Table of Contents:
- What is Lipoprotein?
- Causes of High Lipoprotein Levels
- Health Risks Associated with High Lipoprotein
- Diagnosis and Treatment
- Diet and Lifestyle Changes
- Prevention of High Lipoprotein Levels
- Conclusion
What is Lipoprotein?
Lipoproteins are particles in the blood that carry fats (lipids) such as cholesterol and triglycerides. They are essential for transporting these substances to various tissues in the body.
Causes of High Lipoprotein Levels
High lipoprotein levels can be caused by genetic factors, unhealthy diet, lack of exercise, obesity, smoking, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes and hypothyroidism.
High levels of lipoproteins in the blood, specifically low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and high-density lipoproteins (HDL), can be caused by a variety of factors.
One common cause of high lipoprotein levels is a diet high in saturated fats and cholesterol. These substances can increase the production of LDL cholesterol in the liver, leading to elevated levels in the bloodstream.
Genetics also play a significant role in determining an individual's lipoprotein levels. Certain genetic conditions, such as familial hypercholesterolemia, can result in abnormally high levels of LDL cholesterol.
Lack of physical activity and being overweight or obese can contribute to high lipoprotein levels. Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight can help lower LDL cholesterol and increase HDL cholesterol levels.
Other factors that can increase lipoprotein levels include smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes and hypothyroidism.
It is important to monitor and manage lipoprotein levels through lifestyle changes, medication, and regular blood tests to reduce the risk of heart disease and other related health complications.
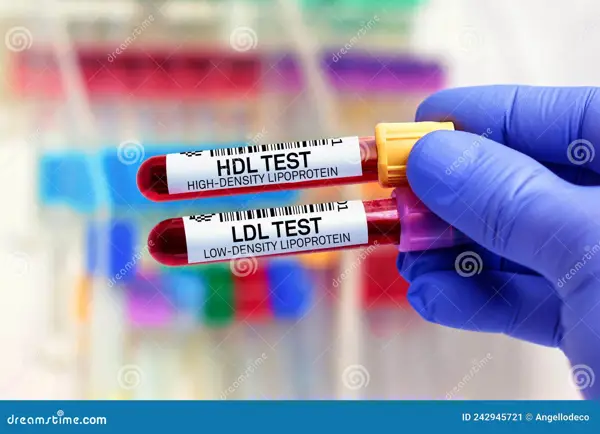
Health Risks Associated with High Lipoprotein
Elevated lipoprotein levels are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes. It can also lead to atherosclerosis, which is the hardening and narrowing of the arteries.
Health Risks Associated with High Lipoprotein Levels in Blood
High levels of lipoprotein in the blood, specifically high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, can increase the risk of developing heart disease and other cardiovascular conditions. LDL cholesterol is often referred to as "bad" cholesterol because it can build up in the walls of arteries, leading to atherosclerosis and potential blockages that can restrict blood flow to the heart.
Individuals potassium high test levels are also at an increased risk for developing other health issues, such as stroke, peripheral artery disease, and high blood pressure. It is important to monitor and manage cholesterol levels through a combination of a healthy diet, regular exercise, and, if necessary, medication prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Regular blood tests can help to identify high lipoprotein levels and allow for timely intervention to reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications. By taking steps to lower cholesterol levels and improve overall heart health, individuals can lower their risk of developing serious health conditions associated with high lipoprotein in the blood.
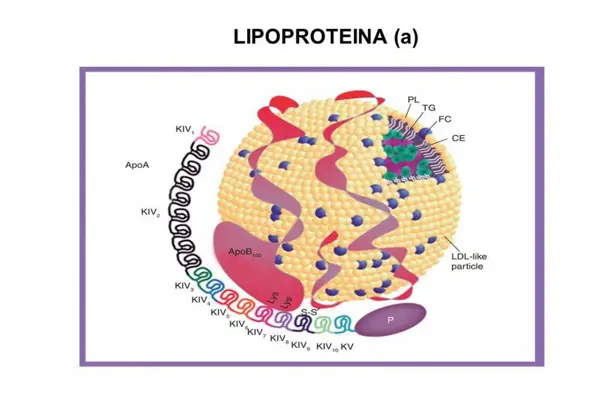
Diagnosis and Treatment
High lipoprotein levels are diagnosed through blood tests. Treatment usually involves lifestyle changes such as adopting a healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and, in some cases, medication may be prescribed.
