Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Non HDL Cholesterol?
- Normal Range
- Implications of High Non HDL Cholesterol
- Reducing Non HDL Cholesterol Levels
- Testing Non HDL Cholesterol
- Summary
Introduction
Non HDL cholesterol normal a type of cholesterol that includes all the 'bad' cholesterol in your blood, except for HDL (high-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, which is considered 'good' cholesterol.
What is Non HDL Cholesterol?
Non HDL cholesterol consists of LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, VLDL (very-low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, and intermediate-density lipoprotein cholesterol. It is a key marker for assessing cardiovascular risk.
Non-HDL cholesterol, also known as "bad" cholesterol, includes all the types of cholesterol except for HDL cholesterol, which is considered to be the "good" cholesterol. This includes LDL cholesterol, VLDL cholesterol, and intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL) cholesterol. Non-HDL cholesterol levels are important to monitor as high levels are associated with an increased risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular problems.
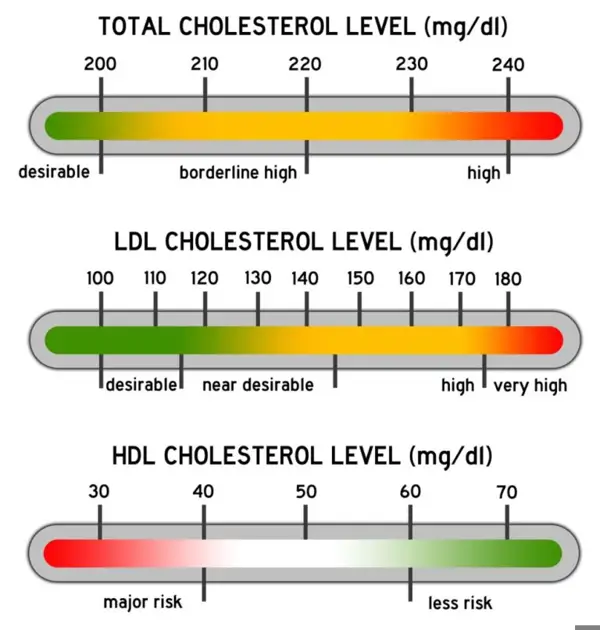
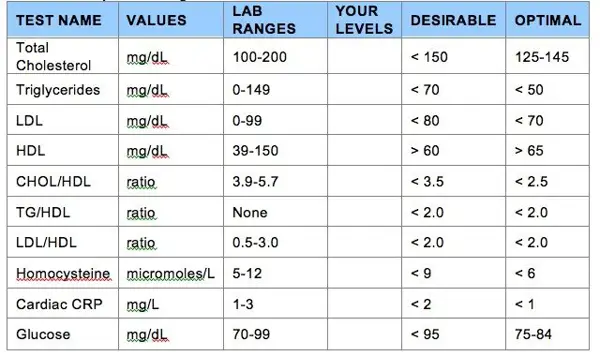
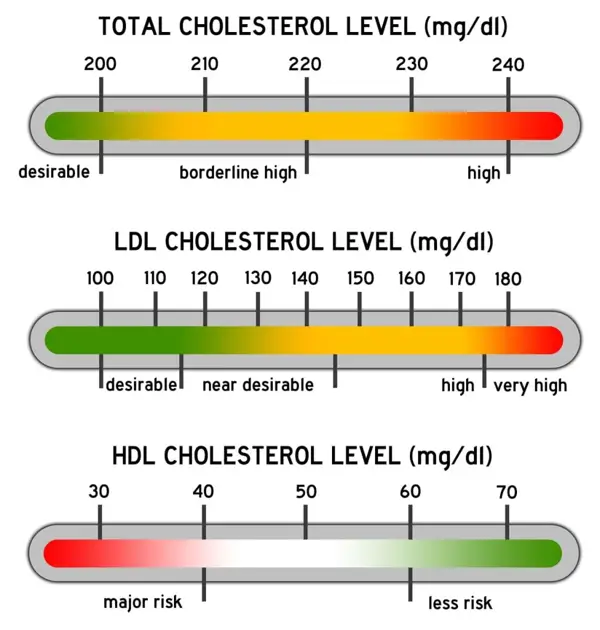
The total range for non-HDL cholesterol is typically measured by subtracting the HDL cholesterol level from the total cholesterol level. A non-HDL cholesterol level of less than 130 mg/dL is considered optimal, while levels between 130-159 mg/dL are borderline high, and levels of 160 mg/dL and above are considered high.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking can help keep non-HDL cholesterol levels in check and reduce the risk of heart disease. Regular monitoring of cholesterol levels and working with a healthcare provider can help manage non-HDL cholesterol levels effectively.

