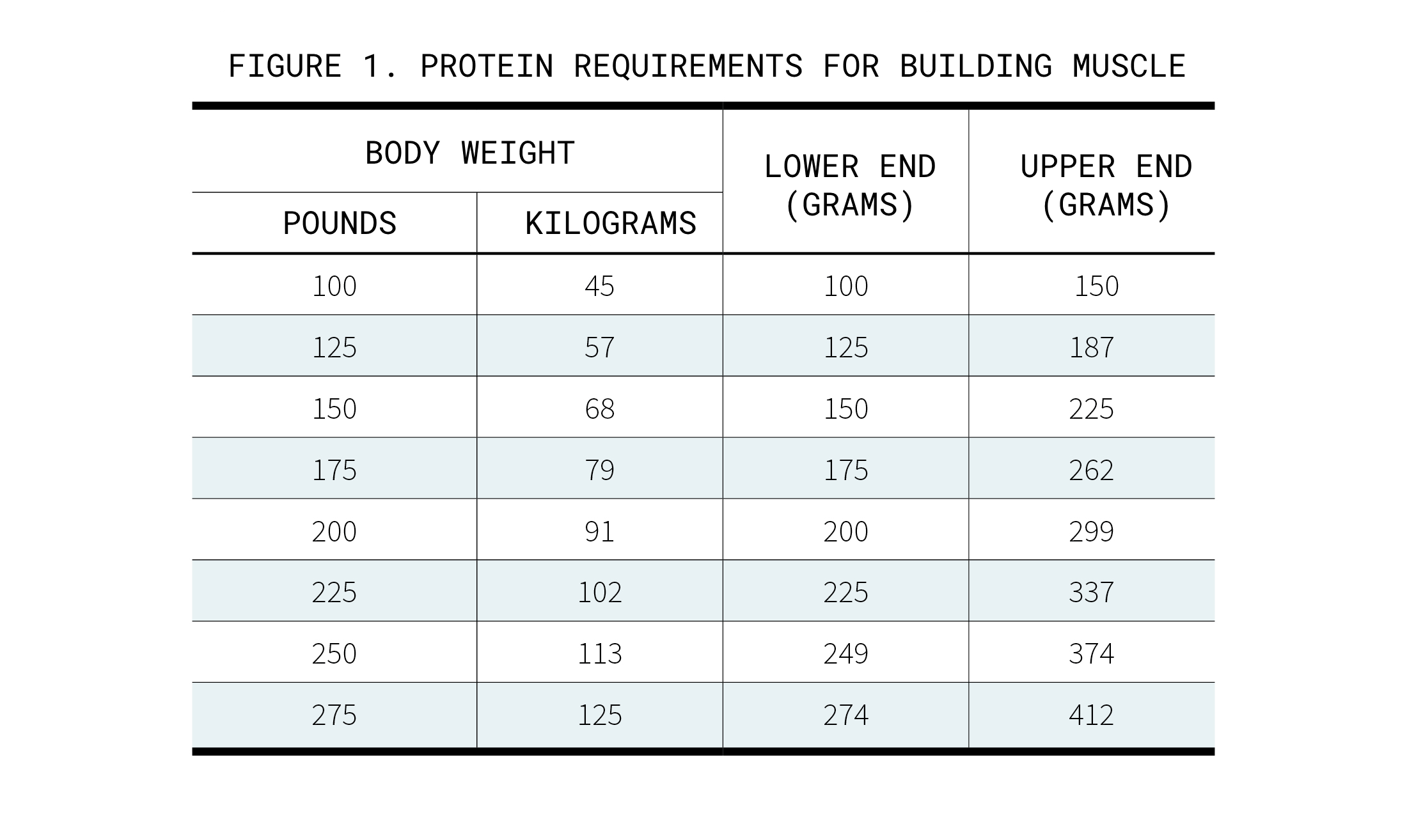
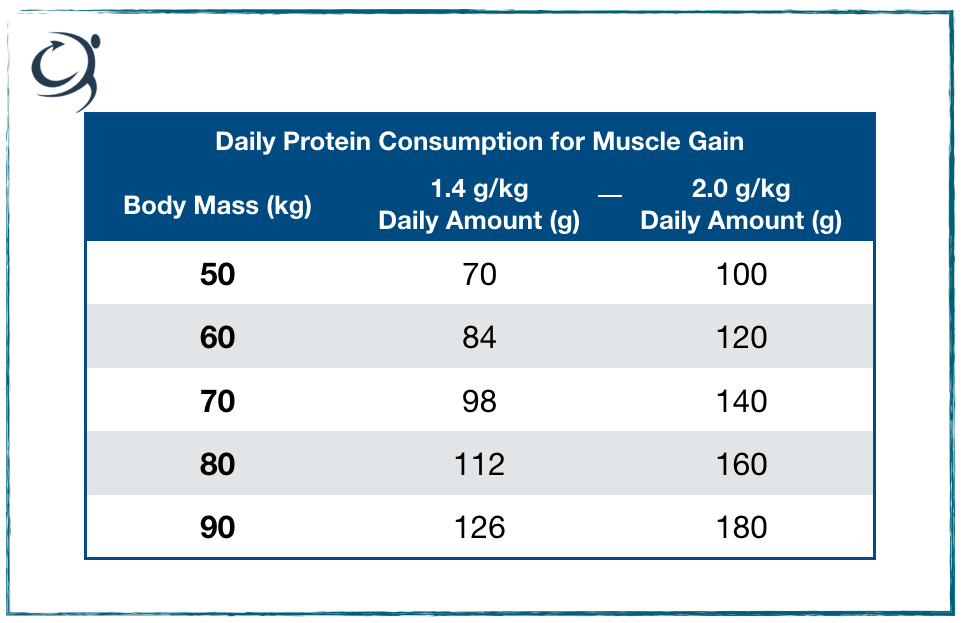
The general protein recommendation for individuals engaged in muscle building activities is about 1.2 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. This range can vary based on factors such as the intensity of your workouts, body composition goals, and overall health.
For example, if you weigh 70 kilograms, you would need approximately 84 to 154 grams of protein daily. This amount should be spread throughout the day to ensure a steady supply of amino acids for muscle synthesis.
Caloric Requirements
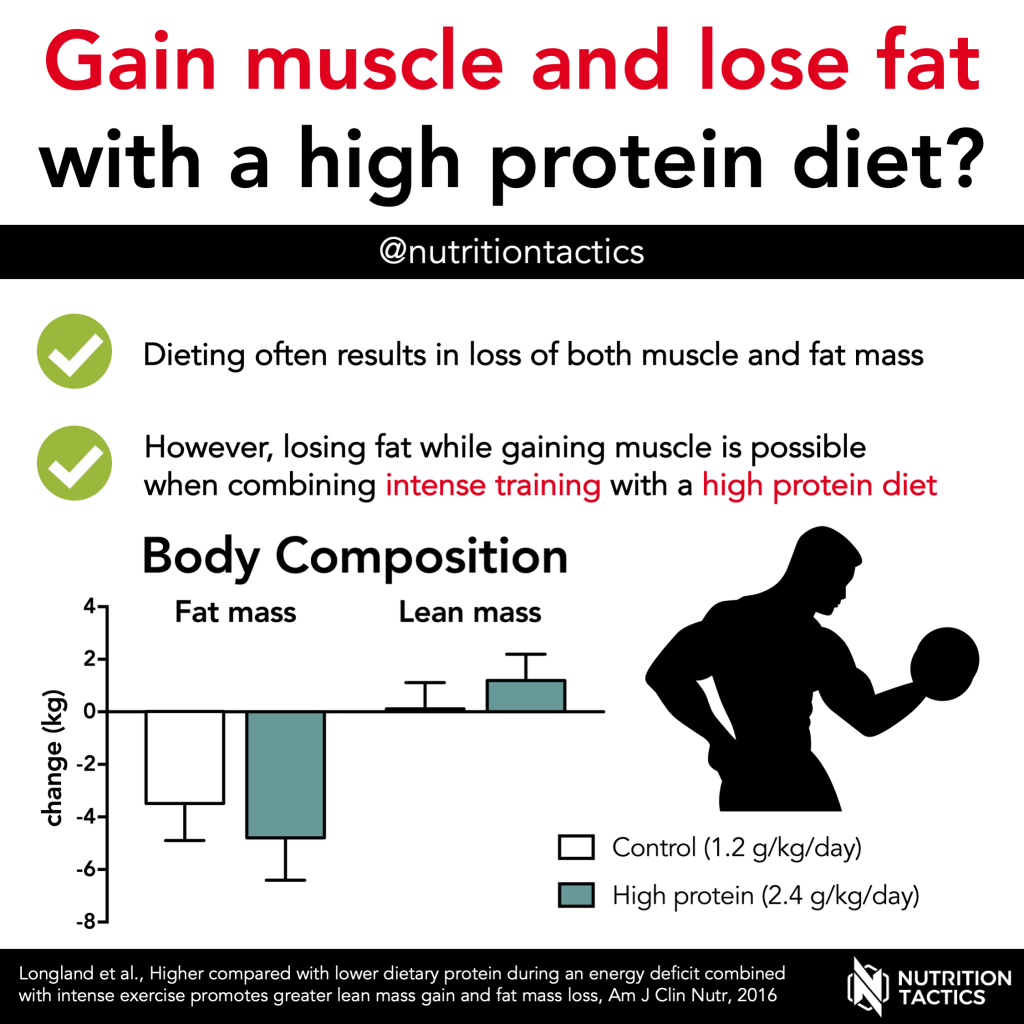
In addition to protein, consuming an adequate amount of calories is essential to support muscle growth. You should aim to consume a slight caloric surplus, typically 250 to 500 calories above your maintenance level, to provide the necessary energy for muscle building.
It is important to focus on consuming nutrient-dense, high-quality foods that not only meet your protein and calorie requirements but also provide other essential vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients.
Importance of Consistency and Individual Differences
