Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Causes of Low Protein in Urine
- Symptoms of Low Protein in Urine
- Diagnosing blood protein does urine
- Treatment Options
- Complications of Low Protein in Urine
- Preventing Low Protein in Urine
Introduction
Having low levels of protein in your urine, also known as hypoalbuminuria, can be a cause for concern as it may indicate an underlying health issue. In this article, we will explore what it means to have low protein in your urine, its possible causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, complications, and prevention measures.
Causes of Low Protein in Urine
Low protein in urine can be caused by a variety of factors, including kidney disease, malnutrition, liver disease, and certain medications. It may also be a sign of a more serious condition such as nephrotic syndrome or chronic kidney disease.
Proteinuria, or the presence of protein in the urine, is a common condition that can be caused by a variety of factors. Low protein in urine, on the other hand, can indicate a few different underlying health issues.
What does it mean to have low protein in your urine?
Low protein in urine, also known as hypoalbuminemia, can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Malnutrition
- Kidney diseases
- Liver diseases
- Chronic inflammation
- Protein-losing enteropathy
If you have low protein in your urine, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of Low Protein in Urine
While low protein in urine may not cause any noticeable symptoms on its own, it is often detected during routine urine tests. In some cases, individuals may experience swelling in the legs, ankles, or face due to fluid retention.
Having low levels of protein in your urine, also known as proteinuria, can be a sign of an underlying health condition. Some common symptoms of low protein in urine include:
- Swelling in the hands, feet, or face
- Fatigue and weakness
- Foamy or bubbly urine
- Changes in urine color
Low protein in urine can be caused by a variety of factors, including kidney disease, malnutrition, and certain medications. It is important to see a healthcare provider if you are experiencing symptoms of low protein in urine to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Diagnosing Low Protein in Urine
Low protein in urine can be detected through a simple urine test called a urine protein test. Your healthcare provider may also perform additional tests to determine the underlying cause of the low protein levels.
Having low levels of protein in your urine, also known as hypoalbuminemia, can indicate potential health issues such as kidney disease, malnutrition, liver disease, or certain autoimmune disorders.
When protein levels in urine are below normal, it may suggest that the kidneys are not functioning properly and are not able to properly filter and retain protein in the body. This can lead to protein deficiencies and other complications if left untreated.
Diagnosing low protein in urine typically involves a urine test, known as a urine protein electrophoresis, which can determine the exact levels of protein present in the urine. If low protein levels are detected, further testing and medical evaluation may be needed to identify the underlying cause and determine the appropriate treatment.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional if you have concerns about your protein levels in urine or if you are experiencing symptoms such as swelling, fatigue, or changes in urination habits.

