Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Plant Viruses
- Types of Plant Viruses
- Symptoms of Plant Virus Infections
- Transmission of Plant Viruses
- Impact of Plant Viruses on Agriculture
- Prevention and Control of Plant Viruses
- Conclusion
Introduction to Plant Viruses
Plant viruses are microscopic pathogens that can infect a wide variety of crops, causing significant damage to agricultural yields. They are transmitted through various means and can have devastating effects on plant health.
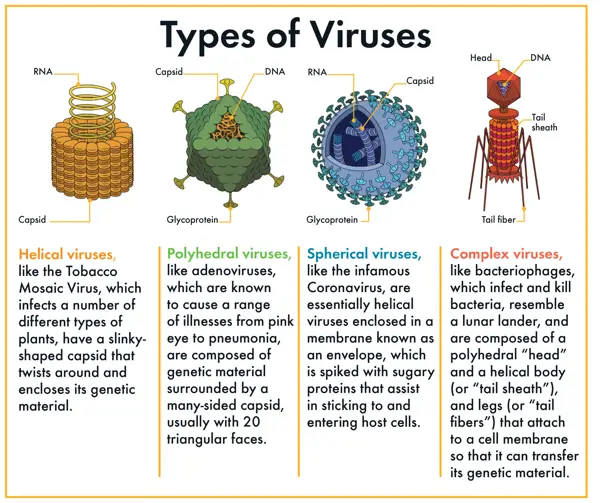
Types of Plant Viruses
There are hundreds of different plant viruses that can infect crops, including tobacco mosaic virus, potato virus Y, and cucumber mosaic virus. Each virus has its own unique characteristics and methods of transmission.
Plant viruses are a type of virus that can infect plants and cause various diseases. There are several types of plant viruses that can affect different plant species.
- Geminiviruses: These are circular single-stranded DNA viruses that are known to infect a wide range of plants, including vegetables, cereals, and ornamental plants.
- Potyviruses: This is the largest group of plant viruses and includes viruses that infect various crops such as potatoes, beans, and peppers.
- Tospoviruses: These are a group of plant viruses transmitted by thrips that can infect a variety of plants, including tomatoes, peppers, and cucurbits.
- Tobamoviruses: These are rod-shaped viruses that can infect a range of plants, including tobacco, tomatoes, and peppers.
These are just a few examples of the many types of plant viruses that can infect plants and cause diseases. It is important for gardeners and farmers to be aware of these viruses in order to take preventive measures and protect their plants.
Symptoms of Plant Virus Infections
The symptoms of plant virus infections can vary depending on the type of virus and the plant species. Common symptoms include stunted growth, leaf discoloration, and distorted fruits.
Plant viruses are pathogens that can infect various plant species and cause a wide range of symptoms. Some common symptoms of plant virus infections include:
- Leaf discoloration: Infected leaves may exhibit abnormal color patterns such as yellowing, mottling, or streaking.
- Stunted growth: Plants infected with viruses may fail to grow to their full potential and appear smaller or less vigorous than healthy plants.
- Leaf curling or distortion: Infected leaves may curl, crinkle, or exhibit other abnormal shapes and textures.
- Necrosis: The death of plant tissue, resulting in brown or black spots, lesions, or dead patches on leaves, stems, or fruit.
- Reduced yield: Infected plants may produce fewer fruits or flowers, or experience lower quality yields.
Some common plant viruses that can infect plants include Tobacco mosaic virus, Tomato spotted wilt virus, and Potato virus Y. These viruses are typically spread through insect vectors, contaminated tools, or infected plant material. Proper management practices, such as crop rotation, use of virus-resistant varieties, and controlling insect pests, can help prevent and control plant virus infections.
Transmission of Plant Viruses
Plant viruses can be transmitted through various means, including insect vectors, contaminated tools, and infected seeds. Once a plant is infected, the virus can spread rapidly throughout the crop.
Plant viruses are tiny infectious agents that can only infect plants and cannot harm humans or animals. These viruses are transmitted from plant to plant through various means such as insect vectors, soil, contaminated tools, and plant debris.
One of the most common plant viruses is the Tobacco mosaic virus, which can infect a wide range of plants including tomatoes, peppers, and tobacco. This virus is mainly spread through contaminated plant sap or through direct contact with infected plants.
Another notorious plant virus is the Potato virus Y, which is spread by aphids feeding on infected plants and then transmitting the virus to healthy plants. This virus can cause severe damage to potato and pepper crops.
