Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Diagnosing Protein Loss Enteropathy
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes and Risk Factors
- Treatment Options
- Prevention and Management
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
In this article, we will explore the diagnosis, symptoms, causes, treatment options, and prevention strategies for Protein Loss Enteropathy. This condition is characterized by the abnormal loss of protein from the gastrointestinal tract, leading to various complications and health issues.
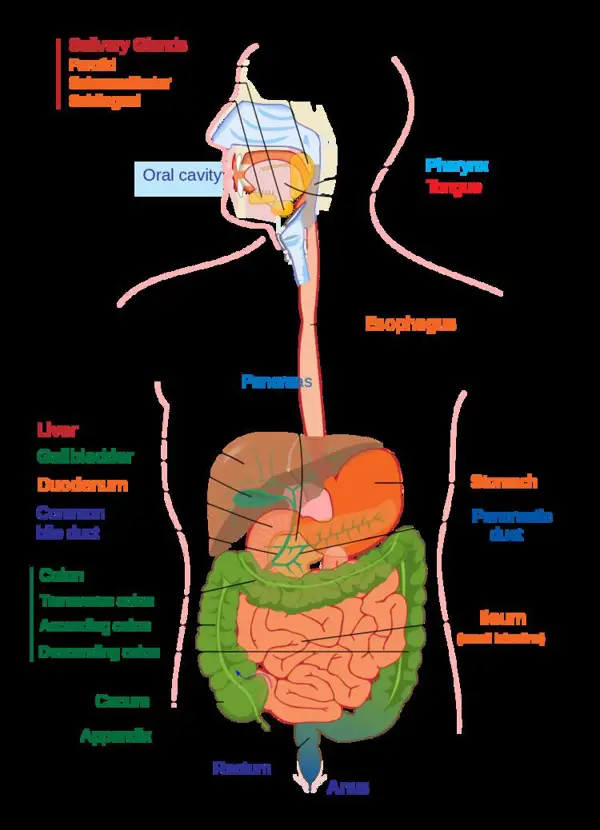
Diagnosing Protein Loss Enteropathy
In this section, we will delve into the various diagnostic methods and tests used to identify Protein Loss Enteropathy. This may involve analyzing blood and stool samples, performing imaging studies, and conducting endoscopic procedures.
What is Protein Loss Enteropathy?
Protein Loss Enteropathy is a medical condition characterized by excessive protein loss in the intestines. It is often associated with gastrointestinal disorders such as Crohn's disease, celiac disease, and ulcerative colitis.
Diagnosing Protein Loss Enteropathy
Diagnosing Protein Loss Enteropathy involves several steps and tests. It is crucial to identify the underlying cause of the condition and determine the severity of protein loss in order to provide appropriate treatment.
Medical History and Physical Examination
During the initial evaluation, your doctor will review your medical history and conduct a physical examination. They will ask questions about your symptoms, previous medical conditions, and any medications you are taking. This information will help in the diagnostic process.
Stool Analysis
A stool analysis is commonly performed to evaluate the presence of excessive protein in the stool. This involves collecting a small sample of your stool and sending it to a laboratory for analysis. The results will indicate if there is abnormal protein loss.