Building muscle requires consistency in both exercise and nutrition. Stick to a well-balanced diet that incorporates lean sources of protein such as chicken, turkey, fish, eggs, legumes, and dairy products. Including a variety of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats will further enhance your muscle-building efforts.
Keep in mind that individual protein and calorie requirements may vary based on factors such as age, gender, activity level, and specific fitness goals. Consulting with a registered dietitian or a fitness professional can help tailor a nutrition plan specific to your needs.
Remember, building muscle takes time, dedication, and the right combination of nutrition and exercise. Ensure you fuel your body adequately with protein and calories to support your muscle-building journey.
Determining Your Calorie Intake
Find out how to calculate your daily calorie needs for muscle building. Understand the concept of a calorie surplus for muscle growth and the potential risks of excessive calorie intake.
When aiming to build muscle, it is crucial to determine your daily calorie intake, especially regarding protein and overall calories. This process ensures that you provide your body with the necessary fuel to support muscle growth and repair.
Step 1: Calculate Your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
Start by calculating your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR), which is the number of calories your body requires at rest. Various online BMR calculators are available to help you determine this figure based on factors like age, weight, height, and gender.
Step 2: Determine Your Activity Level
Next, consider your activity level. If you have a sedentary lifestyle, multiply your BMR by 1.2. For light activity, use 1.375, moderate activity 1.55, high activity 1.725, and very high activity 1.9. This will provide an estimate of your total daily energy expenditure (TDEE).
Step 3: Establish Your Goal
Determine your goal based on whether you want to gain muscle mass or maintain it. For muscle gain, a general guideline is to consume 250-500 additional calories above your TDEE. For maintenance, stick to your TDEE.
Step 4: Focus on Protein Intake
Protein is vital for muscle building. It helps repair and build muscle tissues. As a general rule, aim for around 1.2-2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day. This will ensure adequate protein intake for muscle growth and recovery.
Step 5: Design Your Meal Plan
Design a meal plan that aligns with your calculated calorie intake and protein requirements. Distribute your calories and protein throughout the day by including lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and protein supplements if necessary.
