Table of Contents
- What is Non-HDL Cholesterol?
- Relation to LDL Cholesterol
- Impact on Health
- Testing and Measurement
- Diet and Lifestyle Changes
- Medication Options
- Prevention and Management
What is Non-HDL Cholesterol?
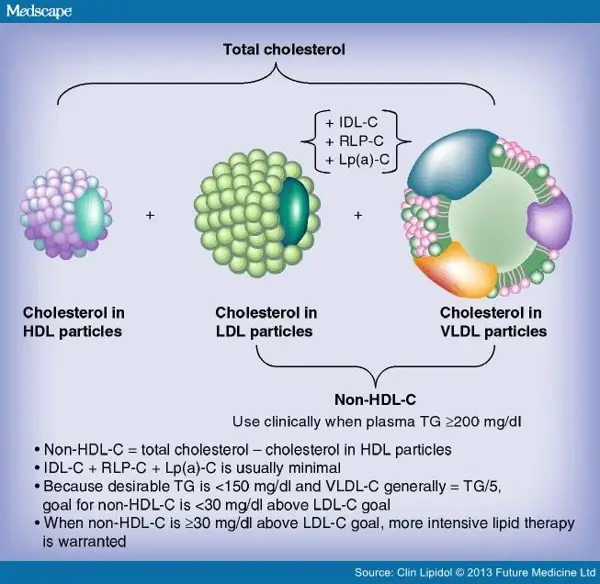
Non-HDL cholesterol is a type of cholesterol that includes all the bad cholesterol in your blood, including LDL cholesterol, as well as other harmful fats. It is considered a better indicator of cardiovascular risk compared to LDL cholesterol alone.
Relation to LDL Cholesterol
Non-HDL cholesterol is closely related to LDL cholesterol, as it includes LDL cholesterol along with other harmful fats. Monitoring both non-HDL and LDL cholesterol levels is important for assessing cardiovascular risk.
Non-HDL cholesterol lower how non hdl all the "bad" cholesterol in your blood, including LDL cholesterol and very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) cholesterol. Since LDL cholesterol is a major component of non-HDL cholesterol, there is a strong relationship between the two.
Having high levels of non-HDL cholesterol, which includes high levels of LDL cholesterol, is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke. It is important to monitor and manage your non-HDL cholesterol levels to reduce your risk of these cardiovascular diseases.
By focusing on reducing LDL cholesterol through lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, you can also lower your non-HDL cholesterol levels and improve your heart health.
Impact on Health
Elevated non-HDL cholesterol levels have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions. Managing non-HDL cholesterol levels is essential for maintaining heart health.
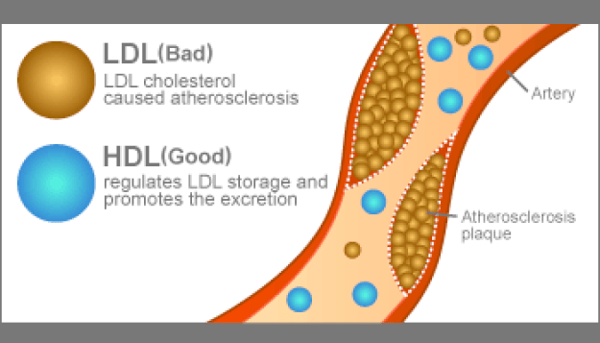
Non-HDL cholesterol and LDL (low-density lipoprotein) are two types of cholesterol that can have a significant impact on your health.
Elevated levels of non-HDL cholesterol and LDL can increase your risk of developing heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems. These types of cholesterol can build up in your arteries, leading to plaque formation and potentially causing blockages that can restrict blood flow to vital organs.
It is important to monitor and manage your levels of non-HDL cholesterol and LDL through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and medication if necessary. By keeping these levels in check, you can lower your risk of developing serious health complications and improve your overall well-being.