Blood Tests
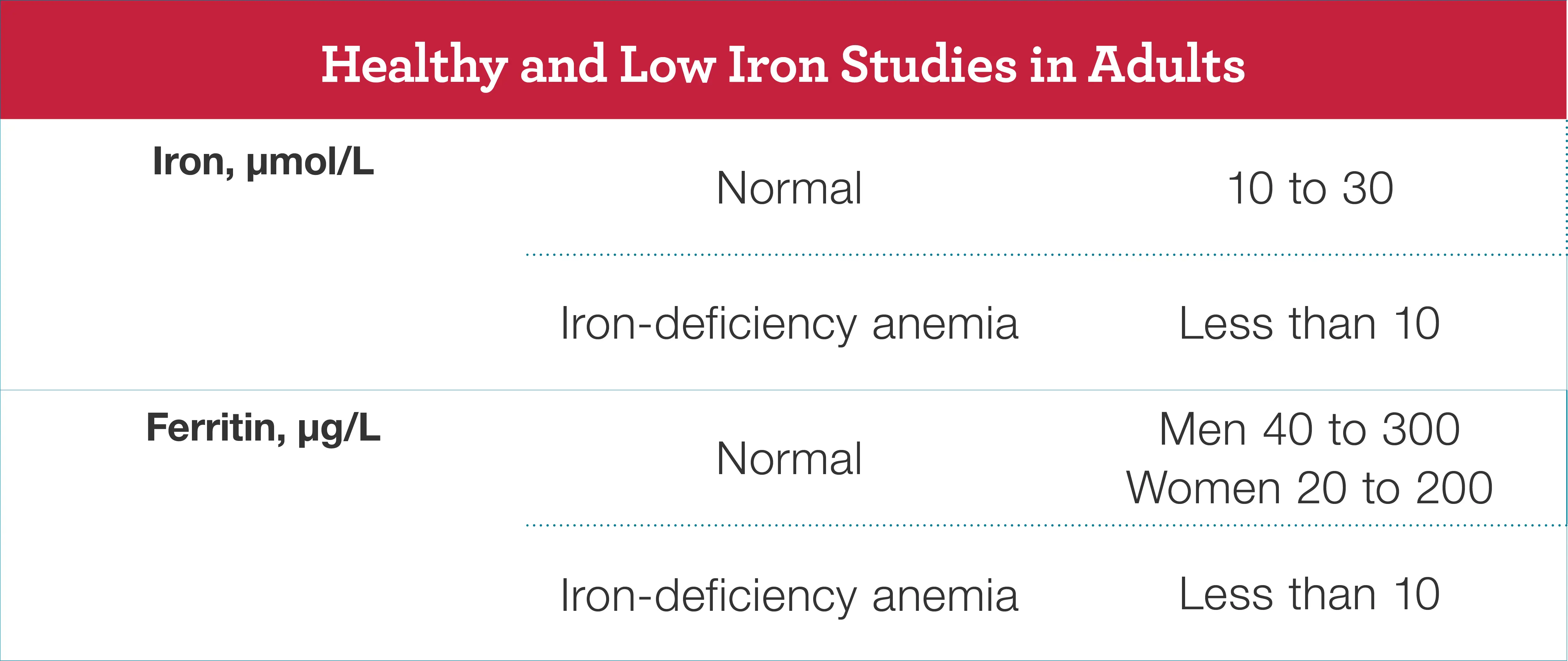
Blood tests are conducted to assess the levels of specific proteins, such as albumin, in your blood. Lower than normal levels of albumin can indicate protein loss. Additionally, other blood tests may be ordered to check for any underlying conditions that could be causing the protein loss.
Endoscopy and Biopsy
An endoscopy may be recommended to examine the intestines and obtain tissue samples for biopsy. This procedure involves inserting a thin, flexible tube with a camera into your digestive tract. The collected tissue samples are then analyzed under a microscope to determine the extent of damage and confirm the diagnosis.
Other Imaging Tests
In some cases, additional imaging tests such as CT scans or MRIs may be required to evaluate the extent of gastrointestinal involvement and rule out other possible causes of protein loss.
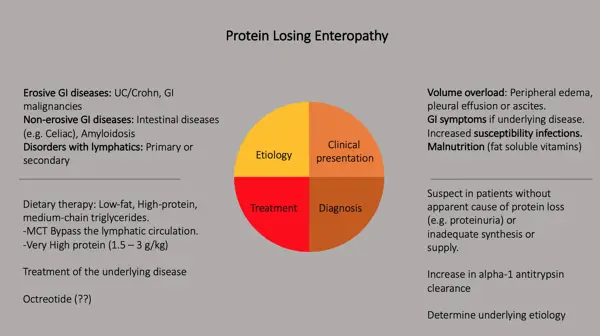
Diagnosing Protein Loss Enteropathy involves a comprehensive approach, combining medical history, physical examination, stool analysis, blood tests, endoscopy, and imaging tests. This thorough diagnostic process allows healthcare professionals to accurately identify the condition and provide appropriate treatment to manage protein loss.