High levels of lipoprotein in a blood test can indicate a risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular problems. It is important to accurately diagnose and effectively treat this condition to prevent complications.
Diagnosis
A blood test is the primary method of diagnosing high lipoprotein levels. Lipoprotein levels can be measured using lipid panels that provide information about total cholesterol, HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, and triglycerides. These results can help determine if a person has high lipoprotein levels and assess their risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
Treatment
Treatment for high lipoprotein levels often involves lifestyle changes and medication. Dietary modifications, such as reducing intake of saturated and trans fats, increasing consumption of fruits and vegetables, and maintaining a healthy weight, can help lower lipoprotein levels. Regular exercise and quitting smoking can also improve lipid levels.
In some cases, medication may be necessary to lower lipoprotein levels. Statins, fibrates, and niacin are commonly prescribed medications that can help reduce cholesterol levels in the blood. It is important for individuals with high lipoprotein levels to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that best suits their needs.
Overall, early diagnosis and proper treatment of high lipoprotein levels are crucial in preventing cardiovascular complications and promoting heart health.
Diet and Lifestyle Changes
Following a healthy diet low in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and refined sugars can help lower lipoprotein levels. Regular physical activity and maintaining a healthy weight are also important.
If you have been diagnosed with high lipoprotein levels in your blood test, making certain diet and lifestyle changes can help lower your levels and reduce your risk of heart disease and other related conditions. Here are some recommendations:
Dietary Changes
- Limit saturated and trans fats, found in red meat, full-fat dairy products, and processed foods.
- Increase your intake of heart-healthy fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts.
- Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables, which are rich in antioxidants and fiber that can help lower cholesterol levels.
- Choose whole grains over refined grains for better heart health.
- Reduce your intake of added sugars and salt.
Lifestyle Changes
- Get regular exercise, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
- Quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke.
- Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity.
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Get regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your lipoprotein levels and overall health.
By implementing these diet and lifestyle changes, you can improve your lipoprotein levels and reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease. Consult with your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian for personalized recommendations and support.

Prevention of High Lipoprotein Levels
Preventing high lipoprotein levels involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding unhealthy habits such as smoking, and regularly monitoring blood lipid levels.
High levels of lipoproteins in the blood can increase the risk of heart disease and other health complications. It is important to prevent high lipoprotein levels through lifestyle changes and regular medical monitoring.
Some ways to prevent high lipoprotein levels include:
- Maintaining a healthy diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol
- Exercising regularly to keep your weight in check and improve cardiovascular health
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Monitoring your blood lipoprotein levels regularly with your healthcare provider
- Taking medication prescribed by your doctor, if necessary
By following these preventive measures, you can reduce your risk of developing high lipoprotein levels and protect your heart health. Stay proactive about managing your lipoprotein levels to live a healthy and fulfilling life.
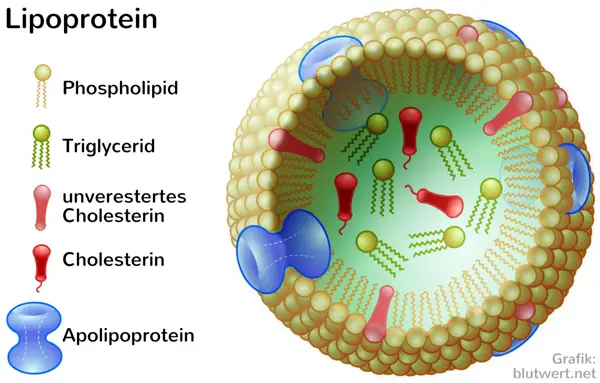
Conclusion
High lipoprotein levels in blood tests can be a warning sign of potential health risks. By making positive lifestyle changes and seeking appropriate medical care, individuals can lower their lipoprotein levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Key Takeaways:
- High lipoprotein levels are associated with increased cardiovascular risks.
- Diet and lifestyle changes can help lower lipoprotein levels.
- Regular monitoring and preventive measures are crucial in managing lipoprotein levels.
FAQ
Q: Can high lipoprotein levels be reversed?
A: Yes, with appropriate lifestyle changes and medical treatment, high lipoprotein levels can be lowered.
Q: How often should I have my lipoprotein levels checked?
A: It is recommended to have your lipoprotein levels checked regularly as part of routine blood tests, especially if you have risk factors for cardiovascular diseases.



Recent Comments