Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Causes of Low Protein in Urine
- Symptoms of Low Protein in Urine
- Diagnosis and Treatment
- Complications of Low Protein in Urine
- Prevention
- Conclusion
Introduction
Having low protein in urine, also known as hypoproteinuria, can indicate underlying health issues that require attention. In this article, we will explore what it means to have low protein in urine and its implications.
Causes of Low Protein in Urine
Low protein does urine mean be caused by a variety of factors, including kidney disorders, malnutrition, and liver disease. It can also be a result of medications or excessive water intake.
Having low protein in the urine, also known as hypoproteinuria, can be caused by a variety of factors. Some common causes include dehydration, certain medications, malnutrition, liver disease, and kidney damage.
Proteins are important for maintaining proper functioning of the body, and low levels in the urine can indicate an underlying health issue. In some cases, it may be a temporary condition that can be easily resolved by increasing protein intake or addressing the underlying cause. However, in other cases, it may be a sign of a more serious health condition that requires medical attention.
Having low protein in the urine can lead to complications such as swelling in the legs and ankles, fatigue, and a weakened immune system. It is important to consult a healthcare provider if you experience symptoms or have concerns about your protein levels in the urine.
Overall, having low protein in the urine can be a sign that something is not functioning properly in the body and should not be ignored. Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential to ensure optimal health and well-being.
Symptoms of Low Protein in Urine
While low protein in urine may not always present noticeable symptoms, some individuals may experience fatigue, swelling, or frequent infections due to a weakened immune system.
When someone has low protein in their urine, it typically means that their body is not able to filter and retain enough protein in the blood. This can be a sign of kidney problems or other underlying health issues. Symptoms of low protein in urine may include swelling in the hands, feet, or face, fatigue, weakness, and frequent infections. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if you experience these symptoms to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of low protein in urine typically involves urine tests and blood work to identify the underlying cause. Treatment may involve addressing the root cause, such as managing kidney function or adjusting medications.
Having low levels of protein in your urine, also known as proteinuria, can be a sign of various health conditions. Normally, small amounts of protein may be present in urine, but if the levels are consistently low, it may indicate kidney problems or other underlying issues.
Diagnosis:
Low protein in urine can be diagnosed through a urine test called a urine protein test. Your doctor may also recommend further tests such as blood tests, imaging tests, or kidney biopsy to determine the underlying cause of low protein in urine.
Treatment:
The treatment for low protein in urine depends on the underlying cause. Your doctor may recommend lifestyle changes, medications, or other interventions to help manage the condition and prevent further complications. It is important to follow your doctor's recommendations and attend regular check-ups to monitor your condition.
Overall, having low protein in urine is a sign that your kidneys may not be functioning properly. It is important to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the cause and appropriate treatment plan.
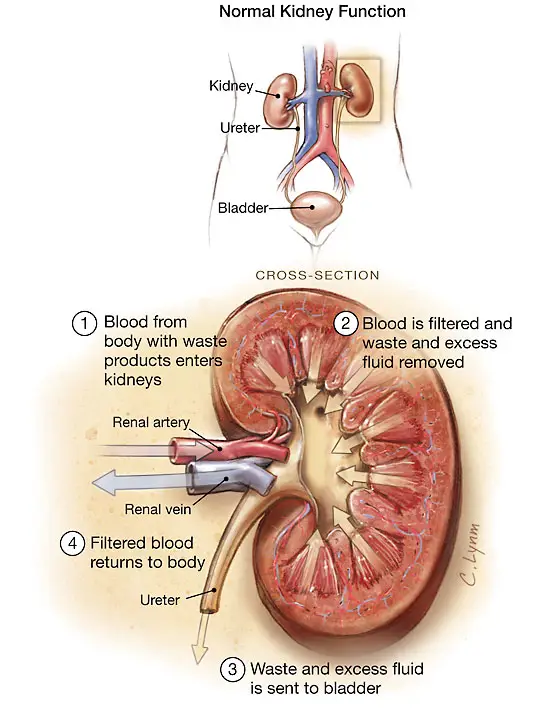
Complications of Low Protein in Urine
If left untreated, low protein in urine can lead to complications such as kidney damage, edema, and impaired immune function. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect low protein in urine.
Having low protein in urine, also known as hypoproteinuria, can be a cause for concern as protein plays an important role in maintaining overall health and functioning of the body. When there is a deficiency of protein in the urine, it can lead to various complications and health issues.
Protein is essential for the proper functioning of organs, muscles, and tissues in the body. It helps in building and repairing cells, transporting nutrients, and regulating various bodily functions. When there is a decrease in the amount of protein in the urine, it can indicate underlying health problems such as kidney disease, malnutrition, or other conditions.
Complications of low protein in urine may include:
- Edema or swelling in the body due to fluid retention
- Decreased immunity and increased risk of infections
- Poor muscle development and weakness
- Impaired growth and development in children
- Changes in blood pressure and circulation
It is important to consult a healthcare provider if you suspect that you have low protein in urine or are experiencing any symptoms related to it. Proper diagnosis and treatment can help address the underlying cause and prevent further complications.
Prevention
Preventing low protein in urine involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption. It is also essential to follow any treatment plans prescribed by a healthcare provider.
Low protein in urine, also known as proteinuria, refers to a condition where there is a lower-than-normal level of protein present in the urine. This can be a sign of a variety of health issues, such as kidney disease, malnutrition, or other underlying medical conditions. Prevention of low protein in urine involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional if you experience symptoms of low protein in urine to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment. By taking proactive steps to address any potential health concerns, you can help prevent complications associated with low protein in urine.

Conclusion
Overall, low protein in urine can indicate underlying health issues that should not be ignored. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and implications of low protein in urine, individuals can take proactive steps to address their health concerns and prevent complications.
Key Takeaways
- Low protein in urine, or hypoproteinuria, can signal underlying health issues.
- Symptoms of low protein in urine may include fatigue, swelling, and frequent infections.
- Diagnosis and treatment of low protein in urine may involve urine tests and blood work.
- Complications of low protein in urine can include kidney damage and impaired immune function.
- Prevention of low protein in urine includes maintaining a healthy lifestyle and following treatment plans.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes low protein in urine?
Low protein in urine can be caused by kidney disorders, malnutrition, liver disease, medications, or excessive water intake.
Are there symptoms of low protein in urine?
While some individuals may experience fatigue, swelling, or frequent infections, low protein in urine may not always present noticeable symptoms.



Recent Comments