Table of Contents:
- What is Starch?
- How Starch Affects Blood Sugar Levels
- The Role of Starch in Energy Production
- Starch and Digestive Health
- Sources of Starch in the Diet
- Health Implications of Starch Consumption
- Tips for Managing Starch Intake
What is Starch?
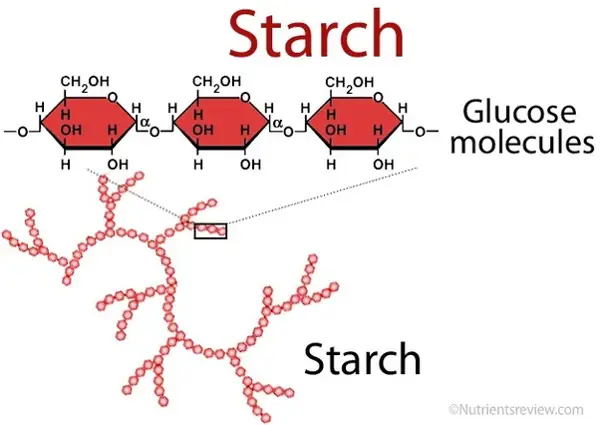
Starch is a complex carbohydrate that is commonly found in plants. It is made up of long chains of glucose molecules and is a primary source of energy for the body.
How Starch Affects Blood Sugar Levels
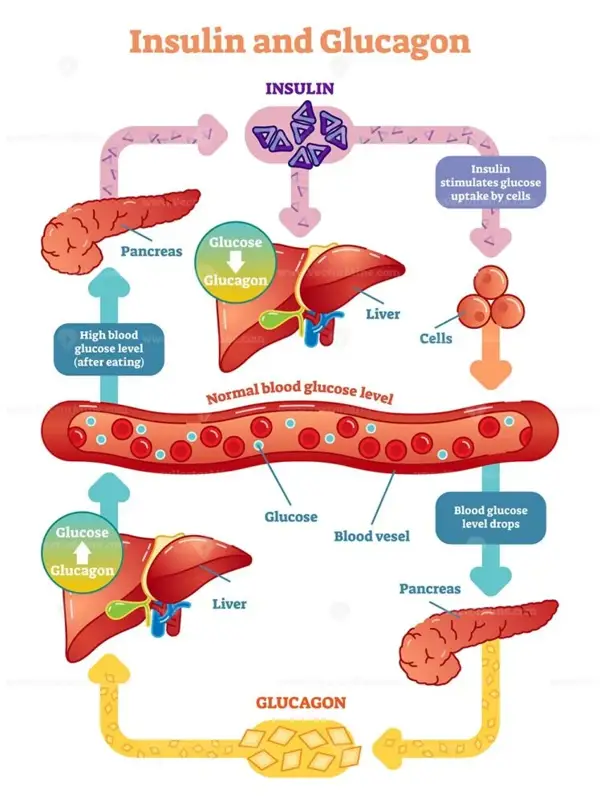
When we consume starch, it is broken down into glucose in the body, which can cause a spike in blood sugar levels. This can lead to insulin resistance and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
Starch is a type of carbohydrate that is found in foods such as bread, pasta, and potatoes. When we eat foods that contain starch, our bodies break down the starch into glucose, which is a form of sugar. This glucose is then released into our bloodstream, causing our blood sugar levels to rise.
The effect of starch does blood sugar body fat affect depending on the type of starch and how it is prepared. Foods that contain refined starches, such as white bread and sugary cereals, can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels, leading to a spike in energy followed by a crash. On the other hand, foods that contain whole grains and complex carbohydrates, such as brown rice and whole wheat bread, are digested more slowly, leading to a more gradual increase in blood sugar levels.
Monitoring your starch intake and choosing whole, unprocessed starches can help to regulate your blood sugar levels and provide a steady source of energy for your body. Additionally, incorporating other nutrients such as protein and fiber into your meals can help to further stabilize your blood sugar levels and promote overall health.

The Role of Starch in Energy Production
Starch is a key source of energy for the body, providing fuel for physical activity and metabolic processes. However, consuming too much starch can lead to weight gain and other health issues.
Starch plays a crucial role in energy production in the human body. When we consume foods that are high in starch, such as grains, potatoes, and legumes, our bodies break down the starch into glucose. Glucose is then used as fuel for our cells, providing us with the energy we need to carry out our daily activities.
Starch also helps regulate blood sugar levels, preventing spikes and crashes that can leave us feeling tired and lethargic. In addition to its energy-producing properties, starch is a valuable source of dietary fiber, which aids in digestion and promotes overall gut health.
It is important to consume starch in moderation, as excessive intake can lead to weight gain and other health issues. However, when included as part of a balanced diet, starch can be a valuable source of sustained energy and nutrition for the body.