Treatment Options
The treatment for low protein in urine will depend on the underlying cause. In some cases, treating the underlying condition, such as kidney disease or malnutrition, may help restore normal protein levels in the urine. Medications and dietary changes may also be recommended.
Having low levels of protein in your urine, also known as proteinuria, can indicate a variety of health conditions. The treatment options for this condition depend on the underlying cause of the low protein levels.
Some potential causes of low protein in urine include kidney disease, malnutrition, or excessive protein loss due to certain medical conditions. To determine the appropriate treatment, a healthcare provider may perform further tests to identify the specific cause.
Treatment options for low protein in urine may include:
1. Treating the underlying health condition causing the proteinuria, such as kidney disease or malnutrition.
2. Dietary changes to ensure adequate protein intake.
3. Medications to manage symptoms or control the underlying condition.
4. Monitoring and regular check-ups to assess kidney function and overall health.
It is important to follow the recommended treatment plan provided by a healthcare professional to manage low protein levels in urine and prevent further complications. If you are experiencing symptoms of proteinuria, consult with your doctor for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
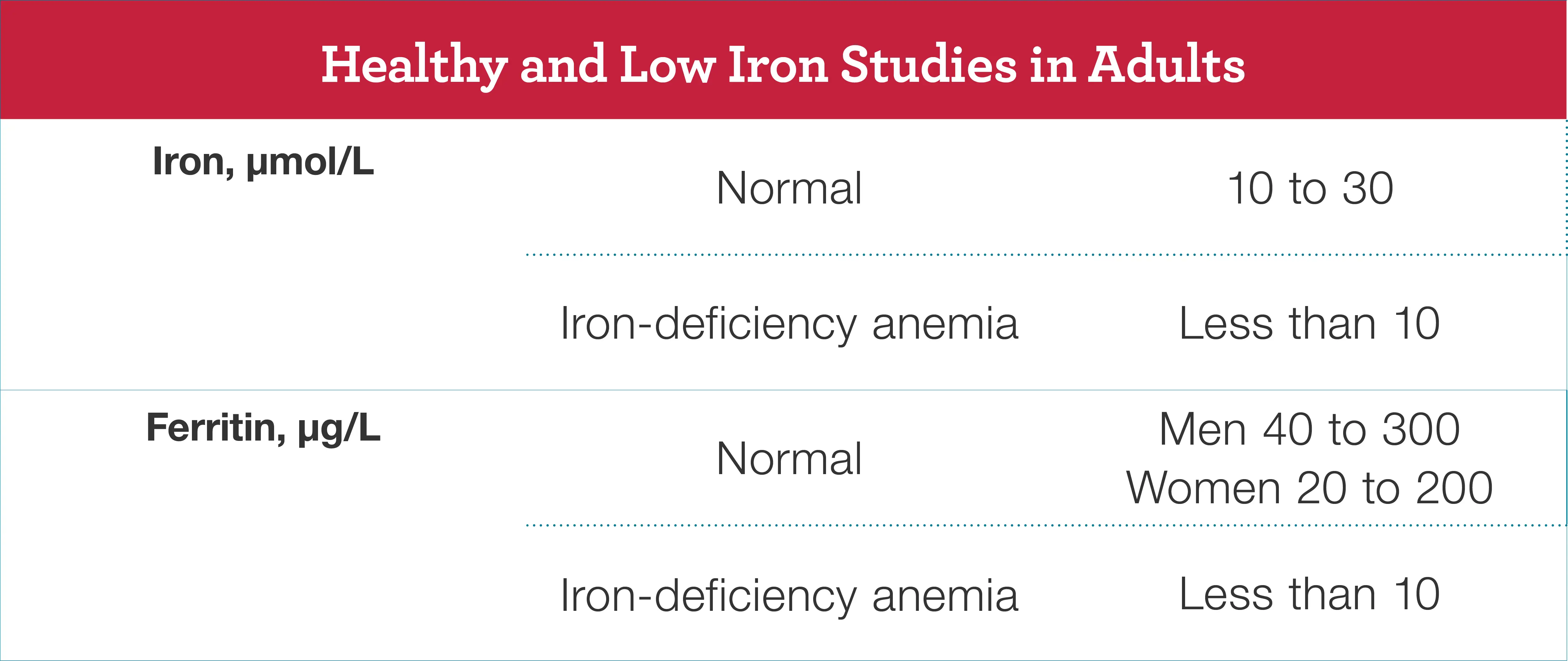
Complications of Low Protein in Urine
If left untreated, low protein in urine can lead to complications such as edema (swelling), increased risk of infections, and poor wound healing. It is important to address the underlying cause of the low protein levels to prevent these complications.
Proteinuria is a condition where there is an abnormal amount of protein in the urine. However, having low levels of protein in your urine, also known as hypoalbuminemia, can also indicate underlying health issues.
When there is a low amount of protein in the urine, it may suggest that the kidneys are not functioning properly. The kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste and excess substances from the blood, including proteins. Therefore, low levels of protein in the urine could be a sign of kidney damage or dysfunction.
Complications of low protein in urine may include:
- Edema (swelling) due to fluid accumulation in the body
- Weakness and fatigue
- Decreased immune function
- Impaired growth and development (particularly in children)
It is important to consult a healthcare provider if you have consistently low levels of protein in your urine to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
Preventing Low Protein in Urine
Preventing low protein in urine involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, and avoiding harmful substances such as tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption. Regular medical check-ups can also help detect and address any underlying health issues early on.
Having low levels of protein in your urine, also known as proteinuria, can be a sign of various health issues such as kidney disease or a poor diet. To prevent low protein in urine, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle by eating a balanced diet rich in proteins, exercising regularly, staying hydrated, and avoiding harmful substances such as alcohol and tobacco. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional if you experience any symptoms of proteinuria, as it can indicate underlying health concerns that may require medical attention.

Key Takeaways
- Low protein in urine, or hypoalbuminuria, may indicate an underlying health issue.
- Causes of low protein in urine include kidney disease, malnutrition, liver disease, and certain medications.
- Treatment for low protein in urine depends on the underlying cause and may involve medications, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications.
- Complications of low protein in urine can include swelling, increased risk of infections, and poor wound healing.
- Prevention measures for low protein in urine include maintaining a healthy lifestyle, regular medical check-ups, and avoiding harmful substances.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does it mean to have low protein in your urine?
Having low protein in your urine may indicate an underlying health issue, such as kidney disease or malnutrition.
How is low protein in urine diagnosed?
Low protein in urine is diagnosed through a simple urine test called a urine protein test.
What are the complications of low protein in urine?
Complications of low protein in urine can include swelling, increased risk of infections, and poor wound healing.



Recent Comments