Symptoms and Signs
Here, we will discuss the common symptoms and signs of Protein Loss Enteropathy. These can include edema, malnutrition, diarrhea, fatigue, and abdominal pain. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
Protein loss enteropathy is a condition characterized by the abnormal loss of protein in the intestines. It can lead to various symptoms and signs that can help in its diagnosis. Some of the common symptoms and signs of protein loss enteropathy include:
- Edema: Swelling and fluid retention, especially in the legs, ankles, and feet.
- Malnutrition: Inadequate absorption of nutrients due to protein loss, resulting in weight loss, weakness, and fatigue.
- Diarrhea: Frequent loose or watery bowel movements that can lead to dehydration.
- Abdominal pain: Discomfort or cramping in the stomach area.
- Anemia: Reduced red blood cell count, causing fatigue, pale skin, and shortness of breath.
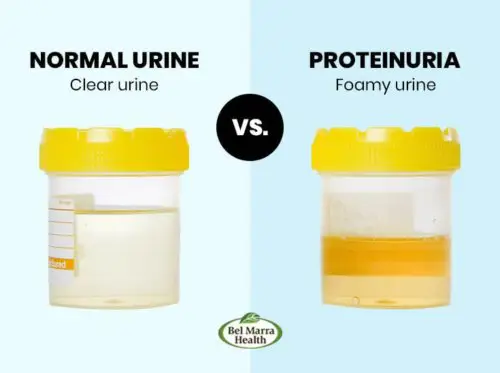
- Foamy urine: Excessive protein loss can manifest as foamy or frothy urine.
- Delayed growth and development: In children, protein loss enteropathy can cause growth retardation and delayed puberty.
- Loss of muscle mass: Progressive muscle wasting due to insufficient protein intake and absorption.
- Weak immune system: Protein loss can weaken the immune system, leading to frequent infections.
If you experience any of these symptoms or signs, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. They may perform diagnostic tests, such as blood tests, stool tests, and endoscopy, to confirm the presence of protein loss enteropathy and identify the underlying cause.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with Protein Loss Enteropathy is vital. We will examine underlying conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease and celiac disease, as well as other factors contributing to this condition.
Protein loss enteropathy is a medical condition characterized by the abnormal loss of protein from the digestive system. This can lead to significant health problems and must be diagnosed promptly to ensure appropriate treatment. Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with protein loss enteropathy is crucial in the diagnosis process.
Causes
There are several causes that can contribute to protein loss enteropathy:
- Intestinal infections: Infections such as giardiasis or tropical sprue can damage the intestines and result in protein loss.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Conditions like Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis can cause chronic inflammation in the intestines, leading to protein loss.
- Lymphatic obstruction: Any blockage in the lymphatic system, such as tumors or lymph node disorders, can disrupt the proper drainage of lymph fluid, resulting in protein loss.
- Small intestine surgery: Surgical procedures involving the small intestine can lead to protein loss if the intestinal lining is damaged.
- Malnutrition: Inadequate intake or absorption of nutrients, including proteins, can contribute to protein loss enteropathy.
Risk Factors
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing protein loss enteropathy:
- Family history: If there is a family history of protein loss enteropathy or related gastrointestinal disorders, the risk may be higher.
- Autoimmune diseases: People with autoimmune conditions like lupus or celiac disease have an increased risk of developing protein loss enteropathy.
- Chronic alcoholism: Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to damage in the intestines, increasing the risk of protein loss enteropathy.
- Long-term medication use: Certain medications, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can cause intestinal damage and contribute to protein loss.
- Age: Older adults are more susceptible to protein loss enteropathy due to age-related changes in the digestive system.
Identifying the causes and risk factors associated with protein loss enteropathy is essential for its accurate diagnosis. By understanding the underlying factors, healthcare professionals can devise appropriate treatment plans to address the condition and minimize potential complications.
Treatment Options
Discover the various treatment options available for Protein Loss Enteropathy, including dietary modifications, medications, and possible surgical interventions. Effective treatment can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall health and well-being.
Protein loss enteropathy (PLE) is a medical condition characterized by excessive loss of proteins through the intestines. It can lead to a variety of complications and health issues. Here, we will explore some treatment options available for PLE diagnosis.