Remember that these guidelines are general and may need adjustments based on individual needs and preferences. Consulting a registered dietitian or nutritionist can provide personalized recommendations tailored to your specific goals.
By determining your calorie intake and focusing on protein, you can optimize your muscle-building journey and achieve the desired results.

The Importance of Protein Quality
Discover the significance of protein quality and amino acid profile in muscle building. Learn which protein sources are rich in essential amino acids necessary for optimal muscle protein synthesis.
When it comes to building muscle, the amount of protein and calories consumed play a crucial role. However, the quality of the protein consumed is equally important. High-quality protein provides the necessary amino acids needed for muscle repair, growth, and recovery. This is why athletes, bodybuilders, and fitness enthusiasts emphasize the significance of protein quality.
Protein Quantity and Calories
Protein is an essential macronutrient that helps repair damaged muscle tissues and stimulate muscle growth. It is recommended to consume around 0.8 to 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight for those aiming to build muscle. The exact amount may vary based on individual goals and physical activity levels.
Furthermore, caloric intake should be in line with protein intake. Consuming enough calories ensures the body has sufficient energy to support muscle growth and repair processes. A caloric surplus, in conjunction with adequate protein intake, is often necessary to promote muscle hypertrophy (growth).
The Significance of Protein Quality
Protein quality refers to the amino acid profile and bioavailability of protein sources. Different protein sources contain varying amounts and combinations of essential amino acids – the building blocks of protein. Essential amino acids cannot be produced by the body, so they must be obtained through diet. A high-quality protein source provides all essential amino acids in optimal proportions.
Animal-based protein sources such as lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, and dairy products are considered complete proteins as they contain all essential amino acids in the right balance. These sources are highly bioavailable, meaning they are efficiently absorbed and utilized by the body.
On the other hand, plant-based protein sources like legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds are often incomplete proteins. They lack certain essential amino acids or have lower bioavailability. Combining different plant-based protein sources, such as rice and beans, can help create a complete amino acid profile.
Maximizing Muscle Gains with Quality Protein
To optimize muscle growth and repair, it is crucial to consume high-quality protein sources. These can provide the necessary amino acids to stimulate muscle protein synthesis and prevent muscle breakdown. Consuming a combination of both animal-based and plant-based protein sources can offer a wide array of essential amino acids and improve overall protein quality.
It is worth noting that while protein quality is essential, a balanced diet comprising other macronutrients, vitamins, and minerals is also crucial for overall health and muscle development.

Optimal Timing and Distribution of Protein and Calories
Get insights into the importance of timing and distributing your protein and calorie intake throughout the day. Learn about pre and post-workout nutrition strategies and how to maximize nutrient absorption.
When it comes to building muscle, both protein and calories play vital roles in achieving optimal results. Properly timing and distributing protein and calorie intake throughout the day can enhance muscle growth and recovery. Here's what you need to know:
Protein:
Protein is essential for muscle repair, growth, and maintenance. To maximize muscle building, it is recommended to consume an adequate amount of protein at regular intervals.
- For most individuals, aiming for around 0.8 to 1 gram of protein per pound of bodyweight is a good starting point.
- Distributing protein evenly across meals and snacks throughout the day ensures a consistent supply for muscle protein synthesis.
- Incorporate high-quality protein sources such as lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and plant-based proteins into your diet.
- Consider including protein-rich snacks or shakes post-workout and before bedtime to provide the body with the necessary amino acids during crucial periods of muscle recovery.
Calories:
Calories are the energy units that fuel the body's activities, including muscle growth. Consuming an appropriate amount of calories is crucial for promoting muscle development.
- Determine your daily calorie needs based on factors such as age, sex, weight, activity level, and fitness goals.
- Aim for a slight caloric surplus (usually 250-500 extra calories per day) to provide the body with enough energy to build muscle without excessive fat gain.
- Focus on consuming nutrient-dense, whole foods to ensure an adequate intake of vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients.
- Consider spreading your calorie intake across three main meals and additional snacks, allowing for consistent energy levels and muscle repair throughout the day.
