Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Benefits of Sufficient Protein Intake
- Protein Requirements for Muscle Gain
- Calculating Your Protein Needs
- High Protein Food Sources
- Timing Your Protein Intake
- Busting the Myth: Excess Protein and Kidney Damage
Introduction
Welcome to our complete guide on protein intake for muscle gain. If you're aiming to build and develop muscle, getting the right amount of protein is essential. This article will walk you through the optimal protein intake, its benefits, how to calculate your requirements, and debunk common misconceptions.
Benefits of Sufficient Protein Intake
Consuming sufficient protein has numerous advantages beyond muscle gain. It helps in repairing and rebuilding muscle tissues, supports a healthy immune system, and contributes to a feeling of fullness, aiding in weight management. Moreover, it provides essential amino acids for various bodily functions, such as hormone production and enzyme synthesis.
Protein is an essential nutrient required by the body for growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues. Sufficient protein intake is particularly important for individuals looking to gain muscle mass. Here are the key benefits of consuming enough protein:
- Muscle Growth: Consuming an adequate amount of protein promotes muscle growth. When you exercise, your muscles undergo stress and protein helps in repairing and rebuilding the damaged muscle fibers. It is recommended to consume a certain amount of protein per pound of body weight to support muscle gain.
- Increased Strength: Sufficient protein intake plays a crucial role in increasing strength. Protein helps in the synthesis of new muscle tissue, which ultimately enhances muscle strength and power.
- Improved Recovery: Protein aids in faster recovery after intense workouts. It assists in replenishing glycogen stores, reducing muscle soreness, and preventing muscle breakdown, enabling you to bounce back stronger and quicker.
- Enhanced Metabolism: Protein has a high thermic effect, which means it requires more energy to digest and metabolize compared to fats or carbohydrates. This leads to a boost in your metabolic rate, helping you burn more calories throughout the day.
- Appetite Control: Protein is highly satiating and keeps you feeling fuller for longer. By incorporating sufficient protein into your meals, you can effectively manage your appetite, prevent overeating, and maintain a healthy weight.
When aiming to gain muscle, it is generally recommended to consume around 0.7 to 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight. However, individual requirements may vary based on factors such as age, gender, activity level, and overall health. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to determine the exact protein intake that suits your needs.
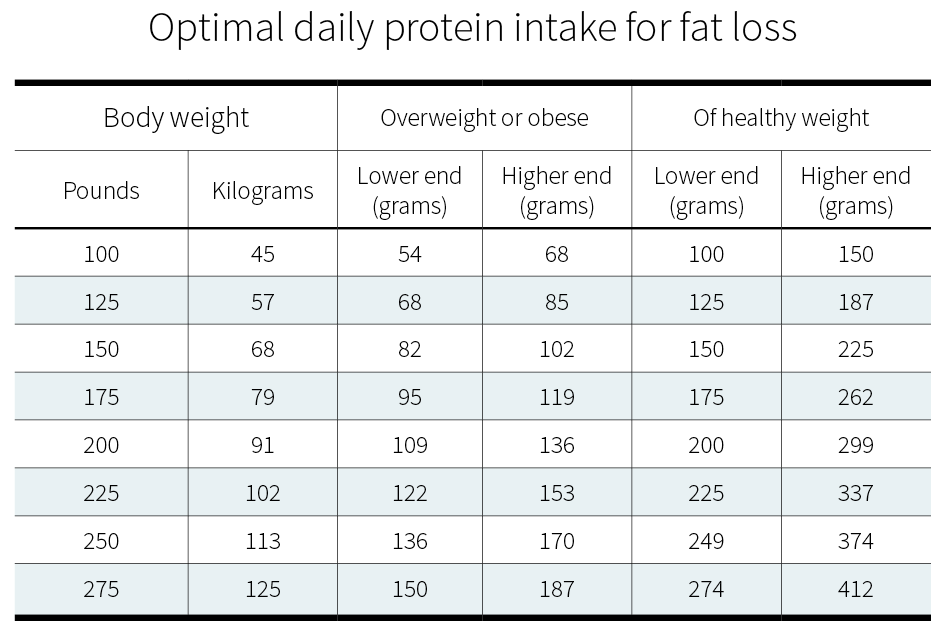
Protein Requirements for Muscle Gain
The recommended protein intake for individuals aiming to build muscle is typically around 0.7 to 1 gram per pound of body weight. However, this can vary based on factors such as age, activity level, and overall health.