Normal Range
The total range of non HDL cholesterol is typically between 80-130 mg/dL. Levels above this range may indicate an increased risk of heart disease.
The normal range for non HDL cholesterol levels in the body typically falls between 100-130 mg/dL. This type of cholesterol is considered a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, as it consists of all the LDL (bad) cholesterol and other non-HDL cholesterol particles in the blood. Maintaining a healthy non-HDL cholesterol level is essential for overall heart health and can be achieved through a combination of proper diet, regular exercise, and, if necessary, medication. It is important to regularly monitor your non-HDL cholesterol levels to ensure they are within the normal range and take necessary steps to lower them if they are elevated.
Implications of High Non HDL Cholesterol
Elevated levels of non HDL cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaque in your arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. It is important to monitor and manage your cholesterol levels to reduce these risks.
Non-HDL cholesterol, also known as "bad" cholesterol, plays a significant role in determining cardiovascular health. High levels of non-HDL cholesterol have been associated with an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular issues.
When the total range of non-HDL cholesterol in the body is elevated, it can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis. This buildup restricts blood flow to the heart and other vital organs, increasing the risk of heart attacks and other cardiovascular events.
Managing non-HDL cholesterol levels through a healthy diet, regular exercise, and medication, if necessary, is essential in reducing the risk of these serious health implications. It is crucial for individuals to monitor their non-HDL cholesterol levels regularly and work with their healthcare provider to develop a plan to lower them and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Reducing Non HDL Cholesterol Levels
To lower your non HDL cholesterol levels, you can make lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking. In some cases, medication may be prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Non HDL cholesterol refers to all the cholesterol found in your blood that is not considered to be "good" cholesterol (HDL). High levels of non HDL cholesterol are associated with an increased risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular issues. To reduce non HDL cholesterol levels and maintain a healthy total cholesterol range, it is important to focus on a balanced diet, regular exercise, and possibly medication prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Including more fiber-rich foods, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your diet can help lower non HDL cholesterol levels. Avoiding trans fats and limiting saturated fats can also have a positive impact. Regular physical activity, such as brisk walking or cycling, can improve cholesterol levels and overall heart health.
If lifestyle changes are not enough to lower your non HDL cholesterol levels to a healthy range, your healthcare provider may recommend medications like statins. It is important to work closely with your doctor to monitor your cholesterol levels and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan. Remember, reducing non HDL cholesterol is essential for maintaining a healthy heart and preventing serious health complications.

Testing Non HDL Cholesterol
Non HDL cholesterol levels can be measured through a simple blood test. It is recommended to have your cholesterol levels checked regularly, especially if you have risk factors for heart disease.
Summary
Understanding the total range of non HDL cholesterol is important for assessing your cardiovascular risk. By monitoring and managing your cholesterol levels, you can lower your risk of heart disease and live a healthier life.
Key Takeaways
- Non HDL cholesterol includes all 'bad' cholesterol except for HDL cholesterol.
- Normal range of non HDL cholesterol is between 80-130 mg/dL.
- Elevated levels of non HDL cholesterol can increase the risk of heart disease.
- Lifestyle changes and medication can help lower non HDL cholesterol levels.
- Regular testing of cholesterol levels is recommended for monitoring cardiovascular health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the risk factors for high non HDL cholesterol?
Risk factors for high non HDL cholesterol include obesity, poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and genetic factors.
Can non HDL cholesterol be lowered through diet alone?
Diet plays a significant role in managing non HDL cholesterol levels, but in some cases, medication may be necessary to achieve target levels.
How often should I have my cholesterol levels tested?
It is recommended to have your cholesterol levels tested at least once every five years, or more frequently if you have risk factors for heart disease.


Recent Comments