Table of Contents
- Overview of Protein Loss Enteropathy
- Causes of Protein Loss Enteropathy
- Symptoms of Protein Loss Enteropathy
- Diagnosis of Protein Loss Enteropathy
- Treatment Options for Protein Loss Enteropathy
- Prevention of Protein Loss Enteropathy
- Complications Associated with Protein Loss Enteropathy
Overview of Protein Loss Enteropathy
Protein loss enteropathy is a condition characterized by the abnormal loss of proteins through the gastrointestinal tract. This can lead to a deficiency in essential nutrients and can result in various health complications.
Causes of Protein Loss Enteropathy
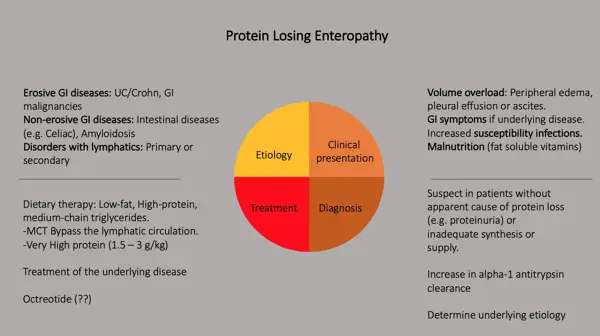
The causes of protein loss enteropathy can vary, with some of the common reasons being inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, and lymphatic disorders.
Protein loss enteropathy is a condition characterized by excessive loss of proteins in the gastrointestinal tract, leading to a deficiency of proteins in the body. The exact causes of protein loss enteropathy are not fully understood, but several factors have been identified as potential triggers.
1. Inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis can cause damage to the lining of the intestines, leading to leakage of proteins into the intestines.
2. Intestinal infections, such as parasites or bacteria, can also disrupt the normal functioning of the intestines and cause protein loss.
3. Lymphatic disorders, such as lymphangitis and lymphangiectasia, can impair the proper transport of proteins from the intestines to the bloodstream, leading to protein loss.
4. Congenital conditions, such as protein-losing enteropathies, can cause structural abnormalities in the intestines that result in protein loss.
5. Surgical procedures on the gastrointestinal tract, such as gastric bypass surgery, can also disrupt the normal absorption of proteins and lead to protein loss enteropathy.
It is important to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment of protein loss enteropathy, as untreated protein deficiency can lead to serious health complications.

Symptoms of Protein Loss Enteropathy
The symptoms of protein loss enteropathy may include edema, fatigue, weight loss, and muscle wasting. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if you experience any of these symptoms.
Protein loss enteropathy is a condition characterized by the abnormal loss of proteins in the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms of protein loss enteropathy can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms may include:
- Swelling in the abdomen (ascites)
- Edema (swelling in the legs or other parts of the body)
- Weight loss
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Anemia
- Hypoalbuminemia (low levels of albumin in the blood)
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
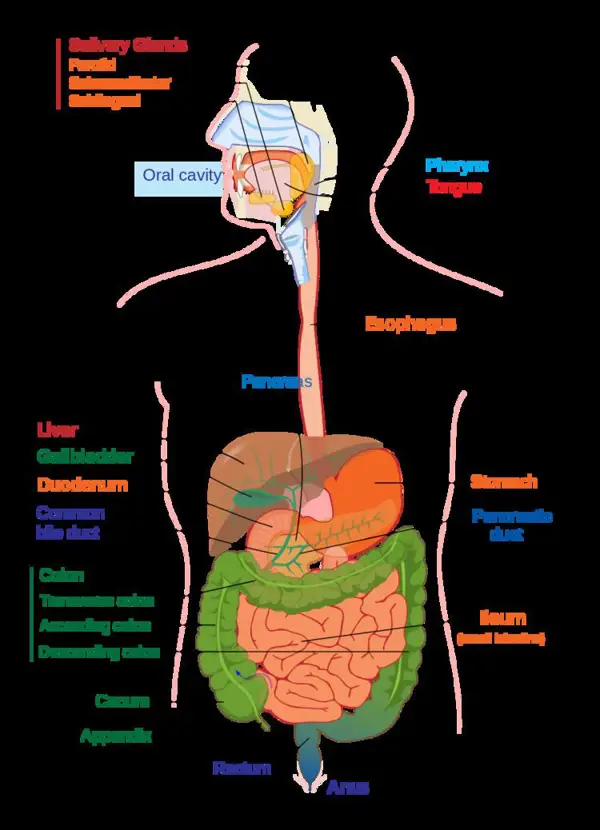
Diagnosis of Protein Loss Enteropathy
Diagnosing protein loss enteropathy typically involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and various tests such as blood tests, endoscopy, and imaging studies.
Protein loss enteropathy is a condition characterized by the abnormal loss of protein from the digestive tract. The diagnosis of protein loss enteropathy involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. These tests may include blood tests to measure levels of albumin and other proteins, as well as stool tests to detect the presence of protein.
In addition, imaging tests such as ultrasound or CT scans may be used to evaluate the gastrointestinal tract for abnormalities that could be causing protein loss. Endoscopic procedures, such as a colonoscopy or upper endoscopy, may also be performed to directly visualize the digestive tract and obtain tissue samples for further analysis.
Overall, a multidisciplinary approach involving gastroenterologists, radiologists, and pathologists is often necessary to accurately diagnose and manage protein loss enteropathy. Treatment may involve dietary modifications, medication, or in severe cases, surgical intervention. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in preventing complications and improving outcomes for patients with protein loss enteropathy.
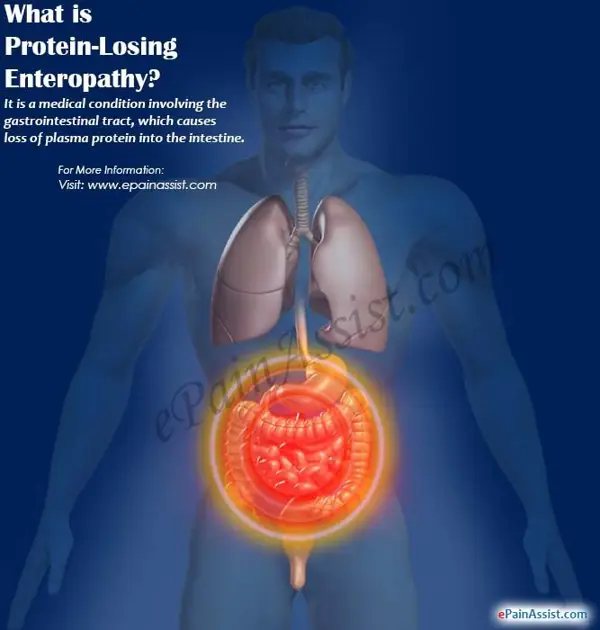
Treatment Options for Protein Loss Enteropathy
Treatment for protein loss enteropathy may involve dietary changes, medications to control inflammation, and in severe cases, surgery to repair damaged tissue.
Protein loss enteropathy is a condition that results in the excessive loss of protein from the body, often through the gastrointestinal tract. There are several treatment options available for individuals with this condition, which may include dietary modifications, medications, and surgical interventions.
1. Dietary modifications: Individuals with protein loss enteropathy may benefit from following a high-protein diet to help replenish lost protein. They may also need to avoid certain foods that exacerbate protein loss, such as fatty foods or foods high in fiber.
2. Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help diagnosis protein loss or manage symptoms associated with protein loss enteropathy. These may include corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or medications to control diarrhea.
3. Surgical interventions: In severe cases of protein loss enteropathy, surgery may be necessary to repair or remove damaged areas of the gastrointestinal tract that are causing the excessive loss of protein. This may involve procedures such as bowel resection or intestinal bypass surgery.
Overall, the treatment approach for protein loss enteropathy will depend on the underlying cause of the condition and the individual's specific symptoms and needs. It is important for individuals with protein loss enteropathy to work closely with their healthcare team to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their unique situation.