In order to effectively gain muscle, it is important to consume an adequate amount of protein. The general guideline for protein intake to support muscle growth is to consume a certain number of grams of protein per pound of body weight.
Protein Intake Formula:
To calculate your recommended daily protein intake for muscle gain, use the following formula:
Protein Intake (in grams) = Body Weight (in pounds) x Protein Intake Ratio
Protein Intake Ratio:
The ideal protein intake ratio varies depending on individual factors, such as activity level, age, and fitness goals. However, a common recommendation for individuals looking to gain muscle is consuming around 0.8 to 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight.
Example:
Let's consider an individual weighing 150 pounds who wants to gain muscle. To calculate their protein requirements, we will use the lower end of the recommended range (0.8 grams per pound of body weight):
Protein Intake = 150 lbs x 0.8 = 120 grams per day
Conclusion:
To maximize muscle gain, it is essential to consume an adequate amount of protein. Aim to include lean protein sources, such as chicken, fish, tofu, eggs, and legumes, in your diet. Additionally, it is advisable to consult with a nutritionist or healthcare professional to determine the specific protein requirements based on your individual needs.
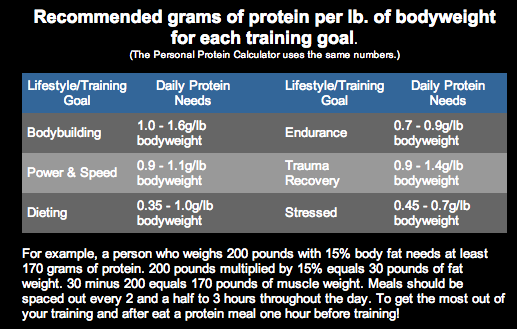
Calculating Your Protein Needs
To calculate your protein needs, multiply your body weight (in pounds) by the recommended protein intake per pound. This will give you an estimate of how many grams of protein you should consume daily.
In order to effectively gain muscle, it is essential to consume an adequate amount of protein. One common method to determine protein intake for muscle growth is calculating your protein needs in grams per pound of body weight.
How Many Grams of Protein Per Pound of Body Weight?
The general recommendation for protein intake to promote muscle growth is around 0.7 to 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight. This range can vary depending on factors such as activity level, fitness goals, and individual differences.
To calculate your protein needs, simply multiply your body weight in pounds by the desired protein intake per pound. For example, if you weigh 150 pounds and aim for 1 gram of protein per pound, you would need to consume 150 grams of protein per day.
It's important to distribute your protein intake evenly throughout the day to support muscle recovery and synthesis. Aim to include protein-rich foods in each meal and consider incorporating protein shakes or supplements if necessary.
Consult a Healthcare Professional
Keep in mind that individual protein requirements may vary, and it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to determine the appropriate protein intake for your specific needs and goals.

High Protein Food Sources
Meeting your protein requirements is easier when you incorporate protein-rich foods into your diet. Some excellent sources of protein include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
In order to gain muscle, it is essential to consume enough protein. One crucial aspect of muscle building is knowing how many grams of protein per pound of body weight should be consumed. Let's explore some high protein food sources to help you achieve your muscle gain goals.
Chicken Breast
Chicken breast is an excellent source of lean protein, containing around 25 grams of protein per 3-ounce serving. It is low in fat and a staple for muscle growth diets.
Salmon
Salmon is a nutrient-rich fish packed with omega-3 fatty acids and about 22 grams of protein per 3-ounce serving. It not only aids in muscle growth but also supports overall health.
Greek Yogurt
Greek yogurt is a protein-packed dairy product, providing approximately 17 grams of protein per 6-ounce serving. It is a versatile food that can be consumed as a snack or used as an ingredient in various recipes.
Eggs
Eggs are a convenient and affordable source of protein, containing approximately 6 grams of protein per large egg. They also offer essential amino acids necessary for muscle repair and growth.
Cottage Cheese
Cottage cheese is a high protein option, delivering around 14 grams of protein per half-cup serving. It can be consumed as a snack or used in recipes to increase protein content.
Whey Protein Powder
Whey protein powder is a popular supplement for individuals aiming to increase protein intake. It typically provides around 20-25 grams of protein per serving, making it a convenient choice to reach your protein goals.
Remember, to gain muscle, it is recommended to consume around 0.7 to 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight. Combining these high protein food sources with a balanced diet and regular exercise will support your muscle-building journey.