Overall, it is important for gardeners and farmers to practice proper plant hygiene and control insect vectors to prevent the spread of plant viruses and protect their crops.
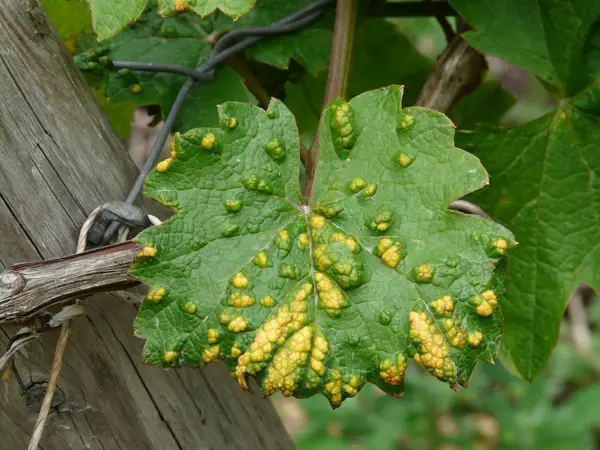

Impact of Plant Viruses on Agriculture
Plant viruses can have a significant impact on agricultural production, leading to reduced yields and poor quality crops. Farmers must take measures to prevent and control virus infections to protect their crops.
Plant viruses can have a significant impact on agriculture by reducing crop yields and quality, as well as increasing the costs of production. These viruses can infect a wide range of plant species, including important crops such as tomatoes, potatoes, and wheat.
One of the most common plant viruses is the Tomato spotted wilt virus, which affects tomatoes, peppers, and other crops. This virus causes discoloration, wilting, and stunted growth in infected plants, leading to reduced yields and lower quality produce.
Another damaging plant virus is the Potato virus Y, which infects potatoes, peppers, and other solanaceous crops. This virus can cause mosaic patterns on leaves, yellowing of foliage, and reduced tuber quality, resulting in significant economic losses for farmers.
In addition to these viruses, there are many other plant viruses that can infect a wide variety of crops, impacting the global food supply and agricultural economy. It is important for farmers to be vigilant in monitoring and controlling plant viruses to protect their crops and ensure food security for the future.
Prevention and Control of Plant Viruses
There are several strategies that farmers can use to prevent and control plant virus infections, including crop rotation, use of disease-resistant varieties, and proper sanitation practices. Early detection is key to limiting the spread of viruses.
Prevention and Control of Plant Viruses
Plant viruses are a major threat to agriculture worldwide, causing significant damage to crops and reducing yields. It is important for farmers and growers to be proactive in preventing and controlling the spread of plant viruses in order to protect their plants and ensure a successful harvest.
There are several ways to prevent and control the spread of plant viruses. One effective method is to use virus-free seeds and plant material. It is also important to practice good hygiene in the garden or field, such as washing hands and tools before working with plants. Additionally, implementing proper sanitation practices, such as removing infected plants and debris, can help reduce the risk of virus transmission.
There are a variety of viruses that can infect plants, including tobacco mosaic virus, cucumber mosaic virus, and potato virus Y. These viruses can be transmitted through plant-to-plant contact, insects, and contaminated soil. It is important to be aware of the symptoms of viral infection in plants, such as stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and mottled patterns, in order to quickly identify and treat infected plants.
By implementing preventive measures and closely monitoring plants for signs of viral infection, farmers and growers can effectively control and mitigate the spread of plant viruses, ultimately safeguarding their crops and ensuring a healthy harvest.
Conclusion
Plant viruses pose a serious threat to agriculture worldwide, affecting crops and livelihoods. By understanding the types of viruses that can infect plants and implementing effective control measures, farmers can mitigate the impact of these pathogens.
Key Takeaways:
- Plant viruses can infect a wide variety of crops, causing damage to agricultural yields.
- Common symptoms of plant virus infections include stunted growth and leaf discoloration.
- Transmission of plant viruses can occur through insect vectors, contaminated tools, and infected seeds.
- Farmers can prevent and control plant viruses through crop rotation, use of disease-resistant varieties, and sanitation practices.
FAQ:
- Q: Can plant viruses be treated with chemicals?
- A: There are no chemical treatments available for plant viruses. Prevention and control methods are the best approach.
- Q: How can I tell if my plants are infected with a virus?
- A: Look for common symptoms such as stunted growth, leaf discoloration, and distorted fruits. Consult with a plant pathologist for a definitive diagnosis.


Recent Comments