Prevention of Protein Loss Enteropathy
While not all cases of protein loss enteropathy can be prevented, maintaining a healthy diet, managing underlying conditions, and avoiding triggers can help reduce the risk of developing this condition.
Protein loss enteropathy is a condition characterized by excessive loss of proteins from the body, leading to a range of symptoms including edema, malnutrition, and immunodeficiency. Preventing protein loss enteropathy is essential for maintaining overall health and wellbeing.
To prevent protein loss enteropathy, it is important to identify and address any underlying causes such as inflammatory bowel disease, lymphatic disorders, or infections. Treatment may include medication, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications.
In addition, individuals at risk for protein loss enteropathy should consume an adequate amount of high-quality protein and maintain proper hydration. Regular monitoring by a healthcare provider is also crucial to ensure early detection and intervention.
By following these preventative measures and working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals can effectively manage and reduce the risk of protein loss enteropathy.
Complications Associated with Protein Loss Enteropathy
If left untreated, protein loss enteropathy can lead to severe complications such as malnutrition, dehydration, and impaired immune function. It is essential to seek medical attention for proper management.
Protein loss enteropathy is a condition where excessive protein is lost from the gastrointestinal tract, leading to complications such as malnutrition, edema, and impaired immune function. This condition can be caused by various factors including inflammatory bowel disease, lymphatic obstruction, and certain medications.
Treatment for protein loss enteropathy typically involves a combination of dietary changes, medications, and sometimes surgical intervention. It is important for individuals with this condition to work closely with healthcare providers to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Complications associated with protein loss enteropathy can be serious and include infections, organ damage, and delayed growth and development in children. Regular monitoring and proper management are essential to prevent these complications and improve overall quality of life for individuals with protein loss enteropathy.
Key Takeaways
- Protein loss enteropathy is a condition characterized by the abnormal loss of proteins through the gastrointestinal tract.
- The causes of protein loss enteropathy can vary and may include inflammatory bowel disease and celiac disease.
- Symptoms of protein loss enteropathy may include edema, fatigue, weight loss, and muscle wasting.
- Diagnosis of protein loss enteropathy involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and various tests.
- Treatment options for protein loss enteropathy may include dietary changes, medications, and surgery.
- Prevention of protein loss enteropathy involves maintaining a healthy diet and managing underlying conditions.
- Complications associated with protein loss enteropathy can be severe if left untreated.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can protein loss enteropathy be cured?
- The condition can be managed with appropriate treatment, but a cure may not always be possible.
- Is protein loss enteropathy a common condition?
- Protein loss enteropathy is relatively rare, but it can occur in individuals with certain underlying health conditions.
- How is protein loss enteropathy diagnosed?
- Diagnosis typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests.
- What are the long-term effects of protein loss enteropathy?
- If left untreated, protein loss enteropathy can lead to serious complications such as malnutrition and immune system dysfunction.


Recent Comments