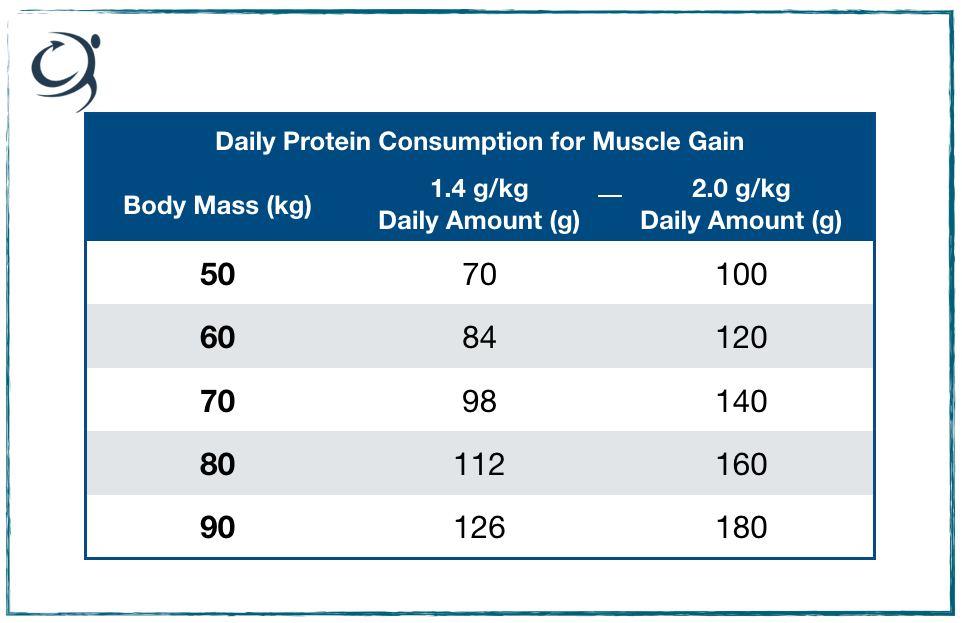
Timing Your Protein Intake
While distributing your protein intake throughout the day is important, research suggests that consuming protein within the first few hours after exercise can be especially beneficial for muscle repair and growth. Aim to consume a protein-rich meal or snack within this timeframe.
When it comes to building muscle, it's important to ensure you are consuming an adequate amount of protein. One common guideline to follow is to consume a certain amount of protein per pound of body weight. This helps support muscle growth and repair after intense workouts.
The recommended protein intake for muscle gain is generally 0.8 to 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight. However, some individuals may benefit from consuming slightly more, up to 1.2 grams per pound, especially if they are engaged in intense weightlifting or endurance training.
To calculate your protein intake, simply multiply your body weight in pounds by the recommended range. For example, if you weigh 150 pounds, you would aim to consume 120 to 150 grams of protein per day.
In addition to the total daily protein intake, the timing of protein consumption also plays a role in muscle development. Many experts suggest distributing your protein intake evenly throughout the day, including pre and post-workout. This ensures a constant supply of amino acids for muscle repair and growth.
It is recommended to consume around 20-30 grams of protein within 30 minutes of finishing your workout. This helps kickstart the muscle recovery process. Eating a protein-rich meal or snack before exercising can also provide your body with the necessary amino acids for optimal performance during your workout.
In conclusion, timing your protein intake and consuming the recommended grams of protein per pound of body weight is crucial for maximizing muscle gain. Consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to determine the ideal protein intake and distribution for your specific goals and needs.
