Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Mechanism of Action
- Clinical Trials
- Side Effects
- Future Perspectives
- Cost Effectiveness
- Conclusion
Introduction
Neuroblastoma is a type of cancer that develops from immature nerve cells. The bivalent vaccine is a promising treatment approach for this aggressive cancer.
Mechanism of Action
The bivalent vaccine works by targeting specific antigens present on neuroblastoma cells, stimulating the immune system to recognize and attack these cancerous cells.
Neuroblastoma is a type of cancer that develops from nerve tissue and commonly affects young children. Bivalent vaccines for neuroblastoma target specific antigens found on neuroblastoma cells in order to trigger an immune response against the cancer cells.
These vaccines work by introducing harmless fragments of the antigens into the body, which then stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies against them. These antibodies can recognize and target neuroblastoma cells, leading to their destruction.
Additionally, bivalent vaccines for neuroblastoma can also activate immune cells such as T cells and natural killer cells to directly attack the cancer cells. This dual mechanism of action helps to enhance the body's natural defenses against neuroblastoma.
Overall, bivalent vaccines for neuroblastoma hold promise as a targeted and effective treatment option for this aggressive form of cancer.
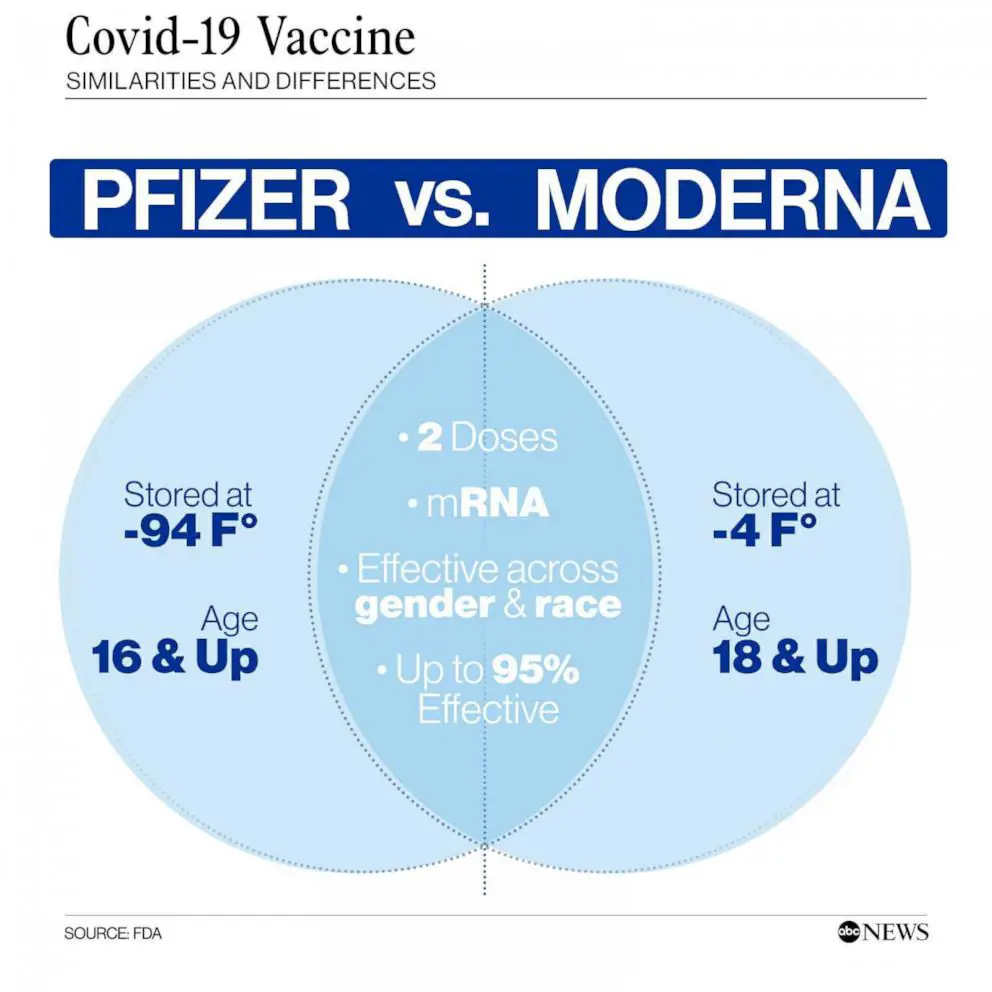
Clinical Trials
Several clinical trials have shown promising results in the use of the bivalent vaccine for neuroblastoma, with improved survival rates and reduced recurrence of the disease.
Clinical trials are currently underway to study the effectiveness of a bivalent vaccine for treating neuroblastoma, a type of cancer that commonly affects children. This vaccine aims to target specific antigens present in neuroblastoma cells in order to stimulate the immune system to recognize and destroy these cancer cells.
The bivalent vaccine being tested in these trials is designed to potentially improve outcomes for patients with neuroblastoma by boosting the body's natural defenses against the disease. Preliminary results have shown promising signs of efficacy and safety, but further research is needed to confirm its effectiveness.
If successful, this bivalent vaccine could offer a new treatment option for patients with neuroblastoma, providing hope for improved outcomes and potentially reducing the need for aggressive chemotherapy and radiation therapies.
Patients interested in participating in these clinical trials or learning more about the bivalent vaccine for neuroblastoma should consult with their healthcare provider or contact the research team conducting the studies.
Side Effects
Like any other medical intervention, the bivalent vaccine may have side effects such as fever, injection site reactions, and fatigue. However, these are generally mild and well-tolerated by patients.
It is important to note that like all vaccines, the bivalent vaccine for neuroblastoma may cause some side effects. These side effects are typically mild and temporary, but it is important to be aware of them before receiving the vaccine.
- Redness, swelling, or soreness at the injection site
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Nausea or vomiting
- Headache
- Muscle or joint pain
- Rash
If you experience any severe or persistent side effects after receiving the bivalent vaccine for neuroblastoma, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. It is also important to discuss any concerns or questions you may have about the vaccine with your healthcare provider.
Future Perspectives
Researchers are continuously exploring ways to improve the efficacy of the bivalent vaccine for neuroblastoma, including combination therapies and personalized medicine approaches.
Neuroblastoma is a type of cancer that develops from immature nerve cells. Current treatments for neuroblastoma often involve surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. However, the development of a bivalent vaccine for neuroblastoma holds great promise for the future of treatment.
A bivalent vaccine is designed to target two specific antigens that are commonly found in neuroblastoma cells. By stimulating the immune system to recognize and attack these antigens, the vaccine has the potential to improve outcomes for patients with neuroblastoma.
Researchers are currently conducting clinical trials to evaluate the safety and efficacy of bivalent vaccines for neuroblastoma. Preliminary results have shown promising results, with some patients experiencing tumor shrinkage and improved survival rates.
As more data is collected and analyzed, the future looks bright for the development of bivalent vaccines as a targeted and effective treatment option for neuroblastoma. Continued research and investment in this area are crucial to advancing the field and providing hope for patients and their families.