Starch and Digestive Health
Starch is a complex carbohydrate that is not easily digested by the body. It can ferment in the gut, leading to gas, bloating, and other digestive issues.
Starch is a type of carbohydrate that plays a vital role in providing energy to the body. When consumed, starch is broken down into glucose, which is the main source of fuel for the cells in our body.
When it comes to digestive health, starch can have both positive and negative effects. On one hand, starch can be beneficial for digestive health as it provides a source of energy for the cells in the digestive tract, helping to maintain overall gut health. Additionally, the fiber content in starch-rich foods can help regulate bowel movements and prevent constipation.
However, consuming too much starch, especially in refined forms like white bread and pastries, can lead to negative effects on digestive health. These foods can cause spikes in blood sugar levels, leading to insulin resistance and other health issues.
It is important to consume starch in moderation and opt for whole grain sources like brown rice, quinoa, and oats to ensure optimal digestive health. Balancing starch intake with other nutrients like fiber, protein, and healthy fats can help support overall gut health and digestion.
Sources of Starch in the Diet
Starchy foods such as bread, pasta, rice, potatoes, and legumes are common sources of starch in the diet. It is important to choose whole grains and limit refined starches for better health.
Starch is a type of complex carbohydrate found in a variety of foods. Some common sources of starch in the diet include:
- Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread
- Legumes such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas
- Potatoes and sweet potatoes
- Corn and corn products
- Root vegetables like carrots and parsnips
Starch is a key source of energy for the body. When consumed, starch is broken down into glucose, which is then used by the body for fuel. This can help to maintain steady blood sugar levels and provide a sustained source of energy throughout the day.
Additionally, the fiber content in starchy foods can help with digestion and promote gut health. Fiber can also help you feel full and satisfied, which can aid in weight management.
However, it is important to consume starch in moderation as excessive intake can lead to weight gain and other health issues. Opt for whole, unprocessed sources of starch and balance your diet with a variety of other nutrients.
Health Implications of Starch Consumption
Consuming too much starch can lead to weight gain, insulin resistance, and an increased risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease. It is important to moderate starch intake and focus on a balanced diet.
Starch is a type of carbohydrate that is found in many foods, such as bread, pasta, rice, and potatoes. When consumed, starch is broken down into glucose, which is the body's main source of energy. However, consuming too much starch can have negative health implications.
1. Weight Gain
Starch is high in calories, and consuming excessive amounts can lead to weight gain. When the body does not use up all the glucose from starch for energy, it is stored as fat.
2. Blood Sugar Spikes
Consuming large amounts of starch can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels, leading to spikes and crashes in energy levels. This can also contribute to the development of insulin resistance and Type 2 diabetes.
3. Digestive Issues
Starch can be difficult for some people to digest, leading to bloating, gas, and other digestive issues. Those with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or other gastrointestinal disorders may experience worsened symptoms after consuming starchy foods.
4. Nutrient Deficiencies
Eating a diet high in starch can displace other nutrient-dense foods, leading to deficiencies in vitamins, minerals, and fiber. It is important to consume a balanced diet that includes a variety of food groups to ensure optimal health.
It is important to consume starch in moderation and focus on incorporating whole, unprocessed sources of carbohydrates into your diet. Consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian for personalized nutrition advice.

Tips for Managing Starch Intake
To manage starch intake, consider incorporating more non-starchy vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your diet. Choose whole grains over refined grains and limit processed foods high in starch and sugar.
Starch is a type of carbohydrate that provides energy to the body, but consuming too much of it can lead to negative effects on your health. Here are some tips for managing your starch intake:
- Choose whole grains: Opt for whole grain sources of starch, such as whole wheat bread, brown rice, and quinoa, which are higher in fiber and nutrients compared to refined grains.
- Watch portion sizes: Be mindful of portion sizes when consuming starchy foods, as eating too much can lead to weight gain and other health issues.
- Balance your meals: Pair starches with protein, healthy fats, and vegetables to create a well-rounded meal that will help stabilize blood sugar levels and keep you feeling full longer.
- Limit processed foods: Processed foods like white bread, pastries, and sugary cereals are often high in starch and low in nutrients. Try to limit your intake of these foods.
- Be aware of hidden sources of starch: Starch can be found in a variety of foods, including fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. Be mindful of these sources when managing your starch intake.
By following these tips and being conscious of your starch intake, you can better manage its effects on your body and overall health.

Key Takeaways:
- Starch is a complex carbohydrate found in plants that serves as a primary source of energy.
- Consuming too much starch can lead to weight gain, insulin resistance, and other health issues.
- Choosing whole grains and limiting refined starches is important for maintaining a healthy diet.
FAQ:
Q: Can I still consume starch in moderation?
A: Yes, starch can be part of a healthy diet when consumed in moderation and balanced with other nutrient-dense foods.
Q: Are there healthier alternatives to starchy foods?
A: Yes, consider replacing refined starches with whole grains, non-starchy vegetables, and lean proteins for better health outcomes.



Recent Comments