Remember, the optimal timing and distribution of protein and calories will vary based on individual needs and preferences. It is essential to listen to your body, monitor progress, and make adjustments accordingly. Consulting with a registered dietitian or nutritionist can also provide personalized guidance for your muscle building journey.
Supplementation for Enhanced Muscle Growth
Explore popular protein supplements such as whey protein and their potential benefits for muscle building. Understand when and how to incorporate supplementation into your nutrition plan.
In order to build muscle effectively, it is crucial to have an adequate intake of protein and calories. Let's discuss the ideal amounts needed to support muscle growth.
Protein Intake:
Protein is an essential macronutrient for muscle repair and growth. For individuals aiming to build muscle, a general guideline is to consume around 0.7-1 gram of protein per pound of body weight per day.
Caloric Intake:
Building muscle requires consuming enough calories to provide energy for muscle synthesis. To create a caloric surplus necessary for muscle growth, it is recommended to consume approximately 250-500 calories above your maintenance level.
Supplementation:
Supplementation can be beneficial for individuals looking to optimize muscle growth. Whey protein, creatine, and branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) are commonly used supplements that may aid in enhancing muscle development.
Conclusion:
To promote muscle growth, it is important to ensure adequate protein intake and maintain a slight caloric surplus. Consider incorporating supplementation, under proper guidance, to maximize the effectiveness of your muscle-building journey.
Sample Meal Plan for Muscle Building
Get a practical example of a well-balanced meal plan tailored for muscle building. Discover delicious and nutritious recipes that can help you meet your protein and calorie goals while keeping your taste buds satisfied.
Building muscle requires an appropriate balance of protein and calories in your diet. The following is a sample meal plan that can help you meet your muscle-building goals effectively.
Meal Plan
Below is a breakdown of the protein and calorie intake recommended for muscle building:
Meal 1 - Breakfast
- 3 egg whites
- 1 cup oatmeal
- 1 tablespoon peanut butter
- Total Protein: 21g | Total Calories: 385
Meal 2 - Mid-Morning Snack
- 1 medium-sized apple
- 1 small handful of almonds
- Total Protein: 6g | Total Calories: 210
Meal 3 - Lunch
- 4 oz grilled chicken breast
- 1 cup brown rice
- 1 cup mixed vegetables
- Total Protein: 40g | Total Calories: 475
Meal 4 - Afternoon Snack
- 1 small container of Greek yogurt
- 1 tablespoon honey
- Total Protein: 20g | Total Calories: 200
Meal 5 - Dinner
- 6 oz grilled salmon
- 1 medium-sized sweet potato
- 1 cup steamed broccoli
- Total Protein: 38g | Total Calories: 510
Meal 6 - Evening Snack
- 1 scoop of whey protein powder
- 8 oz skim milk
- Total Protein: 25g | Total Calories: 200
Total Daily Intake
- Total Protein: 150g
- Total Calories: 1980
Note: This sample meal plan is a general guideline and can be adjusted according to your individual needs and preferences. Consult with a nutritionist or dietitian for personalized advice.

Key Takeaways
- Protein and calories are essential for muscle building and should be consumed in appropriate amounts.
- Protein quality, timing, and distribution throughout the day play significant roles in maximizing muscle protein synthesis.
- Understanding your calorie intake and aiming for a surplus can support muscle growth, but excessive calorie consumption may lead to unwanted weight gain.
- Supplements like whey protein can be beneficial, but a well-rounded meal plan with natural protein sources should be the foundation.
FAQ
1. How much protein should I consume daily to build muscle?
The recommended protein intake for muscle building is around 0.7 to 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight. However, individual needs may vary based on factors such as activity level and goals.
2. Can I build muscle without consuming excess calories?
To build muscle effectively, it's generally recommended to consume a slight calorie surplus. However, exceeding the necessary surplus can lead to unwanted weight gain. Consult with a nutritionist to determine your specific requirements.
3. Are protein supplements necessary for muscle growth?
No, protein supplements are not essential for muscle growth. A well-balanced diet rich in natural protein sources can provide sufficient protein for muscle synthesis. Supplements can be beneficial in some cases, but they are not a necessity.



Recent Comments