Cost Effectiveness
While the bivalent vaccine may initially seem costly, its long-term benefits in terms of improved survival rates and quality of life make it a cost-effective treatment option for neuroblastoma patients.
Neuroblastoma is a type of cancer that affects young children and can be difficult to treat. Researchers have been studying the use of a bivalent vaccine for neuroblastoma, which targets two specific proteins that are often found on neuroblastoma cells.
Studies have shown that this bivalent vaccine can help boost the immune system's ability to recognize and attack neuroblastoma cells, leading to improved outcomes for patients. However, one important factor to consider is the cost effectiveness of this treatment option.
Cost effectiveness analysis can help determine if the benefits of a treatment, such as the bivalent vaccine for neuroblastoma, outweigh the costs. Factors such as the cost of the vaccine, the potential savings from reducing the need for other treatments or hospitalizations, and the overall impact on patient outcomes all play a role in determining cost effectiveness.
By analyzing the cost effectiveness of the bivalent vaccine for neuroblastoma, researchers and healthcare providers can make informed decisions about its use and potential benefits for patients. Ultimately, finding cost effective treatment options is essential for improving outcomes and ensuring that patients have access to the best possible care.

Conclusion
The bivalent vaccine holds great promise in the treatment of neuroblastoma, offering a targeted and effective approach to combating this challenging cancer.
Key Takeaways
- The bivalent vaccine targets specific antigens on neuroblastoma cells to stimulate the immune system.
- Clinical trials have shown promising results in improving survival rates and reducing recurrence of neuroblastoma.
- Safety profile of the bivalent vaccine includes mild and well-tolerated side effects.
- Future research aims to enhance the efficacy of the bivalent vaccine through combination therapies and personalized medicine.
- Cost effectiveness of the bivalent vaccine makes it a valuable treatment option for neuroblastoma patients.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Q: What is a bivalent vaccine?
- A: A bivalent vaccine is a type of vaccine that targets two specific antigens, providing a more targeted immune response.
- Q: How does the bivalent vaccine work for neuroblastoma?
- A: The bivalent vaccine targets antigens present on neuroblastoma cells, stimulating the immune system to recognize and attack these cancerous cells.
- Q: Are there any serious side effects of the bivalent vaccine?
- A: Serious side effects of the bivalent vaccine are rare, with most patients experiencing only mild and well-tolerated reactions.


Recent Comments