Testing and Measurement
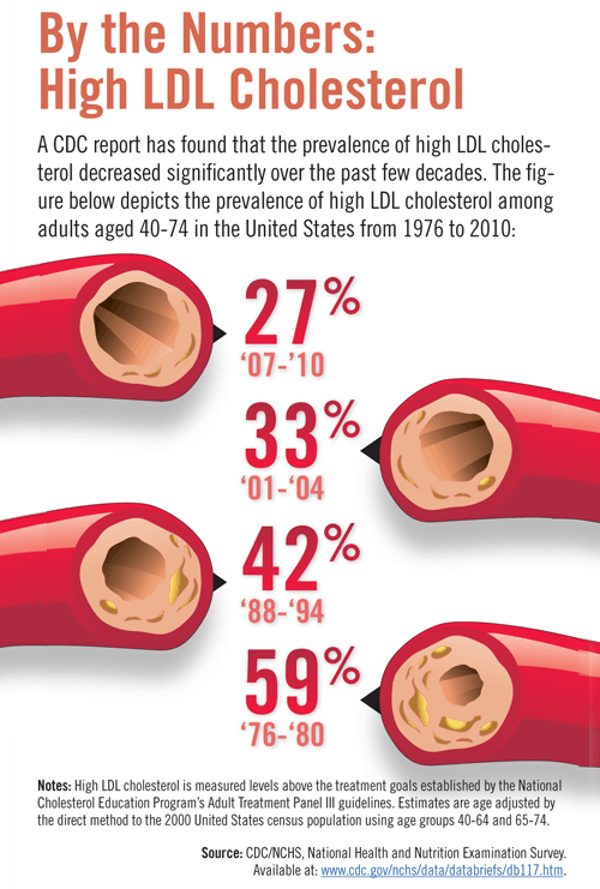
Non-HDL cholesterol levels can be measured through a simple blood test. It is recommended to have your cholesterol levels checked regularly to monitor your cardiovascular risk.
Non-HDL cholesterol, which includes LDL cholesterol, is an important marker for cardiovascular health. Testing and measurement of non-HDL cholesterol LDL levels is crucial in assessing an individual's risk for heart disease.
There are various methods for testing non-HDL cholesterol LDL, including blood tests that measure the levels of cholesterol in the bloodstream. These tests can help healthcare providers determine whether a person's cholesterol levels are within a healthy range or if intervention is needed to lower cholesterol levels.
Monitoring non-HDL cholesterol LDL levels over time can help track the effectiveness of lifestyle changes or medications aimed at reducing cholesterol levels and lowering the risk of heart disease.
Overall, testing and measurement of non-HDL cholesterol LDL is an important aspect of cardiovascular health monitoring and management.
Diet and Lifestyle Changes
Making dietary changes, such as reducing intake of saturated and trans fats, increasing fiber consumption, and engaging in regular physical activity, can help lower non-HDL cholesterol levels and improve heart health.
Non-HDL cholesterol, which includes LDL cholesterol, is a major risk factor for heart disease. Making changes to your diet and lifestyle can help lower your non-HDL cholesterol levels and improve your overall heart health.
Dietary Changes
1. Limit your intake of saturated and trans fats, which can raise your LDL cholesterol levels. Instead, opt for healthy fats such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats found in nuts, seeds, and avocado.
2. Increase your intake of soluble fiber from sources such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, which can help lower LDL cholesterol.
3. Choose lean proteins such as fish, poultry, and plant-based sources like beans and tofu, instead of red meat and processed meats.
Lifestyle Changes
1. Engage in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, for at least 30 minutes most days of the week to help lower your LDL cholesterol levels.
2. Maintain a healthy weight by following a balanced diet and staying physically active. Excess weight can contribute to high non-HDL cholesterol levels.
3. Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption, as these habits can negatively impact your cholesterol levels and overall heart health.
Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to create a personalized plan for lowering your non-HDL cholesterol levels through diet and lifestyle changes.

Medication Options
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help lower non-HDL cholesterol levels. Statins and other cholesterol-lowering drugs can be effective in managing cholesterol levels when lifestyle changes are not sufficient.
There are several medication options available for managing non-HDL cholesterol, which includes LDL cholesterol:
- Statins: These are commonly prescribed medications that help lower LDL cholesterol levels by blocking the enzyme in the liver that produces cholesterol.
- Ezetimibe: This medication works by blocking the absorption of cholesterol from the digestive tract, helping to lower LDL levels.
- PCSK9 inhibitors: These medications are injectable drugs that help lower LDL cholesterol by targeting a specific protein in the liver that regulates cholesterol levels.
- Bile acid sequestrants: These medications bind to bile acids in the digestive tract, helping to lower LDL cholesterol levels.
It is important to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best medication option for managing your non-HDL cholesterol levels.

Prevention and Management
By adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding smoking, you can lower your non-HDL cholesterol levels and reduce your risk of cardiovascular disease.
Non-HDL cholesterol, specifically LDL cholesterol, is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease. To prevent and manage high levels of non-HDL cholesterol, it is important to follow a healthy lifestyle and potentially seek medical treatment.
Prevention Tips
- Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Avoid foods high in saturated and trans fats, such as fried foods and baked goods.
- Exercise regularly to maintain a healthy weight and improve cardiovascular health.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
Management Strategies
- Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action based on your individual risk factors.
- Take prescribed medications, such as statins, to help lower cholesterol levels.
- Monitor cholesterol levels regularly through blood tests.
- Make necessary lifestyle changes to support medication therapy and reduce cardiovascular risk.
By following these prevention and management strategies, individuals can effectively lower their non-HDL cholesterol levels and reduce their risk of heart disease and stroke.
Key Takeaways
- Non-HDL cholesterol includes all the bad cholesterol in your blood, including LDL cholesterol.
- Elevated non-HDL cholesterol levels are associated with an increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Managing non-HDL cholesterol through diet, exercise, and medication can help reduce cardiovascular risk.
FAQ
Q: What are the recommended levels for non-HDL cholesterol?
A: The optimal non-HDL cholesterol level is less than 130 mg/dL. However, individual targets may vary based on other risk factors.
Q: How often should I have my cholesterol levels checked?
A: It is recommended to have your cholesterol levels checked at least once every five years. However, more frequent testing may be necessary if you have risk factors for heart disease.


Recent Comments