Dietary Modifications
One of the first approaches in treating PLE is making dietary modifications. Patients are advised to consume a low-fat, high-protein diet to compensate for the lost proteins. Additionally, they may be prescribed with specific nutritional supplements to ensure they receive adequate protein intake.
Medications
Medications can be used to manage the underlying causes and symptoms of PLE. Corticosteroids are often prescribed to reduce inflammation in the intestines and improve protein absorption. Immunosuppressants may also be recommended to control autoimmune reactions that contribute to PLE.
Surgical Intervention
In severe cases of PLE, surgical intervention might be necessary. Surgery aims to address the root cause of protein loss and repair any damaged tissues in the digestive system. This may involve removing parts of the intestines, repairing blockages, or treating complications like fistulas.
Monitoring and Follow-up
Regular monitoring and follow-up with healthcare professionals are essential for managing PLE. Doctors may request frequent blood tests to monitor protein levels and assess the effectiveness of the chosen treatment plan. Adjustments can be made accordingly to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Lifestyle Changes
Patients diagnosed with PLE are often advised to make certain lifestyle changes to support their overall health. This may include quitting smoking, managing stress levels, exercising regularly, and avoiding trigger foods that worsen PLE symptoms.
It is important to note that the treatment options mentioned here are general recommendations. Each case of PLE is unique, and the treatment plan should be tailored to the individual's specific needs and underlying causes.
Prevention and Management
Preventing Protein Loss Enteropathy involves adopting a healthy lifestyle and managing underlying conditions effectively. Here, we will explore strategies to prevent the onset of this condition and minimize its impact on individuals' lives.
Protein loss enteropathy (PLE) is a condition characterized by the abnormal leakage of protein from the digestive tract. It can lead to malnutrition and various complications if not diagnosed and managed properly. Here are some important points about the prevention and management of PLE:
Prevention
- Ensure a balanced diet: Consuming a diet rich in proteins and essential nutrients can help prevent protein deficiency, reducing the risk of developing PLE.
- Avoid triggers: Some underlying conditions, such as Crohn's disease or celiac disease, can increase the chances of PLE. Properly managing these conditions through medication and dietary modifications can help prevent PLE.
- Practice good hygiene: Maintaining proper hygiene, especially in food preparation and consumption, can reduce the risk of infections that might lead to PLE.
Management
- Diagnostics: Early diagnosis of PLE is crucial for effective management. Doctors may perform tests like stool analysis, blood tests, endoscopy, and imaging studies to identify the underlying cause and severity of PLE.
- Dietary modifications: Following a specific diet plan recommended by a healthcare professional can help manage PLE. This may involve consuming a higher protein diet, avoiding certain trigger foods, and supplementing with vitamins and minerals.
- Medications: Depending on the underlying cause of PLE, medications may be prescribed to control inflammation, manage symptoms, or treat any infections present.
- Fluid replacement: Severe cases of PLE may require intravenous fluids to correct any fluid imbalances and maintain hydration.
- Monitoring and follow-up: Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals are necessary to monitor the progress of PLE, adjust the treatment plan if needed, and prevent complications.
It is important to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance in the prevention and management of PLE. Following the recommended preventive measures and treatment plan can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals diagnosed with PLE.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can Protein Loss Enteropathy be cured completely?
Answer: While there is no known cure, with proper management, individuals can effectively control symptoms and lead a normal life.
2. Is Protein Loss Enteropathy hereditary?
Answer: No, Protein Loss Enteropathy is not inherited; however, certain genetic factors may increase the susceptibility to developing this condition.
Key Takeaways
- Protein Loss Enteropathy is a condition characterized by the abnormal loss of protein from the gastrointestinal tract.
- Diagnosis often involves various tests and procedures, such as blood and stool analysis, imaging studies, and endoscopy.
- Symptoms can include edema, malnutrition, diarrhea, fatigue, and abdominal pain.
- Underlying conditions like inflammatory bowel disease and celiac disease may contribute to Protein Loss Enteropathy.
- Treatment options include dietary changes, medications, and surgery if necessary.
- Prevention involves managing underlying conditions and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
- Protein Loss Enteropathy cannot be cured completely, but proper management can help control symptoms.


Recent Comments