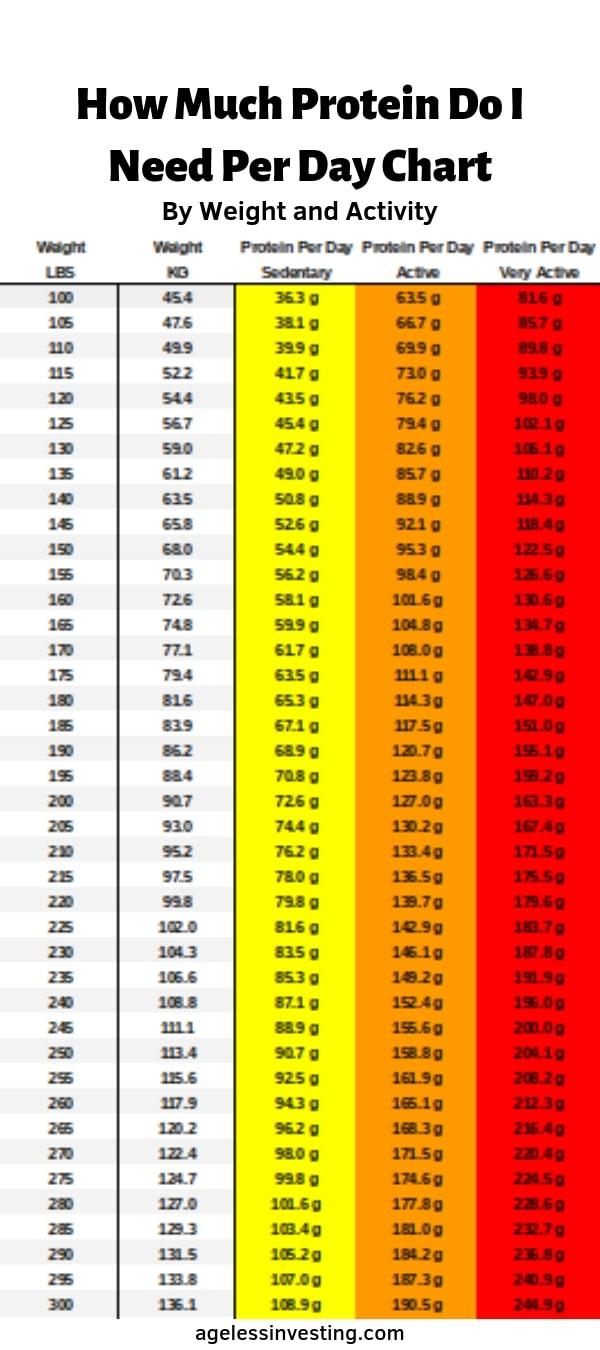
Busting the Myth: Excess Protein and Kidney Damage
Contrary to popular belief, a high protein intake does not directly cause kidney damage in healthy individuals. However, individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions should consult with their healthcare provider regarding protein consumption.
One common myth surrounding muscle gain is that consuming too much protein can lead to kidney damage. However, scientific research suggests that this is largely untrue.
The ideal protein intake for individuals aiming to build muscle varies based on their body weight. Contrary to the common belief, it is not necessary to consume an excessive amount of protein to achieve significant muscle growth.
The recommended protein intake for muscle gain is commonly expressed in terms of grams of protein per pound of body weight. It is generally recommended to consume around 0.7-1 gram of protein per pound of body weight for most individuals engaging in regular resistance training.
This means that if you weigh 150 pounds, a protein intake of 105-150 grams per day would be appropriate to support muscle growth. Consuming protein within this range can help provide the necessary building blocks (amino acids) for muscle repair and growth without overburdening the kidneys.
It's important to note that the recommended protein intake may slightly vary based on individual factors such as age, sex, fitness goals, and overall health. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance on determining your specific protein needs.
In conclusion, the idea that excess protein intake directly causes kidney damage is a myth. Following the recommended protein intake guidelines tailored to your body weight and fitness goals will support muscle growth without posing a risk to your kidneys.

Key Takeaways
- Consuming adequate protein is crucial for muscle gain and other vital bodily functions.
- Most individuals aiming for muscle growth should consume around 0.7 to 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight.
- Calculating protein needs involves multiplying body weight (in pounds) by the recommended protein intake per pound.
- Include a variety of protein-rich foods in your diet, such as lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
- Timing your protein intake, especially after exercise, can enhance muscle repair and growth.
- Excess protein intake does not cause kidney damage in healthy individuals, but consult a healthcare professional if you have pre-existing kidney conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 1. How do I determine my protein needs for muscle gain?
- To estimate your protein needs, multiply your body weight in pounds by the recommended protein intake per pound. This will provide an estimate of the grams of protein you should consume daily.
- 2. Can I get enough protein from a vegetarian or vegan diet?
- Yes, you can obtain sufficient protein from plant-based sources such as legumes, tofu, tempeh, quinoa, and other grains. It's important to include a variety of protein-rich plant foods to meet your needs.
- 3. Can I consume too much protein?
- While protein is important, excessively high protein intake may lead to excess calorie consumption. It is recommended to stay within the recommended protein intake range for optimal results.
- 4. Should I take protein supplements?
- Meeting your protein needs through whole food sources is preferable. However, protein supplements can be useful for convenience, especially in situations where adequate protein intake is challenging.
- 5. Can protein intake alone lead to muscle gain without exercise?
- No, building muscle requires a combination of appropriate protein intake and regular resistance training exercises.



Recent Comments